|
101 |
If the mth, nth and pth term of an Arithmetic Progression and a Geometric Progression are equal and are x, y, z then prove that
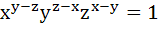
If the mth, nth and pth term of an Arithmetic Progression and a Geometric Progression are equal and are x, y, z then prove that
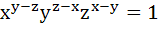
|
IIT 1979 |
06:24 min
|
|
102 |
Fill in the blank If the quadratic equation
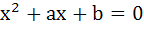 and and 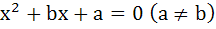 have a common root then the numerical value of a + b is ………… have a common root then the numerical value of a + b is …………
Fill in the blank If the quadratic equation
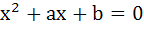 and and 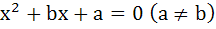 have a common root then the numerical value of a + b is ………… have a common root then the numerical value of a + b is …………
|
IIT 1986 |
01:36 min
|
|
103 |
The equation of the common tangent touching the circle
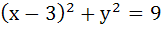 and the parabola and the parabola 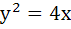 , above X–axis is , above X–axis is a) 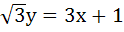 b) 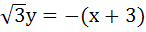 c) 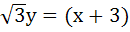 d) 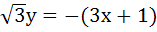
The equation of the common tangent touching the circle
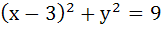 and the parabola and the parabola 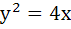 , above X–axis is , above X–axis is a) 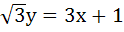 b) 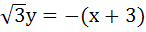 c) 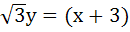 d) 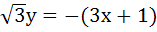
|
IIT 2001 |
05:54 min
|
|
104 |
Fill in the blank The sum of the real roots of the equation
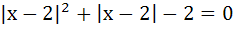 is ……….. is ………..
Fill in the blank The sum of the real roots of the equation
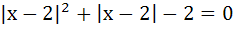 is ……….. is ………..
|
IIT 1997 |
03:01 min
|
|
105 |
If 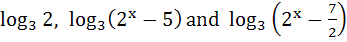 are in Arithmetic Progression, determine the value of x. are in Arithmetic Progression, determine the value of x.
If 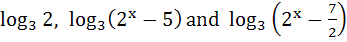 are in Arithmetic Progression, determine the value of x. are in Arithmetic Progression, determine the value of x.
|
IIT 1990 |
02:49 min
|
|
106 |
The angle between the tangents drawn from the point (1, 4) to the parabola 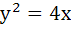 is is a)  b) 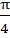 c)  d) 
The angle between the tangents drawn from the point (1, 4) to the parabola 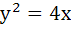 is is a)  b) 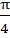 c)  d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
02:56 min
|
|
107 |
The number 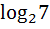 is is a) an integer b) a rational number c) an irrational number d) a prime number
The number 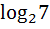 is is a) an integer b) a rational number c) an irrational number d) a prime number
|
IIT 1992 |
00:47 min
|
|
108 |
The fourth power of the common difference of an arithmetic progression with integer entries is added to the product of four consecutive terms of it, prove that the resulting sum is square of an integer.
The fourth power of the common difference of an arithmetic progression with integer entries is added to the product of four consecutive terms of it, prove that the resulting sum is square of an integer.
|
IIT 2000 |
02:57 min
|
|
109 |
A is a point on the parabola 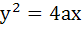 . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB. . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB.
A is a point on the parabola 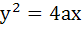 . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB. . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB.
|
IIT 1982 |
06:08 min
|
|
110 |
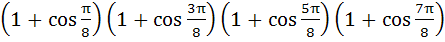 is equal to is equal to
a)  b) 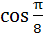 c)  d) 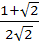
|
IIT 1984 |
03:04 min
|
|
111 |
If a, b, c are positive real numbers then prove that
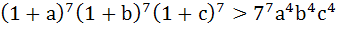
If a, b, c are positive real numbers then prove that
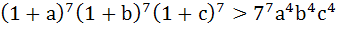
|
IIT 2004 |
02:42 min
|
|
112 |
Show that the locus of a point that divides a chord of slope 2 of the parabola 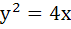 internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex. internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex.
Show that the locus of a point that divides a chord of slope 2 of the parabola 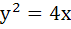 internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex. internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex.
|
IIT 1995 |
06:25 min
|
|
113 |
If the lengths of the sides of a triangle are 3, 5, 7 then the largest angle of the triangle is a)  b) 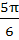 c) 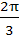 d) 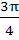
If the lengths of the sides of a triangle are 3, 5, 7 then the largest angle of the triangle is a)  b) 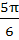 c) 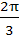 d) 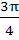
|
IIT 1994 |
01:44 min
|
|
114 |
Three normals with slopes 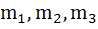 are drawn from a point P not on the axis of the parabola are drawn from a point P not on the axis of the parabola 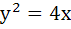 . If . If 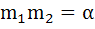 results in the locus of P being a part of the parabola, find the value of α. results in the locus of P being a part of the parabola, find the value of α.
|
IIT 2003 |
05:59 min
|
|
115 |
Let the Harmonic Mean and Geometric Mean of two positive numbers be in the ratio of 4:5. Then the two numbers are in the ratio . . . . .
