|
1276 |
The slope of the line touching both parabolas y2 = 4x and x2 = −32y is a) b) c) d)
The slope of the line touching both parabolas y2 = 4x and x2 = −32y is a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2014 |
|
|
1277 |
Let PQ and RS be tangents at the extremities of the diameter PR of a circle of radius r. If PS and QR intersect at a point x on the circumference of the circle, then 2r equals a) 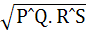 b) 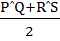 c) 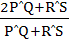 d) 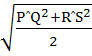
Let PQ and RS be tangents at the extremities of the diameter PR of a circle of radius r. If PS and QR intersect at a point x on the circumference of the circle, then 2r equals a) 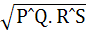 b) 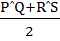 c) 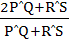 d) 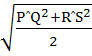
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
1278 |
Multiple choices Let [x] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to x. If f (x) = [xsinπx] then f(x) is a) Continuous at x = 0 b) Continuous in 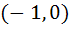 c) f (x) is differentiable at x = 1 d) differentiable in 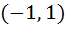 e) None of these
Multiple choices Let [x] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to x. If f (x) = [xsinπx] then f(x) is a) Continuous at x = 0 b) Continuous in 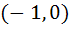 c) f (x) is differentiable at x = 1 d) differentiable in 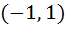 e) None of these
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
1279 |
Let 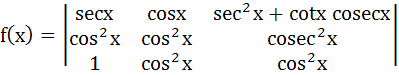 then then 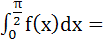 a) 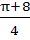 b) 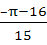 c) 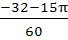 d) 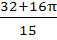
|
IIT 1987 |
|
|
1280 |
Let a, r, s, t be non-zero real numbers. Let P(at2, 2at), Q, R(ar2, 2ar and S(as2, 2as) be distinct points on the parabola y2 = 4ax. Suppose PQ is the focal chord and QR and PK are parallel, where K is point (2a, 0) The value of r is a) b) c) d)
Let a, r, s, t be non-zero real numbers. Let P(at2, 2at), Q, R(ar2, 2ar and S(as2, 2as) be distinct points on the parabola y2 = 4ax. Suppose PQ is the focal chord and QR and PK are parallel, where K is point (2a, 0) The value of r is a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2014 |
|
|
1281 |
Find all solutions of 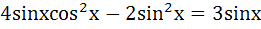 a) 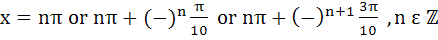 b) 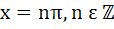 c) 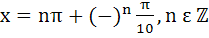 d) 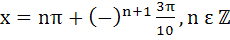
Find all solutions of 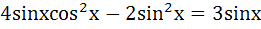 a) 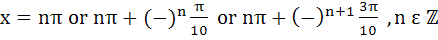 b) 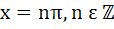 c) 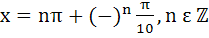 d) 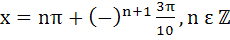
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
1282 |
Multiple choices Which of the following functions are continuous on (0, π) a) tanx b) 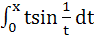 c) 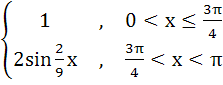 d) 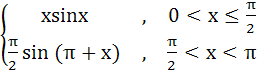
Multiple choices Which of the following functions are continuous on (0, π) a) tanx b) 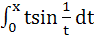 c) 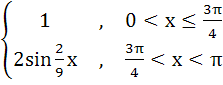 d) 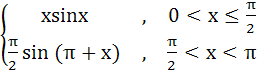
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
1283 |
One or more than one correct option If the normals of the parabola y2 = 4x drawn at the end points of the latus rectum are tangents to the circle (x − 3)2 + (y + 2)2 = r2 then the value of r2 is a) 4 b) 1 c) 2 d) 0
One or more than one correct option If the normals of the parabola y2 = 4x drawn at the end points of the latus rectum are tangents to the circle (x − 3)2 + (y + 2)2 = r2 then the value of r2 is a) 4 b) 1 c) 2 d) 0
|
IIT 2015 |
|
|
1284 |
Multiple choices Let 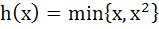 for every real number x then for every real number x then a) h (x) is continuous for all x b) h is differentiable for all x c) 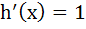 for all x > 1 for all x > 1 d) h is not differentiable for two values of x
