|
1026 |
Consider the following linear equations
ax + by + cz = 0
bx + cy + az = 0
cx + ay + bz = 0
Match the statements/expressions in column 1 with column 2
| Column 1 | Column2 | | i. a + b + c ≠ 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 = ab + bc + ca | A. Equations represent planes meeting at only one single point | | ii. a + b + c = 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 ≠ ab + bc + ca | B. The equations represent the line x = y = z | | iii. a + b + c ≠ 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 ≠ ab + bc + ca | C. The equations represent identical planes | | iv. a + b + c = 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 = ab + bc + ca | D.The equations represent the whole of the three dimensional space |
Consider the following linear equations
ax + by + cz = 0
bx + cy + az = 0
cx + ay + bz = 0
Match the statements/expressions in column 1 with column 2
| Column 1 | Column2 | | i. a + b + c ≠ 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 = ab + bc + ca | A. Equations represent planes meeting at only one single point | | ii. a + b + c = 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 ≠ ab + bc + ca | B. The equations represent the line x = y = z | | iii. a + b + c ≠ 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 ≠ ab + bc + ca | C. The equations represent identical planes | | iv. a + b + c = 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 = ab + bc + ca | D.The equations represent the whole of the three dimensional space |
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
1027 |
The domain of the function y(x) given by the equation 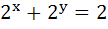 is is a) 0 < x ≤ 1 b) 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 c) 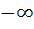 < x ≤ 0 < x ≤ 0 d) 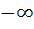 < x < 1 < x < 1
The domain of the function y(x) given by the equation 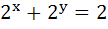 is is a) 0 < x ≤ 1 b) 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 c) 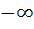 < x ≤ 0 < x ≤ 0 d) 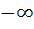 < x < 1 < x < 1
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
1028 |
If A =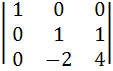 , 6A-1 = A2 + cA + dI , 6A-1 = A2 + cA + dI then (c, d ) is a) (−11, 6) b) (−6, 11) c) (6, 11 ) d) (11, 6 )
If A =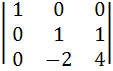 , 6A-1 = A2 + cA + dI , 6A-1 = A2 + cA + dI then (c, d ) is a) (−11, 6) b) (−6, 11) c) (6, 11 ) d) (11, 6 )
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
1029 |
Prove that 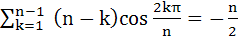
Prove that 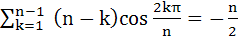
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
1030 |
Tangent at a point P1 (other than (10, 0)) on the curve y = x3 meets the curve again at P2. The tangent at P2 meets the curve at P3 and so on. Show that the abscissae of P1, P2, P3, . . . , Pn form a Geometric Progression. Also find the ratio 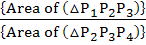 . . a) 32 b) 16 c) 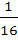 d) 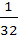
Tangent at a point P1 (other than (10, 0)) on the curve y = x3 meets the curve again at P2. The tangent at P2 meets the curve at P3 and so on. Show that the abscissae of P1, P2, P3, . . . , Pn form a Geometric Progression. Also find the ratio 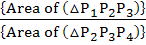 . . a) 32 b) 16 c) 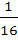 d) 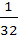
|
IIT 1993 |
|
|
1031 |
In what ratio does the X–axis divide the area of the region bounded by the parabolas y = 4x – x2 and y = x2 – x a) 1:4 b) 21:1 c) 21:4 d) 3:4
In what ratio does the X–axis divide the area of the region bounded by the parabolas y = 4x – x2 and y = x2 – x a) 1:4 b) 21:1 c) 21:4 d) 3:4
|
IIT 1994 |
|
|
1032 |
Let C1 and C2, be respectively, the parabolas 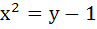 and and 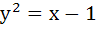 . Let P be any point on C1 and Q be any point on C2. Let P1 and Q1 be the reflections of P and Q respectively with respect to y = x . Prove that P1 lies on C2 and Q1 lies on C1 and . Let P be any point on C1 and Q be any point on C2. Let P1 and Q1 be the reflections of P and Q respectively with respect to y = x . Prove that P1 lies on C2 and Q1 lies on C1 and 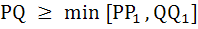 . Hence or otherwise determine points P2 and Q2 on the parabolas C1 and C2 respectively such that . Hence or otherwise determine points P2 and Q2 on the parabolas C1 and C2 respectively such that 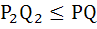 for all points (P, Q) with P on C1 and Q on C2 . for all points (P, Q) with P on C1 and Q on C2 .
