|
926 |
In [0, 1], Lagrange’s Mean Value theorem is not applicable to a) 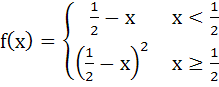 b) 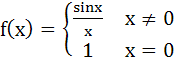 c) 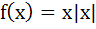 d) 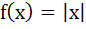
In [0, 1], Lagrange’s Mean Value theorem is not applicable to a) 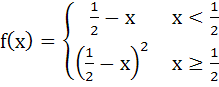 b) 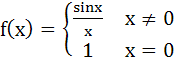 c) 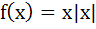 d) 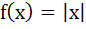
|
IIT 2003 |
|
|
927 |
The area bounded by the angle bisectors of the lines x2 – y2 + 2y = 1 and the line x + y = 3 is a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 6
The area bounded by the angle bisectors of the lines x2 – y2 + 2y = 1 and the line x + y = 3 is a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 6
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
928 |
Multiple choice Let 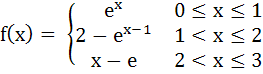 and and 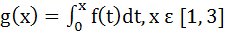
Then g(x) has a) Local maximum at x = 1 + ln2 and local minima at x = e b) Local maximum at x = 1 and local minima at x = 2 c) No local maximas d) No local minimas
Multiple choice Let 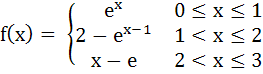 and and 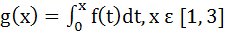
Then g(x) has a) Local maximum at x = 1 + ln2 and local minima at x = e b) Local maximum at x = 1 and local minima at x = 2 c) No local maximas d) No local minimas
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
929 |
For all x in [0, 1], let the second derivative 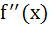 of a function f(x) exists and satisfies of a function f(x) exists and satisfies 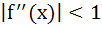 . If f(0) = f(1) then for all x ε [0, 1] . If f(0) = f(1) then for all x ε [0, 1] a) 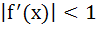 b) 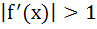 c) None of these
For all x in [0, 1], let the second derivative 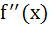 of a function f(x) exists and satisfies of a function f(x) exists and satisfies 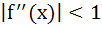 . If f(0) = f(1) then for all x ε [0, 1] . If f(0) = f(1) then for all x ε [0, 1] a) 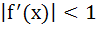 b) 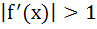 c) None of these
|
IIT 1981 |
|
|
930 |
If 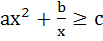 for all positive x where a > 0 and b > 0 then for all positive x where a > 0 and b > 0 then a) 9ab2 ≥ 4c3 b) 27ab2 ≥ 4c3 c) 9ab2 ≤ 4c3 d) 27ab2 ≤ 4c3
If 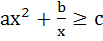 for all positive x where a > 0 and b > 0 then for all positive x where a > 0 and b > 0 then a) 9ab2 ≥ 4c3 b) 27ab2 ≥ 4c3 c) 9ab2 ≤ 4c3 d) 27ab2 ≤ 4c3
|
IIT 1989 |
|
|
931 |
Let ABCD be a square with side of length 2 units. C2 is the circle through the vertices A, B, C, D and C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD. L is a line through A. If P is a point on C1 and Q is another point on C2, then 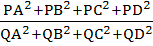 is equal to is equal to a) 0.75 b) 1.25 c) 1 d) 0.5
Let ABCD be a square with side of length 2 units. C2 is the circle through the vertices A, B, C, D and C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD. L is a line through A. If P is a point on C1 and Q is another point on C2, then 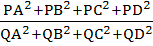 is equal to is equal to a) 0.75 b) 1.25 c) 1 d) 0.5
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
932 |
Let 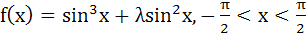 . Find the intervals in which λ should lie in order that f(x) has exactly one minimum and exactly one maximum. . Find the intervals in which λ should lie in order that f(x) has exactly one minimum and exactly one maximum. a) 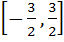 b) 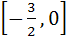 c) 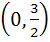 d) 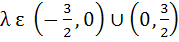
Let 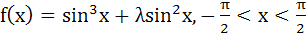 . Find the intervals in which λ should lie in order that f(x) has exactly one minimum and exactly one maximum. . Find the intervals in which λ should lie in order that f(x) has exactly one minimum and exactly one maximum. a) 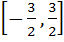 b) 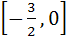 c) 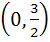 d) 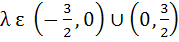
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
933 |
