|
826 |
The value of 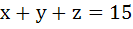 . Given that a, x, y, z, b are in Arithmetic Progression while the value of . Given that a, x, y, z, b are in Arithmetic Progression while the value of 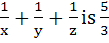 . If a, x, y, z, b are in Harmonic Progression then find a and b. . If a, x, y, z, b are in Harmonic Progression then find a and b.
The value of 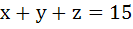 . Given that a, x, y, z, b are in Arithmetic Progression while the value of . Given that a, x, y, z, b are in Arithmetic Progression while the value of 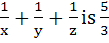 . If a, x, y, z, b are in Harmonic Progression then find a and b. . If a, x, y, z, b are in Harmonic Progression then find a and b.
|
IIT 1978 |
|
|
827 |
If S1, S2, . . . .,Sn are the sums of infinite geometric series whose first terms are 1, 2, 3, . . ., n and whose common ratios are 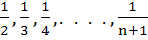 respectively, then find the value of respectively, then find the value of 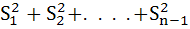
If S1, S2, . . . .,Sn are the sums of infinite geometric series whose first terms are 1, 2, 3, . . ., n and whose common ratios are 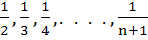 respectively, then find the value of respectively, then find the value of 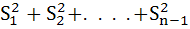
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
828 |
Let a, b are real positive numbers. If a, A1, A2, b are in Arithmetic Progression, a, G1, G2, b are in Geometric Progression and a, H1, H2, b are in Harmonic Progression show that
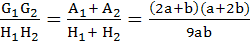
Let a, b are real positive numbers. If a, A1, A2, b are in Arithmetic Progression, a, G1, G2, b are in Geometric Progression and a, H1, H2, b are in Harmonic Progression show that
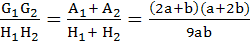
|
IIT 2002 |
|
|
829 |
Consider the lines 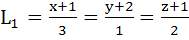 ; ;
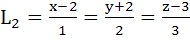
The unit vector perpendicular to both L1 and L2 is
a) 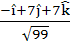 b) 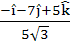 c) 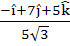 d) 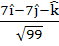
Consider the lines 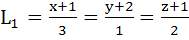 ; ;
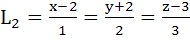
The unit vector perpendicular to both L1 and L2 is
a) 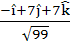 b) 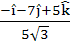 c) 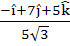 d) 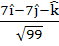
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
830 |
The differential equation 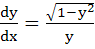 determines a family of circles with determines a family of circles with a) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, 1) b) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, -1) c) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the X-axis d) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the Y-axis
The differential equation 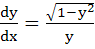 determines a family of circles with determines a family of circles with a) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, 1) b) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, -1) c) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the X-axis d) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the Y-axis
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
831 |
If 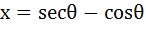 and and 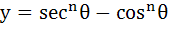 , then show that , then show that
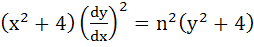
|
IIT 1989 |
|
|
832 |
Let u (x) and v (x) satisfy the differential equations 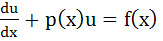 and and 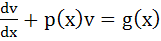 where p (x), f (x) and g (x) are continuous functions. If where p (x), f (x) and g (x) are continuous functions. If  u (x1) > v (x1) for some x1 and f (x) > g (x) for all x > x1, prove that at any point (x, y) where x > x1 does not satisfy the equations y = u (x) and y = v (x) u (x1) > v (x1) for some x1 and f (x) > g (x) for all x > x1, prove that at any point (x, y) where x > x1 does not satisfy the equations y = u (x) and y = v (x)
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
833 |
