|
576 |
If A, B, C are three non-coplanar vectors then
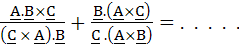
If A, B, C are three non-coplanar vectors then
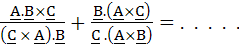
|
IIT 1985 |
02:22 min
|
|
577 |
The triangle PQR is inscribed in the circle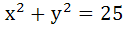 . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to a)  b)  c) 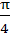 d) 
The triangle PQR is inscribed in the circle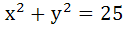 . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to a)  b)  c) 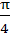 d) 
|
IIT 2000 |
02:46 min
|
|
578 |
Let a, b, c be real numbers, a ≠ 0. If α is a root of 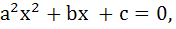 β is a root of β is a root of 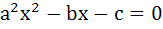 and 0 < α < β then the equation and 0 < α < β then the equation 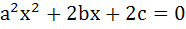 has a root γ that always satisfies has a root γ that always satisfies a) γ = 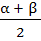 b) γ = 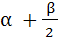 c) γ = α d) α < γ < β
Let a, b, c be real numbers, a ≠ 0. If α is a root of 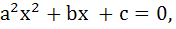 β is a root of β is a root of 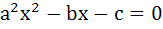 and 0 < α < β then the equation and 0 < α < β then the equation 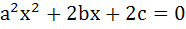 has a root γ that always satisfies has a root γ that always satisfies a) γ = 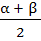 b) γ = 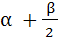 c) γ = α d) α < γ < β
|
IIT 1989 |
03:43 min
|
|
579 |
The projection of a vector a along and perpendicular to a non-zero vector 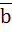 are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively. are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively.
The projection of a vector a along and perpendicular to a non-zero vector 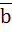 are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively. are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively.
|
IIT 1988 |
03:53 min
|
|
580 |
If the tangent at the point P on the circle 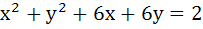 meets the straight line meets the straight line 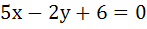 at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is a) 4 b) 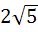 c) 5 d) 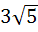
If the tangent at the point P on the circle 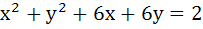 meets the straight line meets the straight line 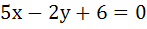 at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is a) 4 b) 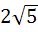 c) 5 d) 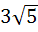
|
IIT 2002 |
01:46 min
|
|
581 |
If p, q, r are positive and are in arithmetic progression the roots of the quadratic 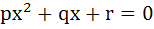 are all real for are all real for a) 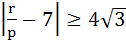 b) 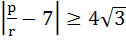 c) 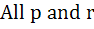 d) 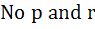
If p, q, r are positive and are in arithmetic progression the roots of the quadratic 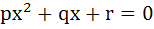 are all real for are all real for a) 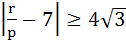 b) 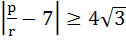 c) 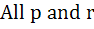 d) 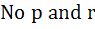
|
IIT 1994 |
02:34 min
|
|
582 |
A non-zero vector a is parallel to the line of intersection of the plane determined by the vectors 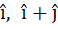 and the plane determined by the vectors and the plane determined by the vectors 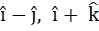 . The angle between a and . The angle between a and 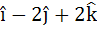 is . . . . . is . . . . .
|
IIT 1996 |
06:39 min
|
|
583 |
A circle is given by 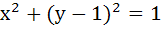 , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is a) 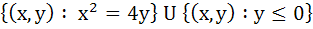 b)  c) 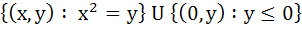 d) 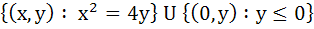
A circle is given by 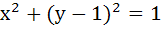 , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is a) 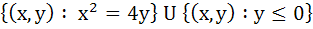 b)  c) 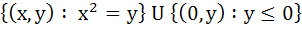 d) 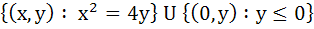
|
IIT 2005 |
05:02 min
|
|
584 |
If α and β (α < β) are roots of the equation 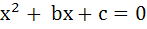 where c < 0 < b then where c < 0 < b then a) 0 < α < β b) α < 0 < β < | α | c) α < β < 0 d) α < 0 < | α | < β
If α and β (α < β) are roots of the equation 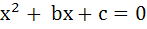 where c < 0 < b then where c < 0 < b then a) 0 < α < β b) α < 0 < β < | α | c) α < β < 0 d) α < 0 < | α | < β
|
IIT 2000 |
02:20 min
|
|
585 |
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the point (2, 0) and whose centre is the limit of the point of intersection of the lines 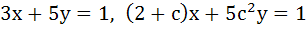 . .
