|
226 |
If a circle passes through the points (a, b) and cuts the circle 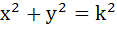 orthogonally, then the equation of the locus of its centre is orthogonally, then the equation of the locus of its centre is a) 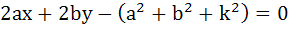 b) 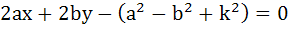 c) 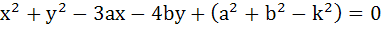 d) 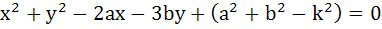
If a circle passes through the points (a, b) and cuts the circle 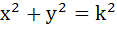 orthogonally, then the equation of the locus of its centre is orthogonally, then the equation of the locus of its centre is a) 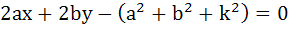 b) 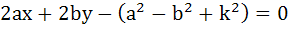 c) 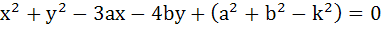 d) 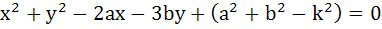
|
IIT 1988 |
04:03 min
|
|
227 |
The number of real solutions of the equation | x |2 – 3 | x | + 2 = 0 is a) 4 b) 1 c) 3 d) 2
The number of real solutions of the equation | x |2 – 3 | x | + 2 = 0 is a) 4 b) 1 c) 3 d) 2
|
IIT 1982 |
01:27 min
|
|
228 |
The locus of the centre of circles which touches externally 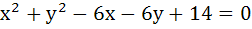 and which touches the Y-axis is given by the equation and which touches the Y-axis is given by the equation a) 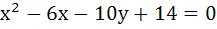 b) 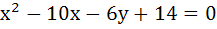 c) 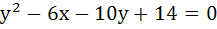 d) 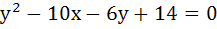
The locus of the centre of circles which touches externally 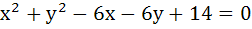 and which touches the Y-axis is given by the equation and which touches the Y-axis is given by the equation a) 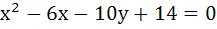 b) 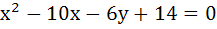 c) 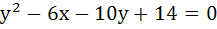 d) 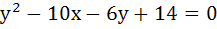
|
IIT 1993 |
04:38 min
|
|
229 |
If p, q, r are any real numbers, then a) Max ( p, q ) < max ( p, q, r ) b) Min ( p, q ) =  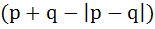 c) Max ( p, q ) < min ( p, q, r ) d) none of these
If p, q, r are any real numbers, then a) Max ( p, q ) < max ( p, q, r ) b) Min ( p, q ) =  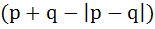 c) Max ( p, q ) < min ( p, q, r ) d) none of these
|
IIT 1982 |
01:52 min
|
|
230 |
A, B, C , D are four points in a plane with position vectors a, b, c, d respectively, such that 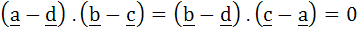 . The point D then is the . . . . . . . of the triangle ABC. . The point D then is the . . . . . . . of the triangle ABC.
A, B, C , D are four points in a plane with position vectors a, b, c, d respectively, such that 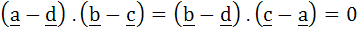 . The point D then is the . . . . . . . of the triangle ABC. . The point D then is the . . . . . . . of the triangle ABC.
|
IIT 1984 |
02:30 min
|
|
231 |
If the vectors
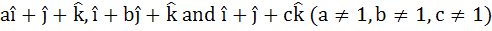 are coplanar then the value of 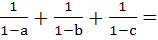 . . . . . . . . . . . .
If the vectors
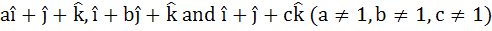 are coplanar then the value of 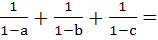 . . . . . . . . . . . .
|
IIT 1987 |
04:15 min
|
|
232 |
The expression 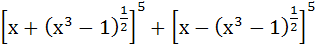 is a polynomial of degree is a polynomial of degree a) 5 b) 6 c) 7 d) 8
The expression 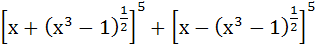 is a polynomial of degree is a polynomial of degree a) 5 b) 6 c) 7 d) 8
|
IIT 1992 |
03:38 min
|
|
233 |
A unit vector coplanar with 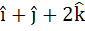 and and 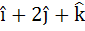 and perpendicular to and perpendicular to 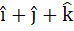 is . . . . . is . . . . .
