|
1 |
Let ℝ be the set of real numbers and f : ℝ → ℝ such that for all x and y in ℝ, 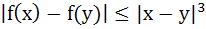 . Then f (x) is a constant. . Then f (x) is a constant. a) True b) False
Let ℝ be the set of real numbers and f : ℝ → ℝ such that for all x and y in ℝ, 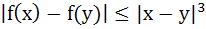 . Then f (x) is a constant. . Then f (x) is a constant. a) True b) False
|
IIT 1988 |
01:50 min
|
|
2 |
Let 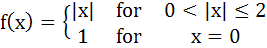 Then at x = 0, f has a) A local maximum b) No local maximum c) A local minimum d) No extremum
Let 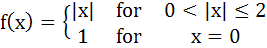 Then at x = 0, f has a) A local maximum b) No local maximum c) A local minimum d) No extremum
|
IIT 2000 |
01:52 min
|
|
3 |
Let C be any circle with centre (0, 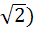 . Prove that at the most two rational points can be there on C (A rational point is a point both of whose coordinates are rational numbers). . Prove that at the most two rational points can be there on C (A rational point is a point both of whose coordinates are rational numbers).
Let C be any circle with centre (0, 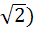 . Prove that at the most two rational points can be there on C (A rational point is a point both of whose coordinates are rational numbers). . Prove that at the most two rational points can be there on C (A rational point is a point both of whose coordinates are rational numbers).
|
IIT 1997 |
01:58 min
|
|
4 |
Find 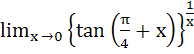 a) 0 b) e c) ez d) e3
Find 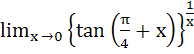 a) 0 b) e c) ez d) e3
|
IIT 1993 |
05:49 min
|
|
5 |
The relatives of a man comprise 4 ladies and 3 gentlemen and his wife has 7 relatives 3 of them are ladies and 4 gentlemen. In how many ways can they invite a dinner party of 3 ladies and 3 gentlemen so that so that three of man’s relatives and three of wife’s relatives are included?
The relatives of a man comprise 4 ladies and 3 gentlemen and his wife has 7 relatives 3 of them are ladies and 4 gentlemen. In how many ways can they invite a dinner party of 3 ladies and 3 gentlemen so that so that three of man’s relatives and three of wife’s relatives are included?
|
IIT 1985 |
04:27 min
|
|
6 |
Let 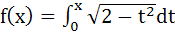 then the real roots of the equation then the real roots of the equation 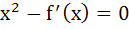 are are
a) ± 1 b) 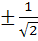 c) 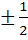 d) 0 and 1
Let 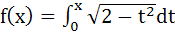 then the real roots of the equation then the real roots of the equation 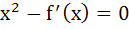 are are
a) ± 1 b) 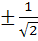 c) 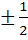 d) 0 and 1
|
IIT 2002 |
01:42 min
|
|
7 |
Consider a family of circles 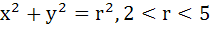 . If in the first quadrant, the common tangent to a circle of the family and the ellipse . If in the first quadrant, the common tangent to a circle of the family and the ellipse 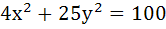 meet the coordinate axes at A and B, then find the locus of the mid-point of AB. meet the coordinate axes at A and B, then find the locus of the mid-point of AB.
Consider a family of circles 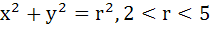 . If in the first quadrant, the common tangent to a circle of the family and the ellipse . If in the first quadrant, the common tangent to a circle of the family and the ellipse 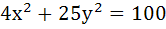 meet the coordinate axes at A and B, then find the locus of the mid-point of AB. meet the coordinate axes at A and B, then find the locus of the mid-point of AB.
