|
126 |
If 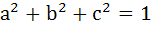 then ab + bc + ca lies in the interval then ab + bc + ca lies in the interval a) 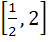 b) 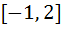 c) 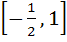 d) 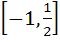
If 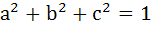 then ab + bc + ca lies in the interval then ab + bc + ca lies in the interval a) 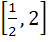 b) 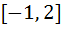 c) 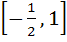 d) 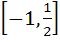
|
IIT 1984 |
02:29 min
|
|
127 |
Find the values of x and y for which the following equation is satisfied 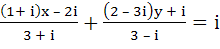 a) x = y = −1 b) x = y = 3 c) x = 1, y = 3 d) x = 3, y = −1
Find the values of x and y for which the following equation is satisfied 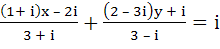 a) x = y = −1 b) x = y = 3 c) x = 1, y = 3 d) x = 3, y = −1
|
IIT 1980 |
05:23 min
|
|
128 |
The equation of the directrix of the parabola y2 + 4y + 4x +2 = 0 is a) x = − 1 b) x = 1 c) 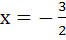 d) 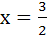
The equation of the directrix of the parabola y2 + 4y + 4x +2 = 0 is a) x = − 1 b) x = 1 c) 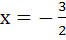 d) 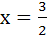
|
IIT 2001 |
01:51 min
|
|
129 |
Let α, β be roots of the equation (x – a) (x – b) = c, c ≠ 0. Then the roots of the equation (x – α) (x – β) + c = 0 are a) a, c b) b, c c) a, b d) a + c, b + c
Let α, β be roots of the equation (x – a) (x – b) = c, c ≠ 0. Then the roots of the equation (x – α) (x – β) + c = 0 are a) a, c b) b, c c) a, b d) a + c, b + c
|
IIT 1992 |
02:15 min
|
|
130 |
If = x + iy then = x + iy then a) x = 3, y = 1 b) x = 1, y = 3 c) x = 0, y = 3 d) x = 0, y = 0
If = x + iy then = x + iy then a) x = 3, y = 1 b) x = 1, y = 3 c) x = 0, y = 3 d) x = 0, y = 0
|
IIT 1998 |
01:25 min
|
|
131 |
It is given that n is an odd integer greater than 3 and not a multiple of 3. Prove that  is a factor of is a factor of 
It is given that n is an odd integer greater than 3 and not a multiple of 3. Prove that  is a factor of is a factor of 
|
IIT 1985 |
07:09 min
|
|
132 |
The focal chord of 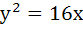 is tangent to is tangent to 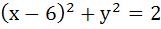 then the possible value of the slope of this chord are then the possible value of the slope of this chord are a) 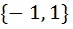 b) 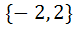 c) 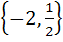 d) 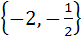
The focal chord of 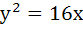 is tangent to is tangent to 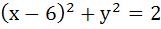 then the possible value of the slope of this chord are then the possible value of the slope of this chord are a) 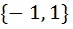 b) 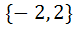 c) 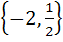 d) 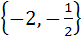
|
IIT 2003 |
02:51 min
|
|
133 |
If p, q ε {1, 2, 3, 4}. The number of equations of the form 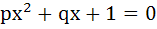 having real roots is having real roots is a) 15 b) 9 c) 7 d) 8
If p, q ε {1, 2, 3, 4}. The number of equations of the form 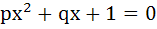 having real roots is having real roots is a) 15 b) 9 c) 7 d) 8
|
IIT 1994 |
03:39 min
|
|
134 |
If A =  and B = and B =  then the value of α for which A2 = B is then the value of α for which A2 = B is a) 1 b) −1 c) 4 d) No real values
If A =  and B = and B =  then the value of α for which A2 = B is then the value of α for which A2 = B is a) 1 b) −1 c) 4 d) No real values
|
IIT 2003 |
01:17 min
|
|
135 |
If 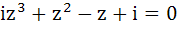 then show that |z| = 1. then show that |z| = 1.
If 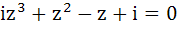 then show that |z| = 1. then show that |z| = 1.
|
IIT 1995 |
02:14 min
|
|
136 |
Suppose that the normals drawn at three different points on the parabola 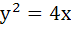 pass through the point (h, 0). Show that h > 2. pass through the point (h, 0). Show that h > 2.
Suppose that the normals drawn at three different points on the parabola 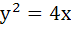 pass through the point (h, 0). Show that h > 2. pass through the point (h, 0). Show that h > 2.
|
IIT 1981 |
03:52 min
|
|
137 |
Through the vertex O of the parabola 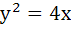 chords OP and OQ are drawn at right angles. Show that for all positions of P, PQ cuts the axis of the parabola at a fixed point. Also find the locus of the midpoint of PQ. chords OP and OQ are drawn at right angles. Show that for all positions of P, PQ cuts the axis of the parabola at a fixed point. Also find the locus of the midpoint of PQ.