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the point (2, 0) and whose centre is the limit of the point of intersection of the lines 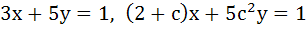 . .
|
IIT 1979 |
06:56 min
|
|
586 |
For the equation 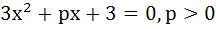 if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to a)  b) 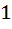 c) 3 d) 
For the equation 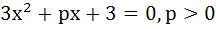 if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to a)  b) 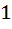 c) 3 d) 
|
IIT 2000 |
03:13 min
|
|
587 |
AB is a diameter of a circle and C is any point on the circumference of the circle. Then a) The area of △ABC is maximum if it is isosceles b) The area of △ABC is minimum if it is isosceles c) The perimeter of △ABC is minimum when it is isosceles d) None of these
AB is a diameter of a circle and C is any point on the circumference of the circle. Then a) The area of △ABC is maximum if it is isosceles b) The area of △ABC is minimum if it is isosceles c) The perimeter of △ABC is minimum when it is isosceles d) None of these
|
IIT 1983 |
05:50 min
|
|
588 |
The abscissas of two points A and B are the roots of the equation 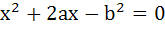 and their ordinates are the roots of the equation and their ordinates are the roots of the equation 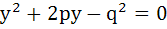 . Find the equation of the circle on AB as diameter. . Find the equation of the circle on AB as diameter.
The abscissas of two points A and B are the roots of the equation 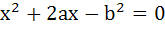 and their ordinates are the roots of the equation and their ordinates are the roots of the equation 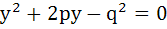 . Find the equation of the circle on AB as diameter. . Find the equation of the circle on AB as diameter.
|
IIT 1984 |
04:47 min
|
|
589 |
The number of solutions of 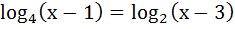 is is a) 3 b) 1 c) 2 d) 0
The number of solutions of 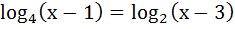 is is a) 3 b) 1 c) 2 d) 0
|
IIT 2001 |
02:44 min
|
|
590 |
Let 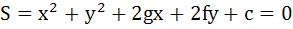 be a given circle. Find the locus of the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin upon any chord of S which subtends a right angle at the origin. be a given circle. Find the locus of the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin upon any chord of S which subtends a right angle at the origin.
Let 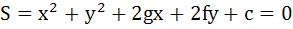 be a given circle. Find the locus of the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin upon any chord of S which subtends a right angle at the origin. be a given circle. Find the locus of the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin upon any chord of S which subtends a right angle at the origin.
|
IIT 1988 |
08:11 min
|
|
591 |
If 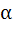 ε ε 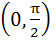 then then 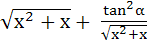 is always greater than or equal to is always greater than or equal to a) 2 tan 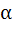 b) 1 c) 2 d) 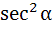
If 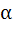 ε ε 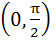 then then 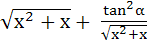 is always greater than or equal to is always greater than or equal to a) 2 tan 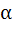 b) 1 c) 2 d) 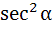
|
IIT 2003 |
02:05 min
|
|
592 |
The circles each of radius 5 units touch each other at (1, 2). If the equation of the common tangent is 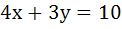 , find the equation of the circles. , find the equation of the circles.
