|
801 |
The value of 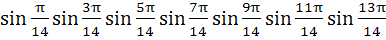 is equal to is equal to a)  b) 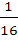 c) 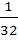 d) 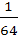
The value of 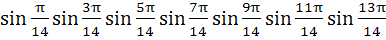 is equal to is equal to a)  b) 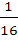 c) 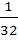 d) 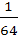
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
802 |
If 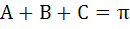 then then 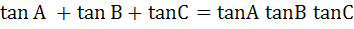 a) True b) False
If 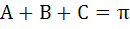 then then 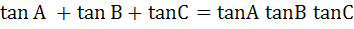 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1979 |
|
|
803 |
Prove that 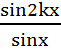 = 2[cosx + cos3x + cos5x + … + cos(2k−1)x] for any positive integer k. Hence prove that = 2[cosx + cos3x + cos5x + … + cos(2k−1)x] for any positive integer k. Hence prove that 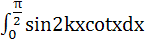 = = 
|
IIT 1990 |
|
|
804 |
The function
f(x) =|px – q| + r |x|, x ε (−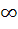 , , 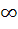 ) )
where p > 0, q > 0, r > 0 assumes minimum value on one point if a) p ≠ q b) r = q c) r ≠ p d) r = p = q
The function
f(x) =|px – q| + r |x|, x ε (−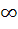 , , 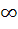 ) )
where p > 0, q > 0, r > 0 assumes minimum value on one point if a) p ≠ q b) r = q c) r ≠ p d) r = p = q
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
805 |
Let p, q, r be three mutually perpendicular vectors of the same magnitude. If x satisfies the equation p 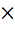 ((x – q) ((x – q) 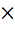 p) + q p) + q 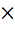 ((x – r) ((x – r) 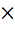 q) + r q) + r 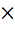 ((x – p) ((x – p) 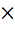 r) = 0 then x is given by r) = 0 then x is given by a) 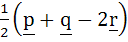 b) 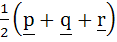 c) 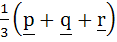 d) 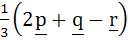
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
806 |
Let f : R → R be any function defined g : R → R by g (x) = |f (x)| for all x. Then g is a) onto if f is onto b) one to one if f is one to one c) continuous if f is continuous d) differentiable if f is differentiable
Let f : R → R be any function defined g : R → R by g (x) = |f (x)| for all x. Then g is a) onto if f is onto b) one to one if f is one to one c) continuous if f is continuous d) differentiable if f is differentiable
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
807 |
Let 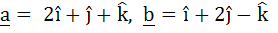 and a unit vector c be coplanar. If c is perpendicular to a then c is equal to and a unit vector c be coplanar. If c is perpendicular to a then c is equal to a) 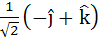 b) 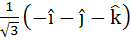 c) 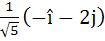 d) 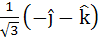
Let 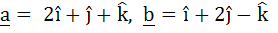 and a unit vector c be coplanar. If c is perpendicular to a then c is equal to and a unit vector c be coplanar. If c is perpendicular to a then c is equal to a) 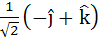 b) 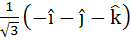 c) 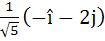 d) 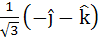
|
IIT 1999 |
|
|
808 |
If f : [ 1, 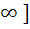 → [ 2, → [ 2, 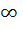 ] is given by f (x) = x + ] is given by f (x) = x +  then then 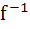 ( x ) is given by ( x ) is given by a) 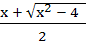 b) 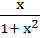 c) 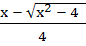 d) 1 + 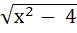
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
809 |
The function of f : R → R be defined by f (x) = 2x + sinx for x ε R . Then f is a) one-one and onto b) one-one but not onto c) onto but not one-one d) neither one-one nor onto
The function of f : R → R be defined by f (x) = 2x + sinx for x ε R . Then f is a) one-one and onto b) one-one but not onto c) onto but not one-one d) neither one-one nor onto
|
IIT 2002 |
|
|
810 |
Multiple choice The vector 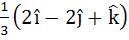 is is a) A unit vector b) Makes an angle  with the vector with the vector 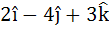 c) Parallel to vector 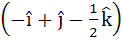 d) Perpendicular to the vector 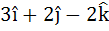
Multiple choice The vector 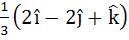 is is a) A unit vector b) Makes an angle  with the vector with the vector 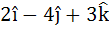 c) Parallel to vector 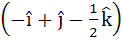 d) Perpendicular to the vector 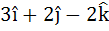
|
IIT 1994 |
|
|
811 |
A1, A2, …… , An are the vertices of a regular polygon with n sides and O is the centre. Show that
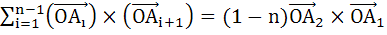
A1, A2, …… , An are the vertices of a regular polygon with n sides and O is the centre. Show that
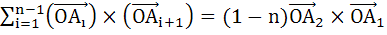
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
812 |
Multiple choice There exists a triangle ABC satisfying the conditions a) bsinA = a, A <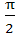 b) bsinA > a, A >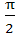 c) bsinA > a, A <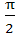 d) bsinA < a, A <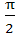 , b > a , b > a e) bsinA < a, A >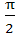 , b = a , b = a
Multiple choice There exists a triangle ABC satisfying the conditions a) bsinA = a, A <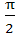 b) bsinA > a, A >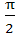 c) bsinA > a, A <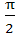 d) bsinA < a, A <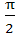 , b > a , b > a e) bsinA < a, A >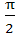 , b = a , b = a
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
813 |
With usual notation if in a triangle ABC, 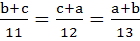 then then 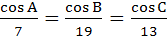 . .