Through the vertex O of the parabola 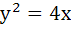 chords OP and OQ are drawn at right angles. Show that for all positions of P, PQ cuts the axis of the parabola at a fixed point. Also find the locus of the midpoint of PQ. chords OP and OQ are drawn at right angles. Show that for all positions of P, PQ cuts the axis of the parabola at a fixed point. Also find the locus of the midpoint of PQ.
|
IIT 1994 |
05:22 min
|
|
138 |
For all x ε ( 0, 1 ) a) 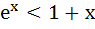 b) ln (1 + x) < x c) sinx > x d) lnx > x
For all x ε ( 0, 1 ) a) 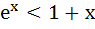 b) ln (1 + x) < x c) sinx > x d) lnx > x
|
IIT 2000 |
02:40 min
|
|
139 |
Given x = cy + bz, y = az + cx, z = bx + ay where x, y, z are not all zero, prove that a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc = 1
Given x = cy + bz, y = az + cx, z = bx + ay where x, y, z are not all zero, prove that a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc = 1
|
IIT 1978 |
03:30 min
|
|
140 |
Let  and and 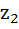 are two complex numbers such that are two complex numbers such that 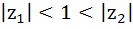 then prove that then prove that 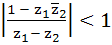 . .
|
IIT 2003 |
04:08 min
|
|
141 |
The number of values of k for which the system of equations (k + 1) x + 8y = 4k kx + ( k + 3 ) y = 3k – 1 has infinitely many solutions is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) Infinity
The number of values of k for which the system of equations (k + 1) x + 8y = 4k kx + ( k + 3 ) y = 3k – 1 has infinitely many solutions is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) Infinity
|
IIT 2002 |
02:56 min
|
|
142 |
Without expanding a determinant at any stage show that
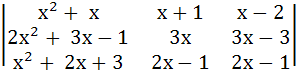 = Ax + B = Ax + B where A, B are non-zero constants
Without expanding a determinant at any stage show that
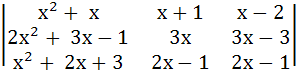 = Ax + B = Ax + B where A, B are non-zero constants
|
IIT 1982 |
04:06 min
|
|
143 |
True/False
If the complex numbers  represent the vertices of an equilateral triangle with represent the vertices of an equilateral triangle with 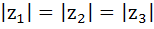 then then 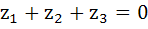 . . a) True b) False
True/False
If the complex numbers  represent the vertices of an equilateral triangle with represent the vertices of an equilateral triangle with 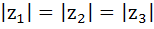 then then 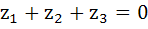 . . a) True b) False
|
IIT 1984 |
02:27 min
|
|
144 |
The order of the differential equation whose general solution is given by 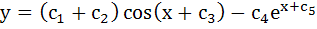 is is a) 5 b) 4 c) 3 d) 2
The order of the differential equation whose general solution is given by 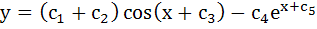 is is a) 5 b) 4 c) 3 d) 2
|
IIT 1998 |
03:42 min
|
|
145 |
If f (x) = 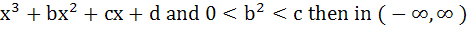 a) f (x) is a strictly increasing function b) f (x) has a local maxima c) f (x) is a strictly decreasing function d) f (x) is bounded
If f (x) = 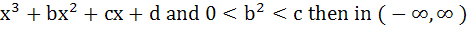 a) f (x) is a strictly increasing function b) f (x) has a local maxima c) f (x) is a strictly decreasing function d) f (x) is bounded
|
IIT 2004 |
02:07 min
|
|
146 |
Let Δa = 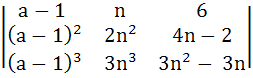
Then show that 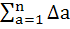 = c, a constant. = c, a constant.
Let Δa = 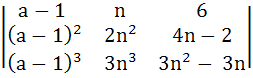
Then show that 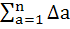 = c, a constant. = c, a constant.
|
IIT 1989 |
05:34 min
|
|
147 |
For any two complex numbers 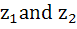 and any real numbers and any real numbers 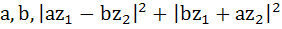 is equal to . . . . is equal to . . . . a) 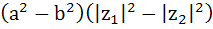 b)  c) 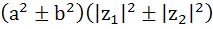 d) 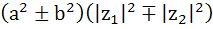
For any two complex numbers 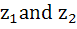 and any real numbers and any real numbers 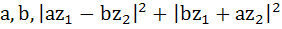 is equal to . . . . is equal to . . . . a) 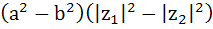 b)  c) 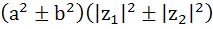 d) 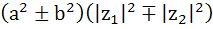
|
IIT 1988 |
02:43 min
|
|
148 |
The locus of a variable point whose distance from 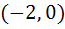 is is  times its distance from the line times its distance from the line 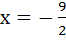 is is a) Ellipse b) Parabola c) Hyperbola d) None of these
The locus of a variable point whose distance from 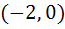 is is  times its distance from the line times its distance from the line 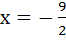 is is a) Ellipse b) Parabola c) Hyperbola d) None of these
|
IIT 1994 |
02:40 min
|
|
149 |
If 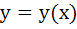 and and 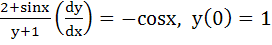 then then 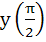 equals equals a)  b)  c) 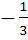 d) 1
If 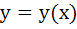 and and 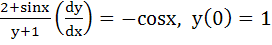 then then 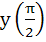 equals equals a)  b)  c) 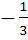 d) 1
|
IIT 2004 |
03:00 min
|
|
150 |
The second degree polynomial satisfying f (0) = 0, f (1) = 1, 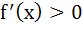 for all x ε [0, 1] is for all x ε [0, 1] is a) 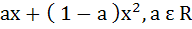 b) No such polynomial c) 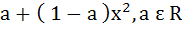 d) 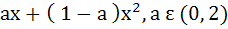
The second degree polynomial satisfying f (0) = 0, f (1) = 1, 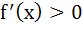 for all x ε [0, 1] is for all x ε [0, 1] is a) 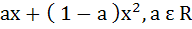 b) No such polynomial c) 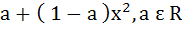 d) 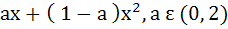
|
IIT 2005 |
03:08 min
|