|
276 |
The axis of the parabola is along the line 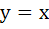 and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are 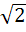 and and 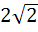 respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is a) 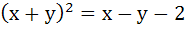 b) 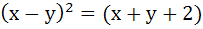 c) 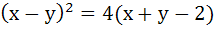 d) 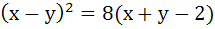
The axis of the parabola is along the line 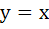 and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are 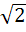 and and 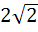 respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is a) 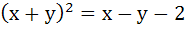 b) 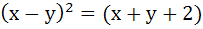 c) 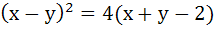 d) 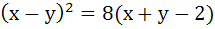
|
IIT 2006 |
05:21 min
|
|
277 |
(Subjective problem) Solve 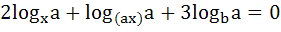
where a > 0, b = a2x.
(Subjective problem) Solve 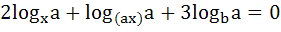
where a > 0, b = a2x.
|
IIT 1978 |
04:27 min
|
|
278 |
Sketch the region bounded by the curves y = x2 and 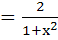 . Find the area. . Find the area. a)  b)  c) 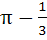 d) 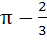
Sketch the region bounded by the curves y = x2 and 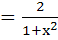 . Find the area. . Find the area. a)  b)  c) 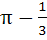 d) 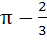
|
IIT 1992 |
06:17 min
|
|
279 |
Find the equation of the normal to the curve 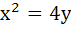 which passes through the point (1, 2). which passes through the point (1, 2).
Find the equation of the normal to the curve 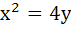 which passes through the point (1, 2). which passes through the point (1, 2).
|
IIT 1984 |
03:23 min
|
|
280 |
The expression
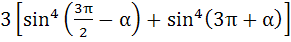
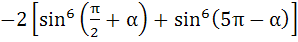 is equal to is equal to a) 0 b) 1 c) 3 d) sin4α + cosα
The expression
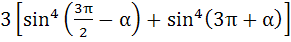
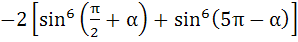 is equal to is equal to a) 0 b) 1 c) 3 d) sin4α + cosα
|
IIT 1986 |
04:12 min
|
|
281 |
If ω be the cube root of unity then the value of
 is is a) 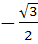 b)  c) 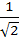 d) 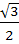
If ω be the cube root of unity then the value of
 is is a) 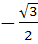 b)  c) 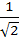 d) 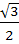
|
IIT 1994 |
02:00 min
|
|
282 |
At any point P on the parabola 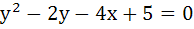 , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio 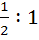 . .
At any point P on the parabola 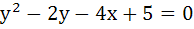 , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio 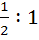 . .
|
IIT 2004 |
06:48 min
|
|
283 |
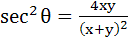 is true if is true if
a) x + y= 0 b) x = y, x ≠ 0 c) x = y d) x ≠ 0, y ≠ 0
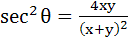 is true if is true if
a) x + y= 0 b) x = y, x ≠ 0 c) x = y d) x ≠ 0, y ≠ 0
|
IIT 1996 |
01:49 min
|
|
284 |
Find the value of the expression 1.(2−ω)(2−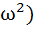 + 2.(3−ω)(3− + 2.(3−ω)(3−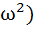 + … (n−1).(n−ω)(n− + … (n−1).(n−ω)(n−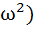 where ω is an imaginary cube root of unity. a)  n(n−1)( n(n−1)(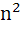 +3n+4) +3n+4) b)  n(n+1)( n(n+1)(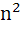 +3n+4) +3n+4) c)  n(n−1)( n(n−1)(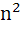 +n+1) +n+1) d)  n(n+1)( n(n+1)(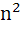 +n+1) +n+1)
|
IIT 1996 |
05:00 min
|
|
285 |
A solution of the differential equation 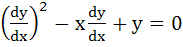 is is a) y = 2 b) y = 2x c) 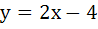 d) 2
A solution of the differential equation 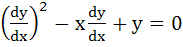 is is a) y = 2 b) y = 2x c) 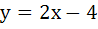 d) 2
|
IIT 1999 |
01:47 min
|
|
286 |
A spherical rain drop evaporates at a rate proportional to its surface area at any instant. The differential equation giving the rate of change of the radius vector of the rain drop is . . . . .
A spherical rain drop evaporates at a rate proportional to its surface area at any instant. The differential equation giving the rate of change of the radius vector of the rain drop is . . . . .