The circles each of radius 5 units touch each other at (1, 2). If the equation of the common tangent is 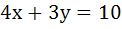 , find the equation of the circles. , find the equation of the circles.
|
IIT 1991 |
05:39 min
|
|
593 |
The function 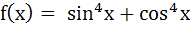 increases if increases if a) 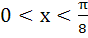 b) 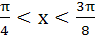 c) 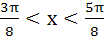 d) 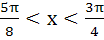
The function 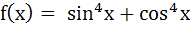 increases if increases if a) 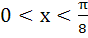 b) 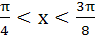 c) 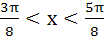 d) 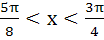
|
IIT 1999 |
02:02 min
|
|
594 |
Let α, β be roots of the equation 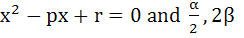 are the roots of the equation are the roots of the equation 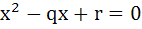 then the value of r is equal to then the value of r is equal to a) 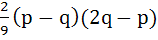 b) 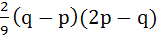 c) 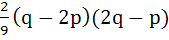 d) 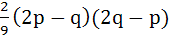
Let α, β be roots of the equation 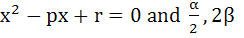 are the roots of the equation are the roots of the equation 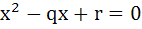 then the value of r is equal to then the value of r is equal to a) 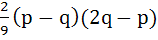 b) 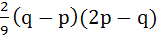 c) 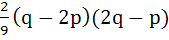 d) 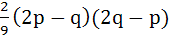
|
IIT 2007 |
02:46 min
|
|
595 |
The triangle formed by the tangent to the curve 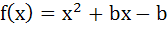 at (1, 1) and the coordinate axes, lies in the first quadrant if its area is 2. Then the value of b is at (1, 1) and the coordinate axes, lies in the first quadrant if its area is 2. Then the value of b is
a) – 1 b) 3 c) – 3 d) 1
The triangle formed by the tangent to the curve 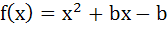 at (1, 1) and the coordinate axes, lies in the first quadrant if its area is 2. Then the value of b is at (1, 1) and the coordinate axes, lies in the first quadrant if its area is 2. Then the value of b is
a) – 1 b) 3 c) – 3 d) 1
|
IIT 2001 |
03:51 min
|
|
596 |
Consider a curve 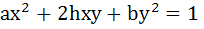 and a point P not on the curve. A line drawn from the point P intersects the curve at points Q and R. If PQ.QR is independent of the slope of the line then show that the curve is a circle. and a point P not on the curve. A line drawn from the point P intersects the curve at points Q and R. If PQ.QR is independent of the slope of the line then show that the curve is a circle.
Consider a curve 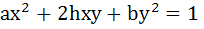 and a point P not on the curve. A line drawn from the point P intersects the curve at points Q and R. If PQ.QR is independent of the slope of the line then show that the curve is a circle. and a point P not on the curve. A line drawn from the point P intersects the curve at points Q and R. If PQ.QR is independent of the slope of the line then show that the curve is a circle.
|
IIT 1997 |
07:57 min
|
|
597 |
Show that square of 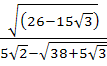 is a rational number. is a rational number.
Show that square of 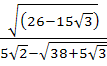 is a rational number. is a rational number.
|
IIT 1978 |
04:58 min
|
|
598 |
The determinants 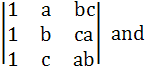 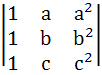 are. are. a) Identical b) Not identical c) Identical if a = b = c d) None of the above
The determinants 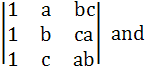 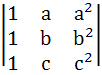 are. are. a) Identical b) Not identical c) Identical if a = b = c d) None of the above
|
IIT 1983 |
02:07 min
|
|
599 |
Given that x = −9 is a root of 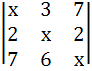 = 0 = 0  . .
a) {2, 7} b) {−2, −7} c) {2, 0} d) {0, 7}
Given that x = −9 is a root of 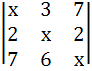 = 0 = 0  . .
a) {2, 7} b) {−2, −7} c) {2, 0} d) {0, 7}
|
IIT 1983 |
02:14 min
|
|
600 |
The area enclosed between y = ax2 and x = ay2 (a > 0) is one square unit. Then the value of a is a) 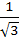 b)  c) 1 d) 
The area enclosed between y = ax2 and x = ay2 (a > 0) is one square unit. Then the value of a is a) 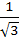 b)  c) 1 d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
04:13 min
|