|
1001 |
Find the area bounded by the curves
x2 = y, x2 = − y and y2 = 4x – 3 a) 1 b) 3 c) 1/3 d) 1/9
Find the area bounded by the curves
x2 = y, x2 = − y and y2 = 4x – 3 a) 1 b) 3 c) 1/3 d) 1/9
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
1002 |
Let E = {1, 2, 3, 4} and F = {1, 2}, then the number of onto functions from E to F is a) 14 b) 16 c) 12 d) 8
Let E = {1, 2, 3, 4} and F = {1, 2}, then the number of onto functions from E to F is a) 14 b) 16 c) 12 d) 8
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
1003 |
For a twice differentiable function f(x), g(x) is defined as 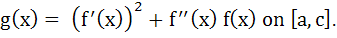 If for a < b < c < d < e, f(a) = 0, f(b) = 2, f(c) = − 1, f(d) = 2, f(e) = 0 then find the maximum number of zeros of g(x). If for a < b < c < d < e, f(a) = 0, f(b) = 2, f(c) = − 1, f(d) = 2, f(e) = 0 then find the maximum number of zeros of g(x). a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 6
For a twice differentiable function f(x), g(x) is defined as 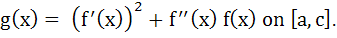 If for a < b < c < d < e, f(a) = 0, f(b) = 2, f(c) = − 1, f(d) = 2, f(e) = 0 then find the maximum number of zeros of g(x). If for a < b < c < d < e, f(a) = 0, f(b) = 2, f(c) = − 1, f(d) = 2, f(e) = 0 then find the maximum number of zeros of g(x). a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 6
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
1004 |
Find the equation of the normal to the curve 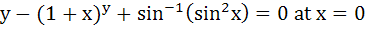
Find the equation of the normal to the curve 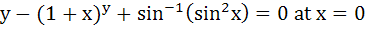
|
IIT 1993 |
|
|
1005 |
The larger of cos (lnθ) and ln (cosθ) if 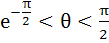 is is a) cos(lnθ) b) ln(cosθ)
The larger of cos (lnθ) and ln (cosθ) if 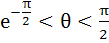 is is a) cos(lnθ) b) ln(cosθ)
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
1006 |
For any real t, 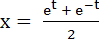 , , 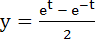 is a point on the hyperbola x2 – y2 = 1. Find the area bounded by the hyperbola and the line joining the centre to the points corresponding to t1 and –t1. is a point on the hyperbola x2 – y2 = 1. Find the area bounded by the hyperbola and the line joining the centre to the points corresponding to t1 and –t1.
For any real t, 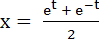 , , 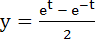 is a point on the hyperbola x2 – y2 = 1. Find the area bounded by the hyperbola and the line joining the centre to the points corresponding to t1 and –t1. is a point on the hyperbola x2 – y2 = 1. Find the area bounded by the hyperbola and the line joining the centre to the points corresponding to t1 and –t1.
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
1007 |
The integral is equal to a) b) c) d)
The integral is equal to a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2014 |
|
|
1008 |
X and Y are two sets and f : X → Y. If 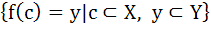 then the true statement is then the true statement is a) 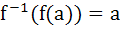 b) 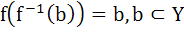 c) 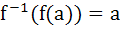 , , 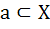 d) 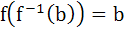
X and Y are two sets and f : X → Y. If 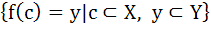 then the true statement is then the true statement is a) 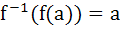 b) 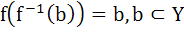 c) 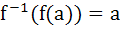 , , 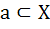 d) 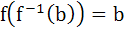
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
1009 |
Let a and b are non-zero real numbers. Then the equation
(ax2 + by2 + c) (x2 – 5xy + 6y2) = 0 represents a) Four straight lines when c = 0 and a, b are of the same sign b) Two straight lines and a circle when a = b and c is of sign opposite to that of a. c) Two straight lines and a hyperbola when a and b are of the same sign d) A circle and an ellipse when a and b are of the same sign and c is of sign opposite to that of a.