|
IIT 1997 |
01:37 min
|
|
287 |
The value of  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
The value of  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
|
IIT 1997 |
01:38 min
|
|
288 |
Let y = 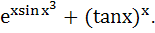 Find Find 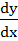 a) 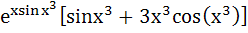 b) 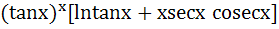 c) 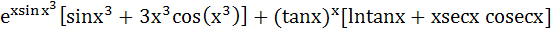 d) 0
Let y = 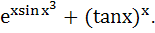 Find Find 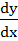 a) 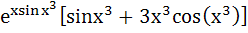 b) 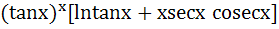 c) 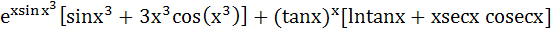 d) 0
|
IIT 1984 |
02:52 min
|
|
289 |
If 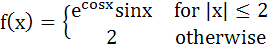 Then 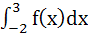 = = a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
If 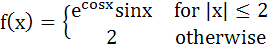 Then 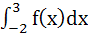 = = a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 2000 |
02:01 min
|
|
290 |
The derivative of an even function is always an odd function. a) False b) True
The derivative of an even function is always an odd function. a) False b) True
|
IIT 1983 |
01:33 min
|
|
291 |
The derivative of 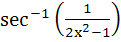 with respect to with respect to 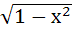 at x = at x =  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
The derivative of 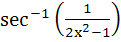 with respect to with respect to 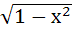 at x = at x =  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
|
IIT 1986 |
04:19 min
|
|
292 |
If f (x) is differentiable and 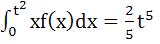 , then , then 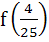 equals equals a)  b) 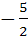 c) 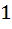 d) 
If f (x) is differentiable and 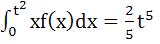 , then , then 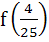 equals equals a)  b) 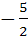 c) 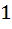 d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
01:33 min
|
|
293 |
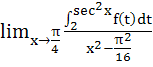 equals equals
a) 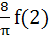 b) 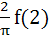 c) 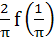 d) 4 f (2)
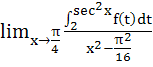 equals equals
a) 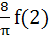 b) 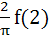 c) 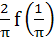 d) 4 f (2)
|
IIT 2007 |
03:41 min
|
|
294 |
The function 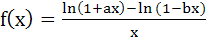 is not defined at x = 0. The value which should be assigned to f at x = 0 so that it is continuous at x = 0 is is not defined at x = 0. The value which should be assigned to f at x = 0 so that it is continuous at x = 0 is a) a – b b) a + b c) lna – lnb d) None of these
The function 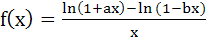 is not defined at x = 0. The value which should be assigned to f at x = 0 so that it is continuous at x = 0 is is not defined at x = 0. The value which should be assigned to f at x = 0 so that it is continuous at x = 0 is a) a – b b) a + b c) lna – lnb d) None of these
|
IIT 1983 |
02:48 min
|
|
295 |
Find the value of 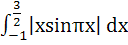 a) 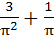 b) 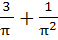 c) 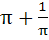 d) 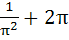
Find the value of 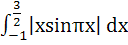 a) 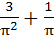 b) 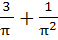 c) 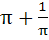 d) 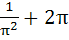
|
IIT 1982 |
07:35 min
|
|
296 |
The set of all points where the function 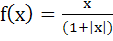 is differentiable is is differentiable is a) 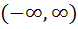 b) [0, ∞) c) 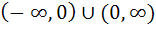 d) (0, ∞) e) None of these
The set of all points where the function 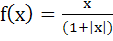 is differentiable is is differentiable is a) 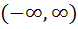 b) [0, ∞) c) 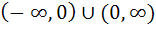 d) (0, ∞) e) None of these
|
IIT 1987 |
04:36 min
|
|
297 |
Given a function f (x) such that
i) it is integrable over every interval on the real axis and
ii) f (t + x) = f (x) for every x and a real t, then show that the integral 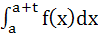 is independent of a. is independent of a.
Given a function f (x) such that
i) it is integrable over every interval on the real axis and
ii) f (t + x) = f (x) for every x and a real t, then show that the integral 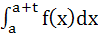 is independent of a. is independent of a.
|
IIT 1984 |
02:15 min
|
|
298 |
The function f(x) = 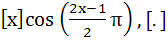 denotes the greatest integer function is discontinuous at denotes the greatest integer function is discontinuous at a) All x b) All integer points c) No x d) x which is not an integer
The function f(x) = 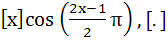 denotes the greatest integer function is discontinuous at denotes the greatest integer function is discontinuous at a) All x b) All integer points c) No x d) x which is not an integer
|
IIT 1993 |
03:16 min
|
|
299 |
If f (x) and g (x) are continuous functions on (0, a) satisfying f (x) = f (a – x) and g (x) + g (a – x) = 2 then show that 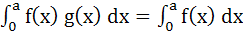
If f (x) and g (x) are continuous functions on (0, a) satisfying f (x) = f (a – x) and g (x) + g (a – x) = 2 then show that 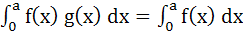
|
IIT 1989 |
02:36 min
|
|
300 |
A cubic f (x) vanishes at x = −2 and has a relative minimum/maximum at x = −1 and 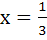 . If . If 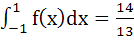 , find the cube f (x). , find the cube f (x). a) x3 + x2 + x + 1 b) x3 + x2 − x + 1 c) x3 − x2 + x + 2 d) x3 + x2 − x + 2
A cubic f (x) vanishes at x = −2 and has a relative minimum/maximum at x = −1 and 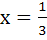 . If . If 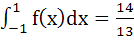 , find the cube f (x). , find the cube f (x). a) x3 + x2 + x + 1 b) x3 + x2 − x + 1 c) x3 − x2 + x + 2 d) x3 + x2 − x + 2
|
IIT 1992 |
05:24 min
|