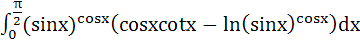 is is
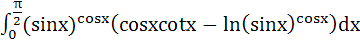 is is
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
834 |
Let f(x) = |x – 1|, then a) 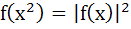 b) 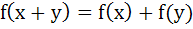 c) 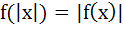 d) None of these
Let f(x) = |x – 1|, then a) 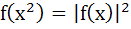 b) 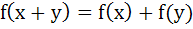 c) 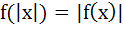 d) None of these
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
835 |
Let 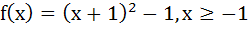 , then the set , then the set 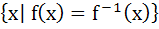 is is a) 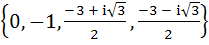 b) 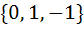 c) 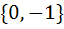 d) ϕ
Let 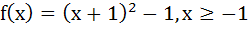 , then the set , then the set 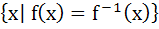 is is a) 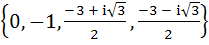 b) 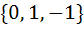 c) 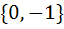 d) ϕ
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
836 |
If f(x) = 3x – 5 then 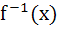 a) is given by 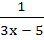 b) is given by 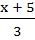 c) does not exist because f is not one-one d) does not exist because f is not onto
If f(x) = 3x – 5 then 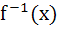 a) is given by 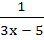 b) is given by 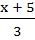 c) does not exist because f is not one-one d) does not exist because f is not onto
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
837 |
The domain of definition of 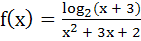 is is a) 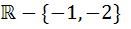 b) 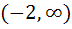 c) 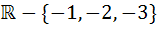 d) 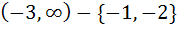
The domain of definition of 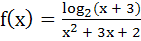 is is a) 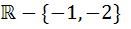 b) 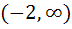 c) 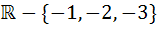 d) 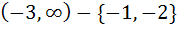
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
838 |
Let f : ℝ → ℝ be defined by f(x) = 2x + sinx for all x  ℝ. Then f is ℝ. Then f is a) One to one and onto b) One to one but not onto c) Onto but not one to one d) Neither one to one nor onto
Let f : ℝ → ℝ be defined by f(x) = 2x + sinx for all x 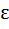 ℝ. Then f is ℝ. Then f is a) One to one and onto b) One to one but not onto c) Onto but not one to one d) Neither one to one nor onto
|
IIT 2002 |
|
|
839 |
Range of 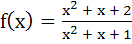 ; x ; x 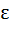 ℝ is ℝ is a) (1, ∞) b) 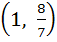 c) 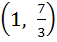 d) 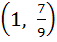
Range of 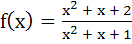 ; x ; x 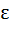 ℝ is ℝ is a) (1, ∞) b) 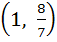 c) 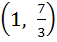 d) 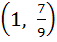
|
IIT 2003 |
|
|
840 |
If 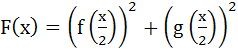 where where 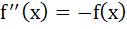
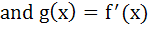 . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to a) 5 b) 10 c) 0 d) 15
If 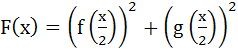 where where 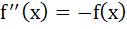
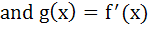 . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to a) 5 b) 10 c) 0 d) 15
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
841 |
Subjective problems
Let 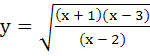 . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. a) [− 1, 2) b) [3, ∞) c) [− 1, 2) ∪ [3, ∞) d) None of the above
Subjective problems
Let 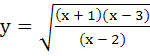 . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. a) [− 1, 2) b) [3, ∞) c) [− 1, 2) ∪ [3, ∞) d) None of the above
|
IIT 1980 |
|
|
842 |
Let R be the set of real numbers and f : R → R be such that for all x and y in R, 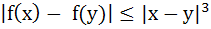 . Prove that f(x) is constant. . Prove that f(x) is constant.