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
1033 |
Suppose 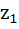 , , 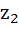 , , 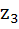 are the vertices of an equilateral triangle inscribed in the circle are the vertices of an equilateral triangle inscribed in the circle 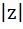 = 2. If = 2. If 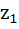 = 1 + i = 1 + i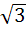 , then find , then find 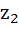 and and 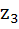 . . a) 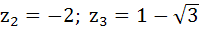 b) 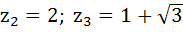 c) 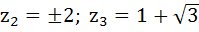 d) None of the above
|
IIT 1994 |
|
|
1034 |
A curve y = f(x) passes through the point P:(1, 1). The equation to the normal at (1, 1) to the curve y = f(x) is (x – 1) + a(y – 1) = 0 and the slope of the tangent at any point on the curve is proportional to the ordinate of the point. Determine the equation of the curve. Also obtain the area bounded by the Y–axis, the curve and the normal at P. a) 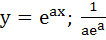 b) y = 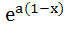 ; ;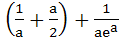 c) 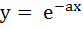 ; ;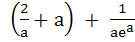 d) 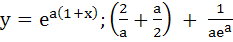
A curve y = f(x) passes through the point P:(1, 1). The equation to the normal at (1, 1) to the curve y = f(x) is (x – 1) + a(y – 1) = 0 and the slope of the tangent at any point on the curve is proportional to the ordinate of the point. Determine the equation of the curve. Also obtain the area bounded by the Y–axis, the curve and the normal at P. a) 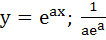 b) y = 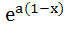 ; ;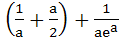 c) 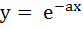 ; ;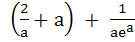 d) 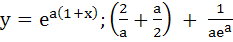
|
IIT 1996 |
|
|
1035 |
Consider the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the parabola y2 = 8x. They intersect P and Q in the first and fourth quadrants respectively. Tangents to the circle at P and Q intersect the X–axis at R and tangents to the parabola at P and Q intersect the X- axis at S. The ratio of areas of the triangle PQS and PQR is a) 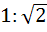 b) 1:2 c) 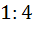 d) 1:8
Consider the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the parabola y2 = 8x. They intersect P and Q in the first and fourth quadrants respectively. Tangents to the circle at P and Q intersect the X–axis at R and tangents to the parabola at P and Q intersect the X- axis at S. The ratio of areas of the triangle PQS and PQR is a) 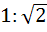 b) 1:2 c) 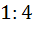 d) 1:8
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
1036 |
Let a + b = 4 where a < 2 and let g(x) be a differentiable function. If 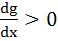 for all x, prove that for all x, prove that 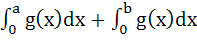 increases as (b – a) increases. increases as (b – a) increases.
Let a + b = 4 where a < 2 and let g(x) be a differentiable function. If 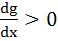 for all x, prove that for all x, prove that 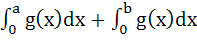 increases as (b – a) increases. increases as (b – a) increases.