|
IIT 1999 |
07:41 min
|
|
8 |
Multiple choices Let g (x) be a function defined on [−1, 1]. If the area of the equilateral triangle with the area of its vertices at ( 0, 0) and ( x, g (x)) is  then the function g (x) is then the function g (x) is a) g (x) = 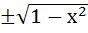 b) g (x) = 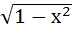 c) g (x) = 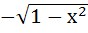 d) g (x) = 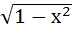
Multiple choices Let g (x) be a function defined on [−1, 1]. If the area of the equilateral triangle with the area of its vertices at ( 0, 0) and ( x, g (x)) is  then the function g (x) is then the function g (x) is a) g (x) = 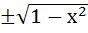 b) g (x) = 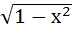 c) g (x) = 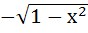 d) g (x) = 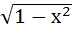
|
IIT 1984 |
02:26 min
|
|
9 |
For a fixed value of n
D = 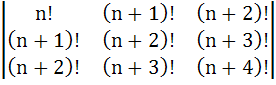
Then show that 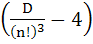 is divisible by n is divisible by n
For a fixed value of n
D = 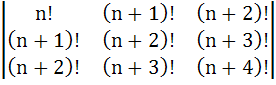
Then show that 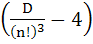 is divisible by n is divisible by n
|
IIT 1992 |
07:32 min
|
|
10 |
The area bounded by the curves 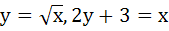 and the X–axis in the first quadrant is a) 9 b) 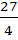 c) 36 d) 18
The area bounded by the curves 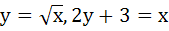 and the X–axis in the first quadrant is a) 9 b) 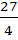 c) 36 d) 18
|
IIT 2003 |
04:28 min
|
|
11 |
Find the point on 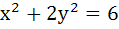 which is nearest to the line which is nearest to the line 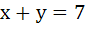
Find the point on 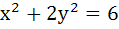 which is nearest to the line which is nearest to the line 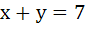
|
IIT 2003 |
04:09 min
|
|
12 |
Which one of the following is true in a triangle ABC? a) 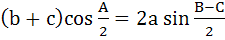 b) 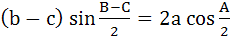 c) 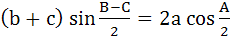 d) 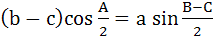
Which one of the following is true in a triangle ABC? a) 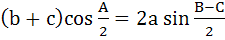 b) 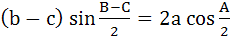 c) 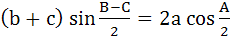 d) 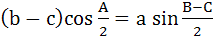
|
IIT 2005 |
02:45 min
|
|
13 |
Given A = 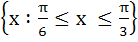 and f (x) = cosx – x (x + 1). Find the range of f (A). and f (x) = cosx – x (x + 1). Find the range of f (A). a) 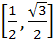 b) 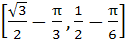 c) 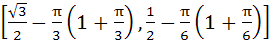 d) 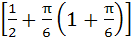
Given A = 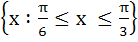 and f (x) = cosx – x (x + 1). Find the range of f (A). and f (x) = cosx – x (x + 1). Find the range of f (A). a) 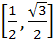 b) 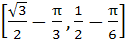 c) 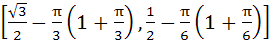 d) 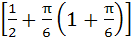
|
IIT 1980 |
02:20 min
|
|
14 |
For any positive integers m, n (with n ≥ m), prove that
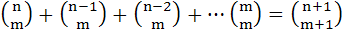
For any positive integers m, n (with n ≥ m), prove that
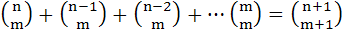
|
IIT 2000 |
05:45 min
|
|
15 |
If f(x) = xa lnx and f(0) = 0 then the value of a for which Rolle’s theorem can be applied in [0, 1] is a) – 2 b) – 1 c) 0 d) 
If f(x) = xa lnx and f(0) = 0 then the value of a for which Rolle’s theorem can be applied in [0, 1] is a) – 2 b) – 1 c) 0 d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
02:30 min
|
|
16 |
The points of intersection of the line 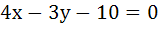 and the circle and the circle 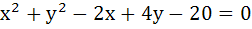 is . . . . . is . . . . .