Let R be the set of real numbers and f : R → R be such that for all x and y in R, 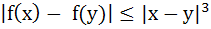 . Prove that f(x) is constant. . Prove that f(x) is constant.
|
IIT 1988 |
|
|
843 |
If f1(x) and f2(x) are defined by domains D1 and D2 respectively then f1(x) + f2(x) is defined as on D1 ⋂ D2 a) True b) False
If f1(x) and f2(x) are defined by domains D1 and D2 respectively then f1(x) + f2(x) is defined as on D1 ⋂ D2 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1988 |
|
|
844 |
If 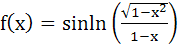 then the domain of f(x) is then the domain of f(x) is
If 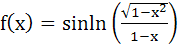 then the domain of f(x) is then the domain of f(x) is
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
845 |
Let f(x) be a non constant differentiable function defined on (−∞, ∞) such that f(x) = f(1 – x) and 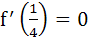 then then a) 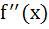 vanishes at twice an (0, 1) vanishes at twice an (0, 1) b) 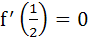 c) 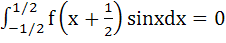 d) 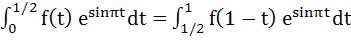
Let f(x) be a non constant differentiable function defined on (−∞, ∞) such that f(x) = f(1 – x) and 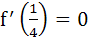 then then a) 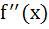 vanishes at twice an (0, 1) vanishes at twice an (0, 1) b) 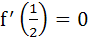 c) 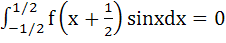 d) 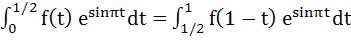
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
846 |
Let n be an odd integer. If sin nθ = 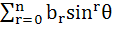 for every value of θ, then for every value of θ, then a) 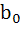 = 1, = 1, 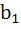 = 3 = 3 b) 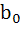 = 0, = 0, 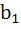 = n = n c) 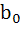 = −1, = −1, 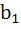 = n = n d) 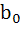 = 1, = 1, 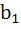 = = 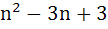
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
847 |
Multiple choices
Let 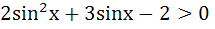 and and 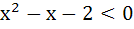 (x is measured in radians) then x lies in the interval (x is measured in radians) then x lies in the interval a) 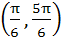 b) 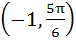 c) 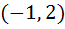 d) 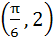
Multiple choices
Let 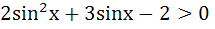 and and 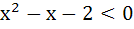 (x is measured in radians) then x lies in the interval (x is measured in radians) then x lies in the interval a) 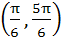 b) 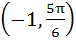 c) 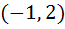 d) 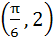
|
IIT 1994 |
|
|
848 |
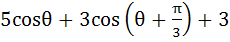 lies between –4 and 10. lies between –4 and 10.
a) True b) False
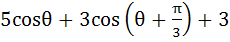 lies between –4 and 10. lies between –4 and 10.
a) True b) False
|
IIT 1979 |
|
|
849 |
Let 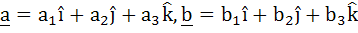 and and 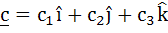 be three non-zero vectors such that c is a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors a and b and the angle between the vectors a and b is be three non-zero vectors such that c is a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors a and b and the angle between the vectors a and b is  then then
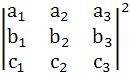 is equal to is equal to a) 1 b) 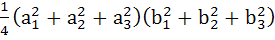 c) 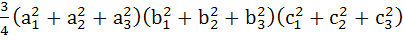 d) None of these
Let 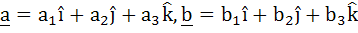 and and 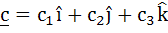 be three non-zero vectors such that c is a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors a and b and the angle between the vectors a and b is be three non-zero vectors such that c is a unit vector perpendicular to both the vectors a and b and the angle between the vectors a and b is  then then
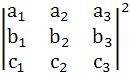 is equal to is equal to a) 1 b) 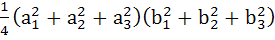 c) 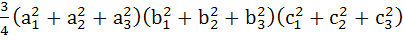 d) None of these
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
850 |
Determine the smallest positive value of x (in degrees) for which 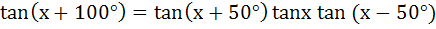 a) 30° b) 50° c) 55° d) 60°
Determine the smallest positive value of x (in degrees) for which 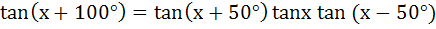 a) 30° b) 50° c) 55° d) 60°
|
IIT 1993 |
|