|
1 |
A solution of the differential equation 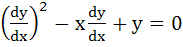 is is a) y = 2 b) y = 2x c) 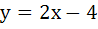 d) 2
A solution of the differential equation 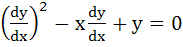 is is a) y = 2 b) y = 2x c) 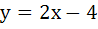 d) 2
|
IIT 1999 |
01:47 min
|
|
2 |
For all x, 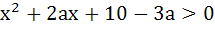 then the interval in which a lies is then the interval in which a lies is a) a < 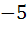 b) 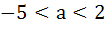 c) 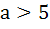 d) 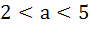
For all x, 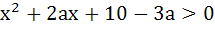 then the interval in which a lies is then the interval in which a lies is a) a < 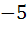 b) 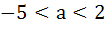 c) 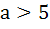 d) 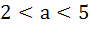
|
IIT 2004 |
01:45 min
|
|
3 |
Let the three digit numbers A28, 3B9 and 62C where A, B, C are integers between 0 and 9, be divisible by a fixed number k. Show that the determinant
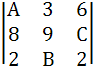 is divisible by k.
Let the three digit numbers A28, 3B9 and 62C where A, B, C are integers between 0 and 9, be divisible by a fixed number k. Show that the determinant
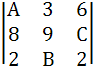 is divisible by k.
|
IIT 1990 |
04:45 min
|
|
4 |
If a and b are real numbers between 0 and 1 such that the points 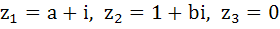 form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . a) 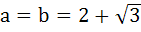 b) 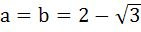 c) 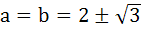 d) 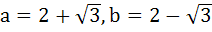
If a and b are real numbers between 0 and 1 such that the points 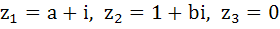 form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . a) 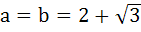 b) 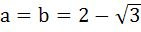 c) 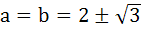 d) 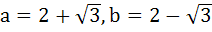
|
IIT 1989 |
03:07 min
|
|
5 |
Let E be the ellipse 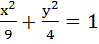 and C be the circle and C be the circle 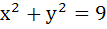 . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then a) Q lies inside C but outside E b) Q lies outside both C and E c) P lies inside both C and E d) P lies inside C but outside E
Let E be the ellipse 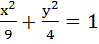 and C be the circle and C be the circle 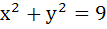 . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then a) Q lies inside C but outside E b) Q lies outside both C and E c) P lies inside both C and E d) P lies inside C but outside E
|
IIT 1994 |
04:15 min
|
|
6 |
Let a, b, c be the sides of a triangle where a ≠ c and λ ε R. If roots of the equation 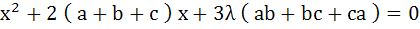 are real then are real then a) 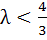 b) 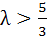 c) 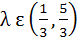 d) 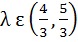
Let a, b, c be the sides of a triangle where a ≠ c and λ ε R. If roots of the equation 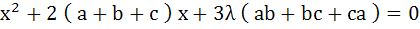 are real then are real then a) 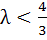 b) 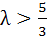 c) 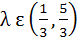 d) 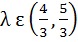
|
IIT 2006 |
04:47 min
|
|
7 |
Find the value of the determinant
 where a, b, c are respectively pth, qth and rth term of a harmonic progression. a) 0 b) 1 c) ½ d) None of the above
Find the value of the determinant
 where a, b, c are respectively pth, qth and rth term of a harmonic progression. a) 0 b) 1 c) ½ d) None of the above
|
IIT 1997 |
04:23 min
|
|
8 |
If tangents are drawn to the ellipse 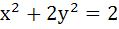 then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is a) 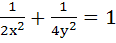 b) 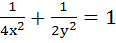 c) 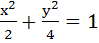 d) 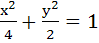
If tangents are drawn to the ellipse 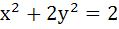 then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is a) 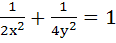 b) 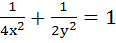 c) 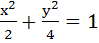 d) 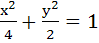
|
IIT 2004 |
03:11 min
|
|
9 |
Let S is the set of all real x, such that 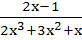 is positive, then S contains is positive, then S contains a) 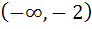 b) 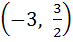 c) 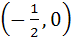 d) 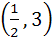
Let S is the set of all real x, such that 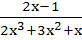 is positive, then S contains is positive, then S contains a) 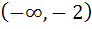 b) 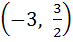 c) 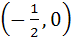 d) 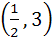
|
IIT 1986 |
04:28 min
|
|
10 |
Let pλ4 + qλ3 + rλ2 + sλ + t = 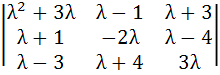 be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. a) 0 b) +1 c) –1 d) ±1
Let pλ4 + qλ3 + rλ2 + sλ + t = 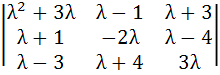 be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. be an identity in λ where p, q, r, s, t are constants. Find the value of t. a) 0 b) +1 c) –1 d) ±1
|
IIT 1981 |
02:38 min
|
|
11 |
Let P be a variable point on the ellipse 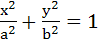 with foci F1 and F2. . If A is the area of with foci F1 and F2. . If A is the area of 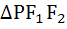 then the maximum value of A is . . . . . then the maximum value of A is . . . . .