Consider a circle with centre lying on the focus of the parabola 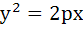 such that it touches the directrix of the parabola. Then a point of intersection of the circle and parabola is such that it touches the directrix of the parabola. Then a point of intersection of the circle and parabola is a) 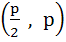 or or 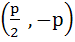 b) 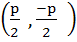 c) 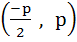 d) 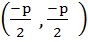
Consider a circle with centre lying on the focus of the parabola 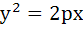 such that it touches the directrix of the parabola. Then a point of intersection of the circle and parabola is such that it touches the directrix of the parabola. Then a point of intersection of the circle and parabola is a) 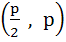 or or 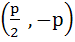 b) 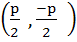 c) 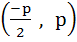 d) 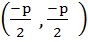
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
934 |
A two metre long object is fired vertically upwards from the mid-point of two locations A and B, 8 metres apart. The speed of the object after t seconds is given by 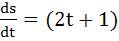 metres per second. Let α and β be the angles subtended by the objects A and B respectively after one and two seconds. Find the value of cos(α − β). metres per second. Let α and β be the angles subtended by the objects A and B respectively after one and two seconds. Find the value of cos(α − β). a) 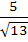 b) 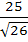 c) 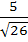 d) 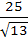
A two metre long object is fired vertically upwards from the mid-point of two locations A and B, 8 metres apart. The speed of the object after t seconds is given by 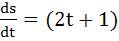 metres per second. Let α and β be the angles subtended by the objects A and B respectively after one and two seconds. Find the value of cos(α − β). metres per second. Let α and β be the angles subtended by the objects A and B respectively after one and two seconds. Find the value of cos(α − β). a) 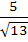 b) 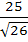 c) 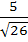 d) 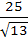
|
IIT 1989 |
|
|
935 |
Investigate for maxima and minima the function
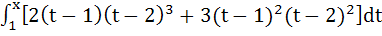 a) Local maximum at x = 1, 7/5, 2 b) Local minimum at x = 1, 7/5, 2 c) Local maximum at x = 1, 2. Local minimum at x = 7/5 d) Local maximum at x = 1. Local minimum at x = 7/5
Investigate for maxima and minima the function
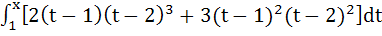 a) Local maximum at x = 1, 7/5, 2 b) Local minimum at x = 1, 7/5, 2 c) Local maximum at x = 1, 2. Local minimum at x = 7/5 d) Local maximum at x = 1. Local minimum at x = 7/5
|
IIT 1988 |
|
|
936 |
A window of perimeter (including the base of the arch) is in the form of a rectangle surmounted by a semicircle. The semi-circular portion is fitted with coloured glass while the rectangular part is fitted with clear glass. The clear glass transmits three times as much light per square meter as the coloured glass. What is the ratio for the sides of the rectangle so that the window transmits the maximum light? a)  b)  c) 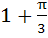 d) 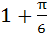
A window of perimeter (including the base of the arch) is in the form of a rectangle surmounted by a semicircle. The semi-circular portion is fitted with coloured glass while the rectangular part is fitted with clear glass. The clear glass transmits three times as much light per square meter as the coloured glass. What is the ratio for the sides of the rectangle so that the window transmits the maximum light? a)  b)  c) 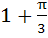 d) 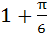
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
937 |
Let 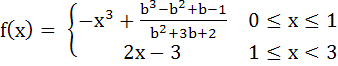 Find all possible values of b such that f(x) has the smallest value at x = 1. a) (−2, ∞) b) (−2, −1) c) (1, ∞) d) (−2, −1) ∪ (1, ∞)
Let 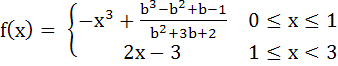 Find all possible values of b such that f(x) has the smallest value at x = 1. a) (−2, ∞) b) (−2, −1) c) (1, ∞) d) (−2, −1) ∪ (1, ∞)
|
IIT 1993 |
|
|
938 |
Use mathematical induction for
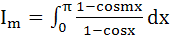
to prove that
Im = mπ, m = 0, 1, 2 . . . .
Use mathematical induction for
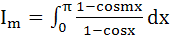
to prove that
Im = mπ, m = 0, 1, 2 . . . .