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
1037 |
A and B are two separate reservoirs of water. Capacity of reservoir A is double the capacity of reservoir B. Both the reservoirs are filled completely with water, their inlets are closed and then water is released simultaneously from both the reservoirs. The rate of flow of water out of each reservoir at any instant of time is proportionate to the quantity of water in the reservoir at the time. One hour after the water is released the quantity of water in reservoir A is 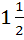 times the quantity of water in reservoir B. After how many hours do both the reservoirs have the same quantity of water? times the quantity of water in reservoir B. After how many hours do both the reservoirs have the same quantity of water? a) 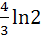 b) 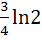 c) ln2 d) 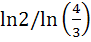
A and B are two separate reservoirs of water. Capacity of reservoir A is double the capacity of reservoir B. Both the reservoirs are filled completely with water, their inlets are closed and then water is released simultaneously from both the reservoirs. The rate of flow of water out of each reservoir at any instant of time is proportionate to the quantity of water in the reservoir at the time. One hour after the water is released the quantity of water in reservoir A is 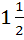 times the quantity of water in reservoir B. After how many hours do both the reservoirs have the same quantity of water? times the quantity of water in reservoir B. After how many hours do both the reservoirs have the same quantity of water? a) 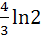 b) 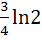 c) ln2 d) 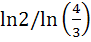
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
1038 |
The area of the quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the end points of latus rectum to the ellipse 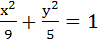 is is a) 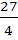 square units square units b) 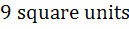 c) 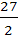 square units square units d) 27 square units
The area of the quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the end points of latus rectum to the ellipse 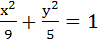 is is a) 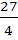 square units square units b) 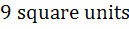 c) 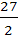 square units square units d) 27 square units
|
IIT 2003 |
|
|
1039 |
The function f(x) = |px – q|+ r|x|, x  when p > 0, q > 0, r > 0 assumes minimum value only on one point if when p > 0, q > 0, r > 0 assumes minimum value only on one point if a) p ≠ q b) r ≠ q c) r ≠ p d) p = q = r
The function f(x) = |px – q|+ r|x|, x  when p > 0, q > 0, r > 0 assumes minimum value only on one point if when p > 0, q > 0, r > 0 assumes minimum value only on one point if a) p ≠ q b) r ≠ q c) r ≠ p d) p = q = r
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
1040 |
Let b ≠ 0 and j = 0, 1, 2, . . . , n. Let Sj be the area of the region bounded by Y–axis and the curve
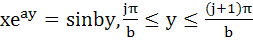 . . Show that S0, S1, S2, . . . , Sn are in geometric progression. Also find the sum for a = − 1 and b = π. a) 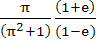 b) 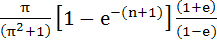 c) 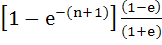 d) 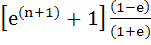
Let b ≠ 0 and j = 0, 1, 2, . . . , n. Let Sj be the area of the region bounded by Y–axis and the curve
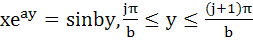 . . Show that S0, S1, S2, . . . , Sn are in geometric progression. Also find the sum for a = − 1 and b = π. a) 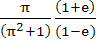 b) 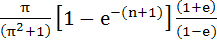 c) 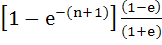 d) 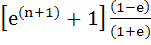
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
1041 |
A tangent to the ellipse x2 + 4y2 = 4 meets the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 at P and Q. Prove that tangents at P and Q of the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 are at right angles.
A tangent to the ellipse x2 + 4y2 = 4 meets the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 at P and Q. Prove that tangents at P and Q of the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 are at right angles.
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
1042 |
Let f(θ) = sinθ (sinθ + sin3θ) then f(θ) a) ≥ 0 only when θ ≥ 0 b) ≤ 0 for all real θ c) ≥ 0 for all real θ d) ≤ θ only when θ ≤ 0
Let f(θ) = sinθ (sinθ + sin3θ) then f(θ) a) ≥ 0 only when θ ≥ 0 b) ≤ 0 for all real θ c) ≥ 0 for all real θ d) ≤ θ only when θ ≤ 0
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
1043 |