Let P be a variable point on the ellipse 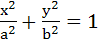 with foci F1 and F2. . If A is the area of with foci F1 and F2. . If A is the area of 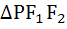 then the maximum value of A is . . . . . then the maximum value of A is . . . . .
|
IIT 1994 |
02:27 min
|
|
12 |
A spherical rain drop evaporates at a rate proportional to its surface area at any instant. The differential equation giving the rate of change of the radius vector of the rain drop is . . . . .
A spherical rain drop evaporates at a rate proportional to its surface area at any instant. The differential equation giving the rate of change of the radius vector of the rain drop is . . . . .
|
IIT 1997 |
01:37 min
|
|
13 |
The value of the determinant 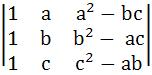 is ………… is ………… a) 0 b) 1 c) a2 + b2 + c2 – abc d) a2 + b2 + c2 – 3abc
The value of the determinant 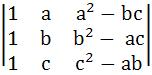 is ………… is ………… a) 0 b) 1 c) a2 + b2 + c2 – abc d) a2 + b2 + c2 – 3abc
|
IIT 1988 |
02:49 min
|
|
14 |
The equation 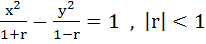 represents represents a) An ellipse b) A hyperbola c) A circle d) None of these
The equation 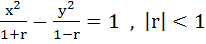 represents represents a) An ellipse b) A hyperbola c) A circle d) None of these
|
IIT 1981 |
01:03 min
|
|
15 |
Find all the real values of x which satisfy 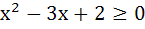 and and 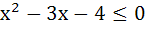 . .
Find all the real values of x which satisfy 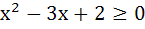 and and 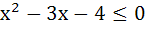 . .
|
IIT 1983 |
02:29 min
|
|
16 |
For the hyperbola 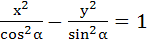 which of the following remains constant with change in α which of the following remains constant with change in α a) Abscissae of vertices b) Abscissae of focii c) Eccentricity d) Directrix
For the hyperbola 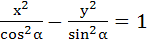 which of the following remains constant with change in α which of the following remains constant with change in α a) Abscissae of vertices b) Abscissae of focii c) Eccentricity d) Directrix
|
IIT 2003 |
01:32 min
|
|
17 |
The value of  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
The value of  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
|
IIT 1997 |
01:38 min
|
|
18 |
For a ≤ 0, determine all real roots of the equation
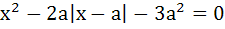
For a ≤ 0, determine all real roots of the equation
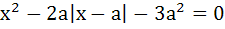
|
IIT 1986 |
03:49 min
|
|
19 |
If a, b, c, d and p are distinct real numbers such that
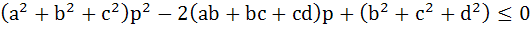
then a, b, c, d a) Are in Arithmetic Progression b) Are in Geometric Progression c) Are in Harmonic Progression d) Satisfy ab = cd e) Satisfy none of these
If a, b, c, d and p are distinct real numbers such that
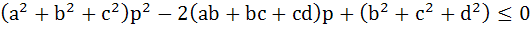
then a, b, c, d a) Are in Arithmetic Progression b) Are in Geometric Progression c) Are in Harmonic Progression d) Satisfy ab = cd e) Satisfy none of these
|
IIT 1987 |
02:16 min
|
|
20 |
Suppose f(x) is a function satisfying the following conditions i) f(0) = 2, f(1) = 1 ii) f has a minimum value at x = 5/2 and iii) for all x 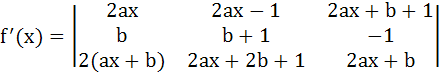
where a, b are constants. Determine the constants a and b, and the function f(x).