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
939 |
Determine the points of maxima and minima of the function
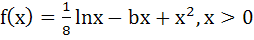 where b ≥ 0 is a constant. where b ≥ 0 is a constant. a) Minima at x = x1, maxima at x = x2 b) Minima at x = x2, maxima at x = x1 c) Minima at x = x1, x2, no maxima d) Maxima at x =x1, x2, no minima where x1 = 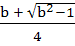 and x2 = and x2 = 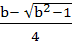
Determine the points of maxima and minima of the function
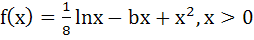 where b ≥ 0 is a constant. where b ≥ 0 is a constant. a) Minima at x = x1, maxima at x = x2 b) Minima at x = x2, maxima at x = x1 c) Minima at x = x1, x2, no maxima d) Maxima at x =x1, x2, no minima where x1 = 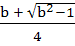 and x2 = and x2 = 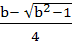
|
IIT 1996 |
|
|
940 |
Consider the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the parabola y2 = 8x. They intersect P and Q in the first and fourth quadrants respectively. Tangents to the circle at P and Q intersect the X–axis at R and tangents to the parabola at P and Q intersect the X- axis at S. The radius of the circum circle of △PRS is a) 5 b) 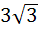 c) 3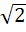 d) 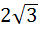
Consider the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the parabola y2 = 8x. They intersect P and Q in the first and fourth quadrants respectively. Tangents to the circle at P and Q intersect the X–axis at R and tangents to the parabola at P and Q intersect the X- axis at S. The radius of the circum circle of △PRS is a) 5 b) 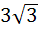 c) 3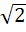 d) 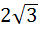
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
941 |
One or more than one correct option Consider the family of circles whose centre lies on the straight line y = x. If the family of circles is represented by the differential equation Py′′ + Qy′ + 1 = 0 where P, Q are functions of x, y and y′ , then which of the following statements is/are true? a) P = y + x b) P = y – x c) P + Q = 1 – x + y + y′ + (y′)2 d) P − Q = x + y − y′ − (y′)2
One or more than one correct option Consider the family of circles whose centre lies on the straight line y = x. If the family of circles is represented by the differential equation Py′′ + Qy′ + 1 = 0 where P, Q are functions of x, y and y′ , then which of the following statements is/are true? a) P = y + x b) P = y – x c) P + Q = 1 – x + y + y′ + (y′)2 d) P − Q = x + y − y′ − (y′)2
|
IIT 2015 |
|
|
942 |
Let (the set of all real numbers) be a positive, non-constant and differentiable function such that and . Then the value of lies in the interval a) b) c) d)
Let (the set of all real numbers) be a positive, non-constant and differentiable function such that and . Then the value of lies in the interval a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2013 |
|
|
943 |
Let the population of rabbits arriving at time t be governed by the differential equation . If p(0) = 100, then p(t) is equal to a) 400 – 300et/2 b) 300 – 200e−t/2 c) 600 – 500et/2 d) 400 – 300e−t/2
Let the population of rabbits arriving at time t be governed by the differential equation . If p(0) = 100, then p(t) is equal to a) 400 – 300et/2 b) 300 – 200e−t/2 c) 600 – 500et/2 d) 400 – 300e−t/2
|
IIT 2014 |
|
|
944 |
Let f:[0, 1] → ℝ (the set all real numbers)be a function. Suppose the function is twice differentiable, f(0) = f(1) = 0 and satisfiesf′′(x) – 2f′(x) + f(x) ≥ ex, x ∈ [0, 1]If the function e−x f(x) assumes its minimum in the interval [0, 1] at then which of the following is true? a) b) c) d)
Let f:[0, 1] → ℝ (the set all real numbers)be a function. Suppose the function is twice differentiable, f(0) = f(1) = 0 and satisfiesf′′(x) – 2f′(x) + f(x) ≥ ex, x ∈ [0, 1]If the function e−x f(x) assumes its minimum in the interval [0, 1] at then which of the following is true? a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2013 |
|
|
945 |
Let k be an integer such that the triangle with vertices (k, −3k), (5, k) and (−k, 2) has area 28 square units. Then the orthocentre of the triangle is at the point a) b) c) d)
Let k be an integer such that the triangle with vertices (k, −3k), (5, k) and (−k, 2) has area 28 square units. Then the orthocentre of the triangle is at the point a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2017 |
|
|
946 |
A straight line L through the point (3, −2) is inclined at an angle of 60° to the line . If the line L also intersects the X- axis then the equation of L is a) b) c) d)
A straight line L through the point (3, −2) is inclined at an angle of 60° to the line . If the line L also intersects the X- axis then the equation of L is a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2011 |
|
|
947 |
The sides of a rhombus are along the lines x – y + 1 = 0 and 7x – y – 5 = 0. If its diagonals intersect at (−1, −2) then which one of the following is a vertex of the rhombus? a) b) c) d)
The sides of a rhombus are along the lines x – y + 1 = 0 and 7x – y – 5 = 0. If its diagonals intersect at (−1, −2) then which one of the following is a vertex of the rhombus? a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2016 |
|
|
948 |
The C be a circle with the centre at (1, 1) and radius 1. If T is the circle centred at (0, k) passing through origin and touches the circle C externally, then the radius of T is equal to a) b) c) d)
The C be a circle with the centre at (1, 1) and radius 1. If T is the circle centred at (0, k) passing through origin and touches the circle C externally, then the radius of T is equal to a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2014 |
|
|
949 |
One or more than one correct option The circle C1 : x2 + y2 = 3 with centre at O intersect the parabola x2 = 2y at the point P in the first quadrant. Let the tangent to the circle C1 at P touches other two circles C2 and C3 at R2 and R3 respectively. Suppose C2 and C3 have equal radii and centres Q2 and Q3 respectively. If Q2 and Q3 lie on the Y- axis, then a) b) c) d)
One or more than one correct option The circle C1 : x2 + y2 = 3 with centre at O intersect the parabola x2 = 2y at the point P in the first quadrant. Let the tangent to the circle C1 at P touches other two circles C2 and C3 at R2 and R3 respectively. Suppose C2 and C3 have equal radii and centres Q2 and Q3 respectively. If Q2 and Q3 lie on the Y- axis, then a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2016 |
|
|
950 |
The circle passing through the point (−1, 0) and touching the Y – axis at (0, 2) also passes through the point a) b) c) d)
The circle passing through the point (−1, 0) and touching the Y – axis at (0, 2) also passes through the point a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2011 |
|