Let y = f(x) is a cubic polynomial having maximum at x = − 1 and 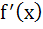 has a minimum at x = 1 and f(−1) = 10, f(1) = − 6. Find the cubic polynomial and also find the distance between the points which are maxima or minima. has a minimum at x = 1 and f(−1) = 10, f(1) = − 6. Find the cubic polynomial and also find the distance between the points which are maxima or minima. a) 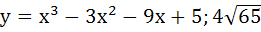 b) 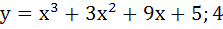 c) 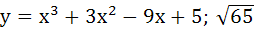 d) 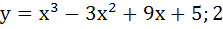
Let y = f(x) is a cubic polynomial having maximum at x = − 1 and 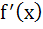 has a minimum at x = 1 and f(−1) = 10, f(1) = − 6. Find the cubic polynomial and also find the distance between the points which are maxima or minima. has a minimum at x = 1 and f(−1) = 10, f(1) = − 6. Find the cubic polynomial and also find the distance between the points which are maxima or minima. a) 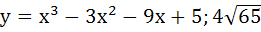 b) 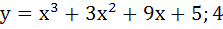 c) 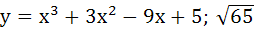 d) 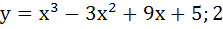
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
1044 |
Each of the following four inequalities given below define a region in the XY–plane. One of these four regions does not have the following property: For any two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) in the region, point 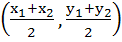 is also in the region. The inequality defining the region that does not have this property is is also in the region. The inequality defining the region that does not have this property is a) x2 + 2y2 ≤ 1 b) max (|x|, |y|) ≤ 1 c) x2 – y2 ≥ 1 d) y2 – x ≤ 0
Each of the following four inequalities given below define a region in the XY–plane. One of these four regions does not have the following property: For any two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) in the region, point 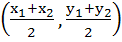 is also in the region. The inequality defining the region that does not have this property is is also in the region. The inequality defining the region that does not have this property is a) x2 + 2y2 ≤ 1 b) max (|x|, |y|) ≤ 1 c) x2 – y2 ≥ 1 d) y2 – x ≤ 0
|
IIT 1981 |
|
|
1045 |
The domain of definition of the function 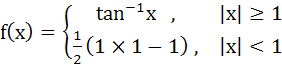 is is a) 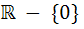 b) 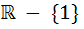 c) 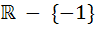 d) 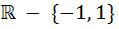
The domain of definition of the function 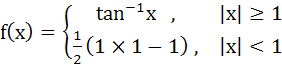 is is a) 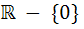 b) 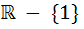 c) 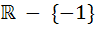 d) 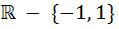
|
IIT 2002 |
|
|
1046 |
The set of values of x which ln(1 + x) ≤ x is equal to . . . . a) (−∞, −1) b) (−1, 0) c) (0, 1) d) (1, ∞)
The set of values of x which ln(1 + x) ≤ x is equal to . . . . a) (−∞, −1) b) (−1, 0) c) (0, 1) d) (1, ∞)
|
IIT 1987 |
|
|
1047 |
For any positive integers m, n (with n ≥ m), we are given that
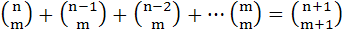
Deduce that
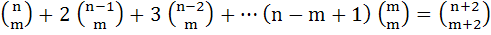
For any positive integers m, n (with n ≥ m), we are given that
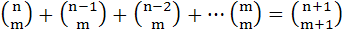
Deduce that
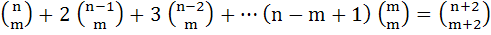
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
1048 |
If A and B are two independent events such that P (A) > 0 and P (B) ≠ 1 then 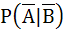 is equal to is equal to a) 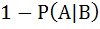 b) 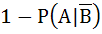 c) 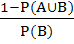 d) 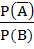
If A and B are two independent events such that P (A) > 0 and P (B) ≠ 1 then 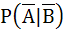 is equal to is equal to a) 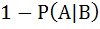 b) 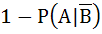 c) 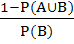 d) 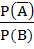
|
IIT 1980 |
|
|
1049 |
If , , 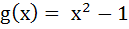 then g(f(x)) is invertible in the domain then g(f(x)) is invertible in the domain a) 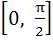 b) 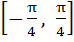 c) 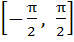 d) 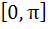
If , , 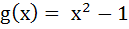 then g(f(x)) is invertible in the domain then g(f(x)) is invertible in the domain a) 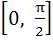 b) 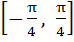 c) 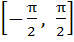 d) 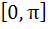
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
1050 |
Evaluate 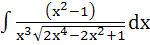 a) 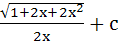 b) 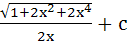 c) 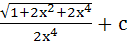 d) 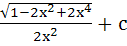
|
IIT 2006 |
|