Let a and b are non-zero real numbers. Then the equation
(ax2 + by2 + c) (x2 – 5xy + 6y2) = 0 represents a) Four straight lines when c = 0 and a, b are of the same sign b) Two straight lines and a circle when a = b and c is of sign opposite to that of a. c) Two straight lines and a hyperbola when a and b are of the same sign d) A circle and an ellipse when a and b are of the same sign and c is of sign opposite to that of a.
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
1010 |
Statement 1: The value of the integral is equal toStatement 2: a) Statement 1 is correct, statement 2 is correct. Statement 2 is correct explanation of statement 1 b) Statement 1 is correct, statement 2 is correct. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation of statement 1 c) Statement 1 is correct, statement 2 is false d) Statement 1 is incorrect, statement 2 is correct
Statement 1: The value of the integral is equal toStatement 2: a) Statement 1 is correct, statement 2 is correct. Statement 2 is correct explanation of statement 1 b) Statement 1 is correct, statement 2 is correct. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation of statement 1 c) Statement 1 is correct, statement 2 is false d) Statement 1 is incorrect, statement 2 is correct
|
IIT 2013 |
|
|
1011 |
Multiple choices
If f(x) =  where [x] stands for the greatest integer function then where [x] stands for the greatest integer function then a)  b)  c) 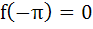 d) 
Multiple choices
If f(x) =  where [x] stands for the greatest integer function then where [x] stands for the greatest integer function then a)  b)  c) 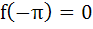 d) 
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
1012 |
A circle C of radius 1 is inscribed in an equilateral triangle PQR. The point of contacts of C with its sides PQ, QR and RP are D, E, F respectively. The line PQ is given by 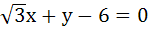 and the point D is and the point D is 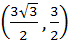 . Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ. Points E and F are given by . Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ. Points E and F are given by a) 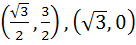 b) 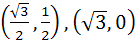 c) 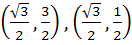 d) 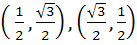
A circle C of radius 1 is inscribed in an equilateral triangle PQR. The point of contacts of C with its sides PQ, QR and RP are D, E, F respectively. The line PQ is given by 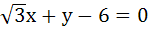 and the point D is and the point D is 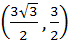 . Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ. Points E and F are given by . Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ. Points E and F are given by a) 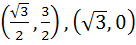 b) 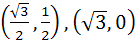 c) 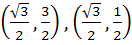 d) 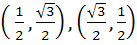
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
1013 |
One or more than one correct options If then a) b) c) d)
One or more than one correct options If then a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2017 |
|
|
1014 |
ConsiderL1: 2x + 3y + p – 3 = 0; L2: 2x + 3y + p + 3 = 0 where p is a real number and C : x2 + y2 + 6x – 10y + 30 = 0 Statement 1 – If the line L1 is a chord of the circle C then L2 is not always a diameter of C. Statement 2 - If the line L1 is a diameter of the circle C then L2 is not a chord of the circle.
Which of the following four statements is true? a) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1. b) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1. c) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false. d) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true
ConsiderL1: 2x + 3y + p – 3 = 0; L2: 2x + 3y + p + 3 = 0 where p is a real number and C : x2 + y2 + 6x – 10y + 30 = 0 Statement 1 – If the line L1 is a chord of the circle C then L2 is not always a diameter of C. Statement 2 - If the line L1 is a diameter of the circle C then L2 is not a chord of the circle.