Multiple choices Let 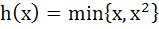 for every real number x then for every real number x then a) h (x) is continuous for all x b) h is differentiable for all x c) 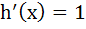 for all x > 1 for all x > 1 d) h is not differentiable for two values of x
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
1285 |
Number of divisors of the form 4n + 2(n ≥ 0) of integer 240 is a) 4 b) 8 c) 10 d) 3
Number of divisors of the form 4n + 2(n ≥ 0) of integer 240 is a) 4 b) 8 c) 10 d) 3
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
1286 |
The smallest positive root of the equation tan x – x = 0 lies in a) 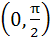 b) 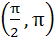 c) 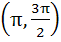 d) 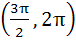 e) None of these
The smallest positive root of the equation tan x – x = 0 lies in a) 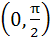 b) 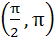 c) 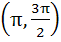 d) 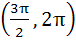 e) None of these
|
IIT 1987 |
|
|
1287 |
Let f (x) be defined on the interval 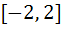 such that such that 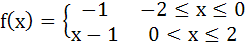
g (x) = f (|x|) + |f(x)| Test the differentiability of g (x) in 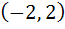 a) g(x) is differentiable at all x 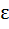 ℝ ℝ b) g(x) is differentiable at all x 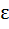 ℝ except at x = 1 ℝ except at x = 1 c) g(x) is differentiable at all x 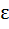 ℝ except at x = 0, 1 ℝ except at x = 0, 1 d) g(x) is differentiable at all x 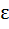 ℝ except at x = 0, 1, 2 ℝ except at x = 0, 1, 2
Let f (x) be defined on the interval 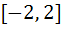 such that such that 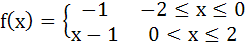
g (x) = f (|x|) + |f(x)| Test the differentiability of g (x) in 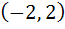 a) g(x) is differentiable at all x 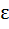 ℝ ℝ b) g(x) is differentiable at all x 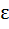 ℝ except at x = 1 ℝ except at x = 1 c) g(x) is differentiable at all x 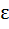 ℝ except at x = 0, 1 ℝ except at x = 0, 1 d) g(x) is differentiable at all x 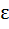 ℝ except at x = 0, 1, 2 ℝ except at x = 0, 1, 2
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
1288 |
If the LCM of p, q is 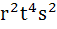 where r, s, t are prime numbers and p, q are positive integers then the number of ordered pairs (p, q) is where r, s, t are prime numbers and p, q are positive integers then the number of ordered pairs (p, q) is a) 252 b) 254 c) 225 d) 224
If the LCM of p, q is 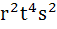 where r, s, t are prime numbers and p, q are positive integers then the number of ordered pairs (p, q) is where r, s, t are prime numbers and p, q are positive integers then the number of ordered pairs (p, q) is a) 252 b) 254 c) 225 d) 224
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
1289 |
Consider a family of circles passing through two fixed points A (3, 7) and B (6, 5). Show that the chords in which the circle 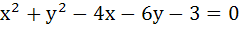 cuts the members of the family are concurrent at a point. Find the coordinates of this point. cuts the members of the family are concurrent at a point. Find the coordinates of this point.
Consider a family of circles passing through two fixed points A (3, 7) and B (6, 5). Show that the chords in which the circle 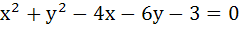 cuts the members of the family are concurrent at a point. Find the coordinates of this point. cuts the members of the family are concurrent at a point. Find the coordinates of this point.
|
IIT 1993 |
|
|
1290 |
In how many ways can a pack of 52 cards be divided into four groups of 13 cards each.
In how many ways can a pack of 52 cards be divided into four groups of 13 cards each.