|
IIT 1992 |
04:49 min
|
|
234 |
The centre of the circle inscribed in the square formed by the lines 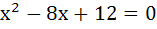 and and 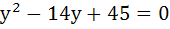 a) (4, 7) b) (7, 4) c) (9, 4) d) (4, 9)
The centre of the circle inscribed in the square formed by the lines 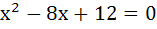 and and 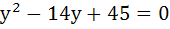 a) (4, 7) b) (7, 4) c) (9, 4) d) (4, 9)
|
IIT 2003 |
02:21 min
|
|
235 |
The equation 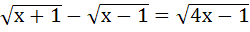 has has a) No solution b) One solution c) Two solutions d) More than two solutions
The equation 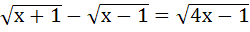 has has a) No solution b) One solution c) Two solutions d) More than two solutions
|
IIT 1997 |
03:20 min
|
|
236 |
If a, b, c, d are positive real numbers such that a + b + c + d = 2 then M = ( a + b ) ( c + d ) satisfies a) 0 ≤ M ≤ 1 b) 1 ≤ M ≤ 2 c) 2 ≤ M ≤ 3 d) 3 ≤ M ≤ 4
If a, b, c, d are positive real numbers such that a + b + c + d = 2 then M = ( a + b ) ( c + d ) satisfies a) 0 ≤ M ≤ 1 b) 1 ≤ M ≤ 2 c) 2 ≤ M ≤ 3 d) 3 ≤ M ≤ 4
|
IIT 2000 |
01:54 min
|
|
237 |
Let a, b, c be non-zero real numbers such that
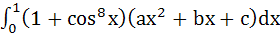
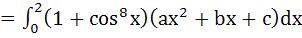
Then the quadratic function 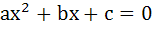 has has a) no root in (0, 2) b) at least one root in (1, 2) c) a double root in (0, 2) d) two imaginary roots
Let a, b, c be non-zero real numbers such that
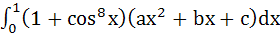
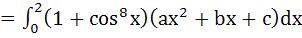
Then the quadratic function 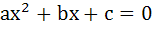 has has a) no root in (0, 2) b) at least one root in (1, 2) c) a double root in (0, 2) d) two imaginary roots
|
IIT 1981 |
04:42 min
|
|
238 |
Let α, β be the roots of 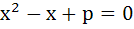 and γ, δ roots of and γ, δ roots of 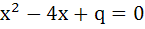 . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are a) −2, −32 b) −2, 3 c) −6, 3 d) −6, −32
Let α, β be the roots of 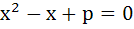 and γ, δ roots of and γ, δ roots of 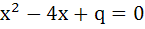 . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are a) −2, −32 b) −2, 3 c) −6, 3 d) −6, −32
|
IIT 2001 |
05:16 min
|
|
239 |
Let 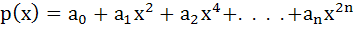 be a polynomial in a real variable x with 0 be a polynomial in a real variable x with 0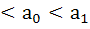 < <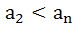 then the function p(x) has then the function p(x) has a) neither maximum nor minimum b) only one maximum c) only one minimum d) only one maximum and only one minimum e) none of these
Let 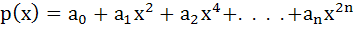 be a polynomial in a real variable x with 0 be a polynomial in a real variable x with 0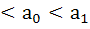 < <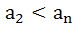 then the function p(x) has then the function p(x) has a) neither maximum nor minimum b) only one maximum c) only one minimum d) only one maximum and only one minimum e) none of these
|
IIT 1986 |
02:37 min
|
|
240 |
Let a given line L1 intersect the X-axis and Y-axis at P and Q respectively. Let another line L2 perpendicular to L1 cut the X and Y axis at R and S respectively. Show that the locus of the point of intersection of the lines PS and QR is a circle passing through the origin.
Let a given line L1 intersect the X-axis and Y-axis at P and Q respectively. Let another line L2 perpendicular to L1 cut the X and Y axis at R and S respectively. Show that the locus of the point of intersection of the lines PS and QR is a circle passing through the origin.