a) True b) False
With usual notation if in a triangle ABC, 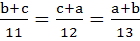 then then 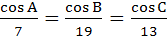 . .
a) True b) False
|
IIT 1984 |
|
|
814 |
If A, B, C are such that |B| = |C|. Prove that 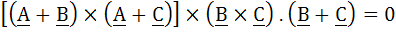
If A, B, C are such that |B| = |C|. Prove that 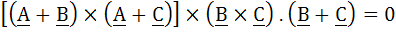
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
815 |
If in a triangle ABC, cosA cosB + sinA sinB sin C = 1 then show that a : b : c = 1 : 1 : 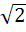 a) True b) False
If in a triangle ABC, cosA cosB + sinA sinB sin C = 1 then show that a : b : c = 1 : 1 : 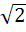 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
816 |
Let u and v be unit vectors. If w is a vector such that 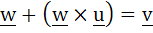 , then prove that , then prove that 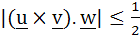 and that equality holds if and only if and that equality holds if and only if 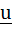 is perpendicular to is perpendicular to 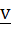
|
IIT 1999 |
|
|
817 |
If the lines 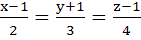 and and 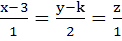 intersect then the value of k is intersect then the value of k is a)  b)  c) 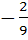 d) 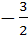
If the lines 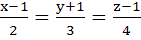 and and 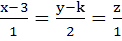 intersect then the value of k is intersect then the value of k is a)  b)  c) 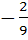 d) 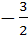
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
818 |
The points with position vectors 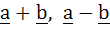 and and 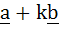 are collinear for all real values of k. are collinear for all real values of k. a) True b) False
The points with position vectors 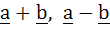 and and 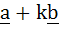 are collinear for all real values of k. are collinear for all real values of k. a) True b) False
|
IIT 1984 |
|
|
819 |
If 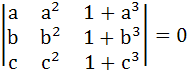 and the vectors (1, a, a2), (1, b, b2), (1, c, c2) are non-coplanar then the product abc is
If 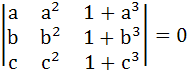 and the vectors (1, a, a2), (1, b, b2), (1, c, c2) are non-coplanar then the product abc is
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
820 |
The area of a triangle whose vertices are
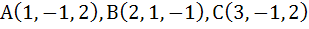 is is
The area of a triangle whose vertices are
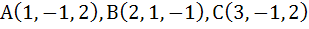 is is
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
821 |
Let 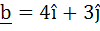 and c be two vectors perpendicular to each other in the XY–plane. All vectors in the same plane having projections 1 and 2 along b and c respectively, are given by and c be two vectors perpendicular to each other in the XY–plane. All vectors in the same plane having projections 1 and 2 along b and c respectively, are given by
Let 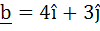 and c be two vectors perpendicular to each other in the XY–plane. All vectors in the same plane having projections 1 and 2 along b and c respectively, are given by and c be two vectors perpendicular to each other in the XY–plane. All vectors in the same plane having projections 1 and 2 along b and c respectively, are given by
|
IIT 1987 |
|
|
822 |
If b > a then the equation ( x – a ) ( x – b )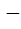 1 = 0 has 1 = 0 has a) Both roots in [ a, b ] b) Both roots in ( 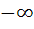 , a ) , a ) c) Both roots in ( 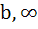 ) ) d) One root in ( 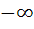 , a ) and other in ( , a ) and other in (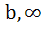 ) )
If b > a then the equation ( x – a ) ( x – b )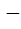 1 = 0 has 1 = 0 has a) Both roots in [ a, b ] b) Both roots in ( 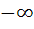 , a ) , a ) c) Both roots in ( 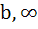 ) ) d) One root in ( 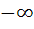 , a ) and other in ( , a ) and other in (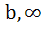 ) )
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
823 |
Prove that for all values of θ
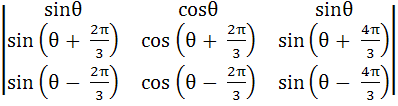 = 0 = 0
Prove that for all values of θ
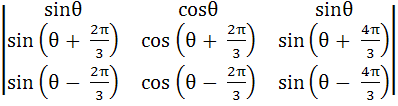 = 0 = 0
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
824 |
A = 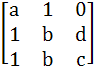 , B = , B = 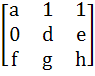 , U = , U = 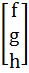 , V = , V = 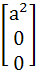 If AX = U has infinitely many solutions, prove that BX = V has no unique solution. Also prove that if afd ≠ 0 then BX = V has no solution. X is a vector.
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
825 |
Let λ and α be real. Find the set of all values of λ for which the system of linear equations
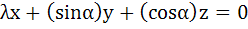
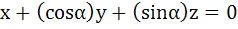
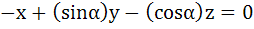
has a non-trivial solution. For λ = 1 find the value of α.
|
IIT 1993 |
|