a) 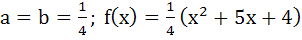 b) 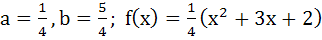 c) 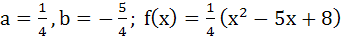 d) 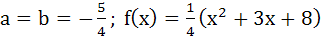
Suppose f(x) is a function satisfying the following conditions i) f(0) = 2, f(1) = 1 ii) f has a minimum value at x = 5/2 and iii) for all x 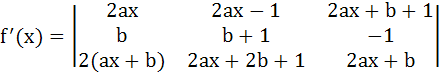
where a, b are constants. Determine the constants a and b, and the function f(x).
a) 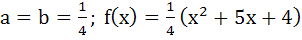 b) 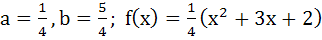 c) 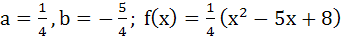 d) 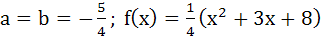
|
IIT 1998 |
06:16 min
|
|
21 |
Solve 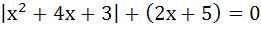
Solve 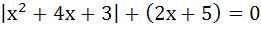
|
IIT 1988 |
03:54 min
|
|
22 |
If 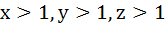 are in Geometric Progression then are in Geometric Progression then
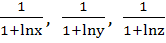 are in are in a) Arithmetic Progression b) Geometric Progression c) Harmonic Progression d) None of these
If 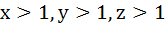 are in Geometric Progression then are in Geometric Progression then
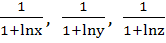 are in are in a) Arithmetic Progression b) Geometric Progression c) Harmonic Progression d) None of these
|
IIT 1998 |
02:25 min
|
|
23 |
Let 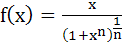 for n ≥ 2 and for n ≥ 2 and
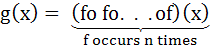 Then 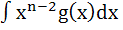 equals equals a) 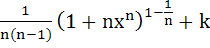 b) 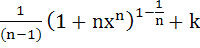 c) 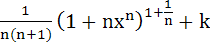 d) 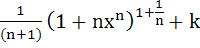
Let 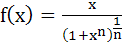 for n ≥ 2 and for n ≥ 2 and
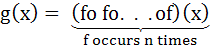 Then 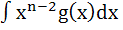 equals equals a) 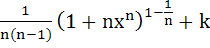 b) 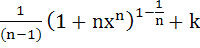 c) 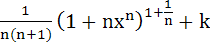 d) 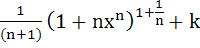
|
IIT 2007 |
08:22 min
|
|
24 |
India played two matches each with Australia and West indies. In any match the probability of India getting the points 0, 1, and 2 are 0.45, 0.05 and 0.50 respectively. Assuming that the outcomes are independent, the probability of India getting at least seven points is a) 0.8730 b) 0.0875 c) 0.0625 d) 0.0250
India played two matches each with Australia and West indies. In any match the probability of India getting the points 0, 1, and 2 are 0.45, 0.05 and 0.50 respectively. Assuming that the outcomes are independent, the probability of India getting at least seven points is a) 0.8730 b) 0.0875 c) 0.0625 d) 0.0250
|
IIT 1992 |
03:03 min
|
|
25 |
Let Tn denote the number of triangles which can be formed using the vertices of a regular polygon of n sides. If 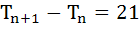 then n equals then n equals a) 5 b) 7 c) 6 d) 4
Let Tn denote the number of triangles which can be formed using the vertices of a regular polygon of n sides. If 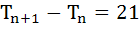 then n equals then n equals a) 5 b) 7 c) 6 d) 4
|
IIT 2001 |
02:30 min
|