Which of the following four statements is true? a) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1. b) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1. c) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false. d) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
1015 |
One or more than one correct options If then a) b) c) d)
One or more than one correct options If then a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2009 |
|
|
1016 |
If E and F are events with P (E) ≤ P (F) and P (E ∩ F) > 0 then a) occurrence of E ⇒ occurrence of F b) occurrence of F ⇒ occurrence of E c) non-occurrence of E ⇒ non-occurrence of F d) none of the above occurrences hold
If E and F are events with P (E) ≤ P (F) and P (E ∩ F) > 0 then a) occurrence of E ⇒ occurrence of F b) occurrence of F ⇒ occurrence of E c) non-occurrence of E ⇒ non-occurrence of F d) none of the above occurrences hold
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
1017 |
 = = 
where t2 = cot2x – 1 a) True b) False
 = = 
where t2 = cot2x – 1 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1987 |
|
|
1018 |
equals a) 8 b) 2 c) 4 d) 0
equals a) 8 b) 2 c) 4 d) 0
|
IIT 2014 |
|
|
1019 |
Fill in the blank The system of equations
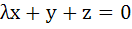
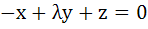
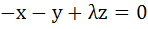
will have a non-zero solution if real value of λ is given by …………
Fill in the blank The system of equations
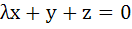
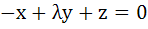
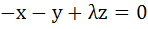
will have a non-zero solution if real value of λ is given by …………
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
1020 |
The function  is not one to one is not one to one a) True b) False
The function  is not one to one is not one to one a) True b) False
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
1021 |
For any real number x, let [x] denote the greater integer less than or equal to x. Let f be a real valued function defined on the interval [−10, 10] by then the value of is a) 2 b) 0 c) 6 d) 4
For any real number x, let [x] denote the greater integer less than or equal to x. Let f be a real valued function defined on the interval [−10, 10] by then the value of is a) 2 b) 0 c) 6 d) 4
|
IIT 2010 |
|
|
1022 |
Let 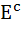 denotes the complement of an event E. Let E, F, G are pair wise independent events with P (G) > 0 and P (E ∩ F ∩ G) = 0 then denotes the complement of an event E. Let E, F, G are pair wise independent events with P (G) > 0 and P (E ∩ F ∩ G) = 0 then 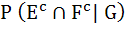 equals equals a) 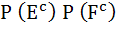 b) 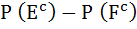 c) 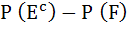 d) 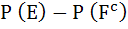
Let 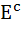 denotes the complement of an event E. Let E, F, G are pair wise independent events with P (G) > 0 and P (E ∩ F ∩ G) = 0 then denotes the complement of an event E. Let E, F, G are pair wise independent events with P (G) > 0 and P (E ∩ F ∩ G) = 0 then 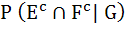 equals equals a) 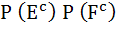 b) 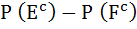 c) 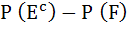 d) 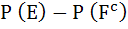
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
1023 |
Let A be a set of n distinct elements. Then find the total number of distinct functions from A to A is and out of these onto functions are . . .
Let A be a set of n distinct elements. Then find the total number of distinct functions from A to A is and out of these onto functions are . . .
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
1024 |
is equal to a) b) c) d)
is equal to a) b) c) d)
|
IIT 2016 |
|
|
1025 |
(One or more correct answers)
For any two events in the sample space a) 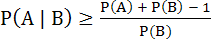 is always true is always true b) 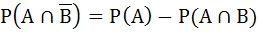 does not hold does not hold c) 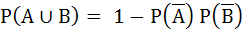 if A and B are independent if A and B are independent d) 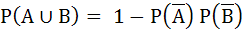 if A and B are disjoint if A and B are disjoint
(One or more correct answers)
For any two events in the sample space a) 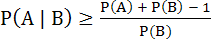 is always true is always true b) 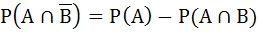 does not hold does not hold c) 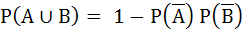 if A and B are independent if A and B are independent d) 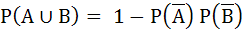 if A and B are disjoint if A and B are disjoint
|
IIT 1991 |
|