|
IIT 1987 |
07:55 min
|
|
241 |
If  are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of 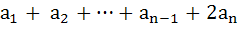 is is a) 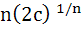 b) 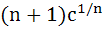 c) 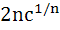 d) 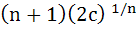
If  are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of 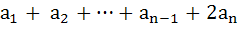 is is a) 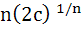 b) 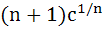 c) 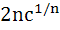 d) 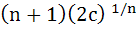
|
IIT 2002 |
02:06 min
|
|
242 |
The function defined by 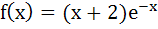 is is a) Decreasing for all x b) Decreasing in 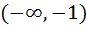 and increasing in and increasing in 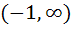 c) Increasing for all x d) Decreasing in 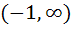 and increasing in and increasing in 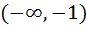
The function defined by 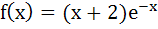 is is a) Decreasing for all x b) Decreasing in 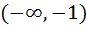 and increasing in and increasing in 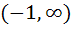 c) Increasing for all x d) Decreasing in 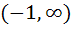 and increasing in and increasing in 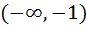
|
IIT 1994 |
01:20 min
|
|
243 |
For all x, 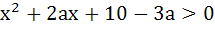 then the interval in which a lies is then the interval in which a lies is a) a < 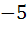 b) 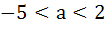 c) 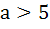 d) 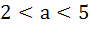
For all x, 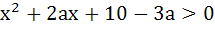 then the interval in which a lies is then the interval in which a lies is a) a < 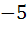 b) 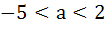 c) 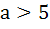 d) 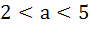
|
IIT 2004 |
01:45 min
|
|
244 |
Let the three digit numbers A28, 3B9 and 62C where A, B, C are integers between 0 and 9, be divisible by a fixed number k. Show that the determinant
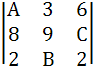 is divisible by k.
Let the three digit numbers A28, 3B9 and 62C where A, B, C are integers between 0 and 9, be divisible by a fixed number k. Show that the determinant
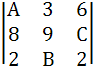 is divisible by k.
|
IIT 1990 |
04:45 min
|
|
245 |
Let a circle be given by 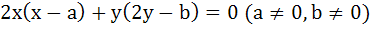 . Find the condition on a and b if two chords each bisected by the X–axis can be drawn from . Find the condition on a and b if two chords each bisected by the X–axis can be drawn from 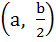 . .
Let a circle be given by 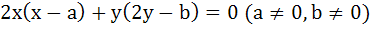 . Find the condition on a and b if two chords each bisected by the X–axis can be drawn from . Find the condition on a and b if two chords each bisected by the X–axis can be drawn from 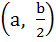 . .
|
IIT 1992 |
06:10 min
|
|
246 |
Let a, b, c be the sides of a triangle where a ≠ c and λ ε R. If roots of the equation 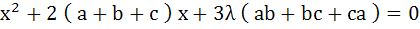 are real then are real then a) 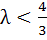 b) 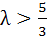 c) 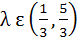 d) 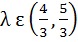
Let a, b, c be the sides of a triangle where a ≠ c and λ ε R. If roots of the equation 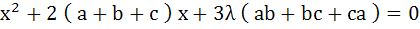 are real then are real then a) 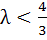 b) 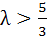 c) 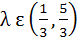 d) 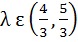
|
IIT 2006 |
04:47 min
|
|
247 |
Find the value of the determinant
 where a, b, c are respectively pth, qth and rth term of a harmonic progression. a) 0 b) 1 c) ½ d) None of the above
Find the value of the determinant
 where a, b, c are respectively pth, qth and rth term of a harmonic progression. a) 0 b) 1 c) ½ d) None of the above
|
IIT 1997 |
04:23 min
|
|
248 |
Consider the following Statement (S) and Reason (R) S: Both sinx, cosx are decreasing functions in the interval 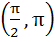 R: If a differentiable function decreases in an interval (a, b) then the derivative also decreases in (a, b) Which of the following is true? a) Both S and R are wrong b) Both S and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of S c) S is correct and R is the correct explanation of S d) S is correct and R is wrong
Consider the following Statement (S) and Reason (R) S: Both sinx, cosx are decreasing functions in the interval 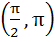 R: If a differentiable function decreases in an interval (a, b) then the derivative also decreases in (a, b) Which of the following is true? a) Both S and R are wrong b) Both S and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of S c) S is correct and R is the correct explanation of S d) S is correct and R is wrong
|
IIT 2000 |
02:40 min
|
|
249 |
Let S is the set of all real x, such that 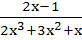 is positive, then S contains is positive, then S contains a) 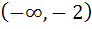 b) 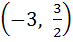 c) 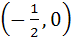 d) 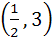
Let S is the set of all real x, such that 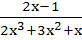 is positive, then S contains is positive, then S contains a) 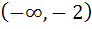 b) 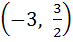 c) 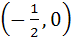 d) 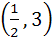
|
IIT 1986 |
04:28 min
|
|
250 |
Let pλ4 + qλ3 + rλ2 + sλ + t = 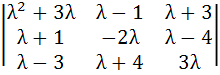 be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. a) 0 b) +1 c) –1 d) ±1
Let pλ4 + qλ3 + rλ2 + sλ + t = 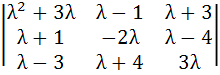 be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. a) 0 b) +1 c) –1 d) ±1
|
IIT 1981 |
02:38 min
|