|
IIT 1979 |
|
|
1291 |
In a triangle ABC, let ∠ C = 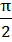 . If r is the inradius and R is the circumradius of the triangle then 2(r+R) = …………. . If r is the inradius and R is the circumradius of the triangle then 2(r+R) = …………. a) a+b b) b+c c) c+a d) a+b+c
In a triangle ABC, let ∠ C = 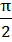 . If r is the inradius and R is the circumradius of the triangle then 2(r+R) = …………. . If r is the inradius and R is the circumradius of the triangle then 2(r+R) = …………. a) a+b b) b+c c) c+a d) a+b+c
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
1292 |
Determine the values of x for which the following function fails to be continuous or differentiable. 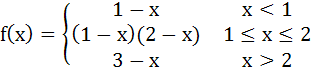
Justify your answer. a) f(x) is continuous and differentiable b) f(x) is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at
x = 1, 2 c) f(x) is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 2 d) f(x) is neither continuous nor differentiable at x = 1, 2
Determine the values of x for which the following function fails to be continuous or differentiable. 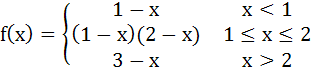
Justify your answer. a) f(x) is continuous and differentiable b) f(x) is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at
x = 1, 2 c) f(x) is continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 2 d) f(x) is neither continuous nor differentiable at x = 1, 2
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
1293 |
Let 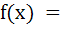 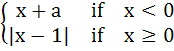 And 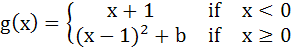 where a and b are non-negative real numbers. Determine the composite function gof. If (gof)(x) is continuous for all real x, determine the values of a and b. Is gof differentiable at x = 0? a) a = b = 0 b) a = 0, b = 1 c) a = 1, b = 0 d) a = b = 1
Let 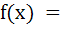 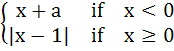 And 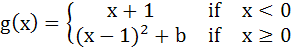 where a and b are non-negative real numbers. Determine the composite function gof. If (gof)(x) is continuous for all real x, determine the values of a and b. Is gof differentiable at x = 0? a) a = b = 0 b) a = 0, b = 1 c) a = 1, b = 0 d) a = b = 1
|
IIT 2002 |
|
|
1294 |
Find the equation of the circle touching the line 2x + 3y + 1 = 0 at the point (1, −1) and is orthogonal to the circle which has the line segment having end points (0, −1) and (−2, 3) as diameter.
Find the equation of the circle touching the line 2x + 3y + 1 = 0 at the point (1, −1) and is orthogonal to the circle which has the line segment having end points (0, −1) and (−2, 3) as diameter.
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
1295 |
Show that the value of 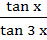 wherever defined wherever defined a) always lies between  and 3 and 3 b) never lies between  and 3 and 3 c) depends on the value of x
Show that the value of 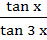 wherever defined wherever defined a) always lies between  and 3 and 3 b) never lies between  and 3 and 3 c) depends on the value of x
|
IIT 1992 |
|
|
1296 |
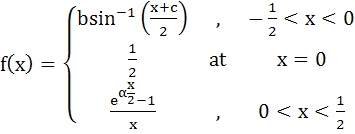
Show that f(x) is differentiable at the value of α = 1. Also, a) b2 +c2 = 4 b) 4 b2 = 4 − c2 c) 64 b2 = 4 − c2 d) 64 b2 = 4 + c2
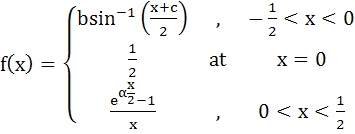
Show that f(x) is differentiable at the value of α = 1. Also, a) b2 +c2 = 4 b) 4 b2 = 4 − c2 c) 64 b2 = 4 − c2 d) 64 b2 = 4 + c2
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
1297 |
The product of r consecutive natural numbers is divisible by r! a) True b) False
The product of r consecutive natural numbers is divisible by r! a) True b) False
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
1298 |
The area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the X–axis and the ordinates x = 1, x = b is (b – 1) sin (3b + 4). Then f(x) is a) (x – 1) cos (3x + b) b) sin (3x + 4) c) sin (3x + 4) + 3 (x – 1) cos (3x + 4) d) none of these
The area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the X–axis and the ordinates x = 1, x = b is (b – 1) sin (3b + 4). Then f(x) is a) (x – 1) cos (3x + b) b) sin (3x + 4) c) sin (3x + 4) + 3 (x – 1) cos (3x + 4) d) none of these
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
1299 |
The sum 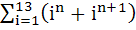 where where 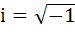 equals equals a) i b) i – 1 c) – i d) 0
The sum 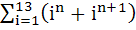 where where 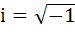 equals equals a) i b) i – 1 c) – i d) 0
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
1300 |
Fill in the blank The value of f (x) = 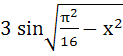 lies in the interval ……………. lies in the interval ……………. a) 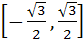 b) 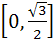 c) 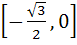 d) 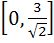
Fill in the blank The value of f (x) = 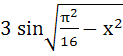 lies in the interval ……………. lies in the interval ……………. a) 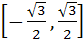 b) 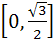 c) 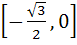 d) 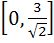
|
IIT 1983 |
|