The points of intersection of the line 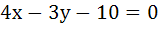 and the circle and the circle 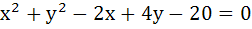 is . . . . . is . . . . .
|
IIT 1983 |
03:18 min
|
|
17 |
Let the angles A, B, C of Δ ABC be in arithmetic progression and
b : c = 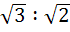 . Find the angle A. . Find the angle A. a)  b)  c) 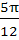 d) 
Let the angles A, B, C of Δ ABC be in arithmetic progression and
b : c = 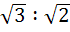 . Find the angle A. . Find the angle A. a)  b)  c) 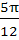 d) 
|
IIT 1981 |
03:05 min
|
|
18 |
A = 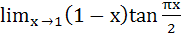 is equal to is equal to a) 0 b) 1 c)  d) 
A = 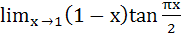 is equal to is equal to a) 0 b) 1 c)  d) 
|
IIT 1978 |
02:30 min
|
|
19 |
Multiple choice For which value of m, is the area of the region bounded by the curve y = x –x2 and the line y = mx equal to  a) – 4 b) – 2 c) 2 d) 4
Multiple choice For which value of m, is the area of the region bounded by the curve y = x –x2 and the line y = mx equal to  a) – 4 b) – 2 c) 2 d) 4
|
IIT 1999 |
04:39 min
|
|
20 |
The equation of the line passing through the points of intersection of the circles
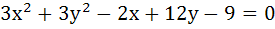 and and
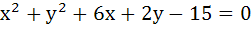 is . . . . . is . . . . .
The equation of the line passing through the points of intersection of the circles
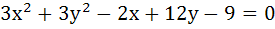 and and
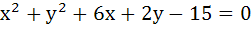 is . . . . . is . . . . .
|
IIT 1986 |
02:45 min
|
|
21 |
For the function 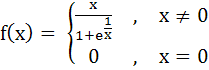 The derivative from right 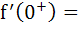 . . . . and the derivative from the left . . . . and the derivative from the left 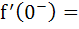 . . . . . . . . a) 0, 0 b) 0, 1 c) 1, 0 d) 1, 1
For the function 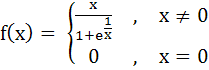 The derivative from right 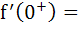 . . . . and the derivative from the left . . . . and the derivative from the left 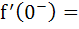 . . . . . . . . a) 0, 0 b) 0, 1 c) 1, 0 d) 1, 1
|
IIT 1983 |
03:28 min
|
|
22 |
Let z1 and z2 be nth roots of unity which subtend a right angle at the origin then n must be of the form a) 4k + 1 b) 4k + 2 c) 4k + 3 d) 4k
Let z1 and z2 be nth roots of unity which subtend a right angle at the origin then n must be of the form a) 4k + 1 b) 4k + 2 c) 4k + 3 d) 4k
|
IIT 2001 |
05:59 min
|
|
23 |
If the triangle 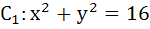 another circle C2 of radius 5 in such a manner that the common chord is of maximum length and a slope equal to another circle C2 of radius 5 in such a manner that the common chord is of maximum length and a slope equal to  , then the coordinates of the centre of C2 are . . . . . , then the coordinates of the centre of C2 are . . . . .
If the triangle 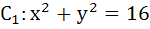 another circle C2 of radius 5 in such a manner that the common chord is of maximum length and a slope equal to another circle C2 of radius 5 in such a manner that the common chord is of maximum length and a slope equal to  , then the coordinates of the centre of C2 are . . . . . , then the coordinates of the centre of C2 are . . . . .
|
IIT 1988 |
06:55 min
|
|
24 |
Let ABC be a triangle such that
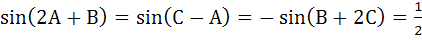 If A, B, C are in arithmetic progression, determine the values of A, B, C. a) 30°, 60°, 90° b) 30°, 75°, 75° c) 45°, 60°, 75° d) 60°, 60°, 60°
Let ABC be a triangle such that
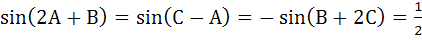 If A, B, C are in arithmetic progression, determine the values of A, B, C. a) 30°, 60°, 90° b) 30°, 75°, 75° c) 45°, 60°, 75° d) 60°, 60°, 60°
|
IIT 1990 |
02:17 min
|
|
25 |
If f (x) = 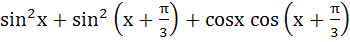 and and 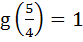 then (gof)(x) = ………… a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
If f (x) = 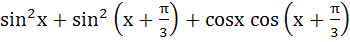 and and 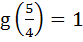 then (gof)(x) = ………… a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 1996 |
03:24 min
|