Let the Harmonic Mean and Geometric Mean of two positive numbers be in the ratio of 4:5. Then the two numbers are in the ratio . . . . .
|
IIT 1992 |
02:26 min
|
|
116 |
The order of the differential equation whose general solution is given by 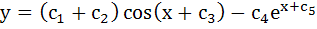 is is a) 5 b) 4 c) 3 d) 2
The order of the differential equation whose general solution is given by 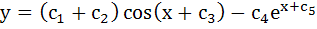 is is a) 5 b) 4 c) 3 d) 2
|
IIT 1998 |
03:42 min
|
|
117 |
If 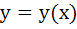 and and 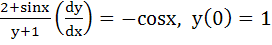 then then 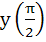 equals equals a)  b)  c) 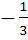 d) 1
If 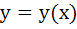 and and 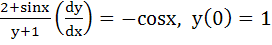 then then 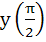 equals equals a)  b)  c) 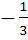 d) 1
|
IIT 2004 |
03:00 min
|
|
118 |
Let 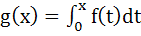 , where f is such that , where f is such that 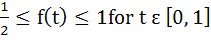 and and 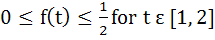 then g(2) satisfies the inequality then g(2) satisfies the inequality a) 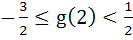 b) 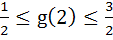 c) 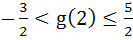 d) 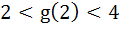
Let 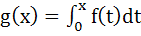 , where f is such that , where f is such that 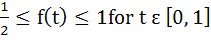 and and 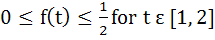 then g(2) satisfies the inequality then g(2) satisfies the inequality a) 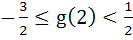 b) 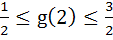 c) 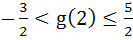 d) 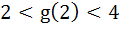
|
IIT 2000 |
02:05 min
|
|
119 |
If y = 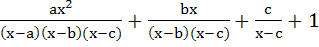 Prove that 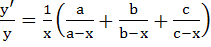
If y = 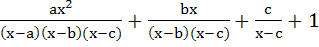 Prove that 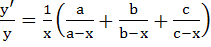
|
IIT 1998 |
03:49 min
|
|
120 |
The value of 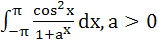 is is a) π b) aπ c)  d) 2π
The value of 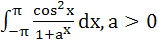 is is a) π b) aπ c)  d) 2π
|
IIT 2001 |
04:30 min
|
|
121 |
Let F(x) = f (x) g (x) h (x) for all real x, where f (x), g (x) and h (x) are differentiable functions. At some point x0 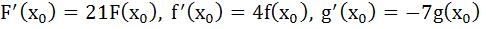 and and
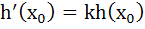 then k is equal to then k is equal to
a) 12 b) 20 c) 24 d) 28
Let F(x) = f (x) g (x) h (x) for all real x, where f (x), g (x) and h (x) are differentiable functions. At some point x0 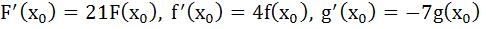 and and
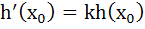 then k is equal to then k is equal to
a) 12 b) 20 c) 24 d) 28
|
IIT 1997 |
01:17 min
|
|
122 |
If 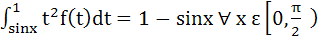 then f then f 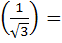 a) 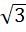 b)  c) 3 d) None
If 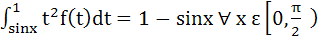 then f then f 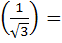 a) 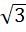 b)  c) 3 d) None
|
IIT 2005 |
02:29 min
|
|
123 |
If G(x)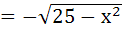 then then 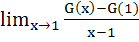 is is a) 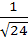 b)  c) 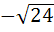 d) 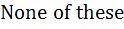
If G(x)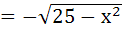 then then 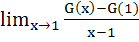 is is a) 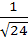 b)  c) 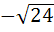 d) 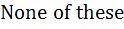
|
IIT 1983 |
01:40 min
|
|
124 |
Show that 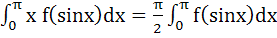
Show that 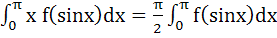
|
IIT 1982 |
01:38 min
|
|
125 |
If 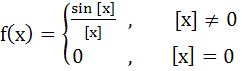 Where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x then 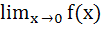 equals equals a) 1 b) 0 c) – 1 d) None of these
If 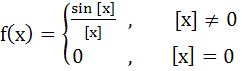 Where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x then 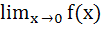 equals equals a) 1 b) 0 c) – 1 d) None of these
|
IIT 1985 |
02:39 min
|