|
826 |
True / False Let 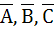 are unit vectors. Suppose that are unit vectors. Suppose that 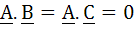 and the angle between B and and the angle between B and 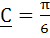 then then 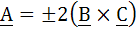 a) True b) False
True / False Let 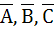 are unit vectors. Suppose that are unit vectors. Suppose that 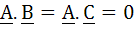 and the angle between B and and the angle between B and 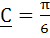 then then 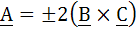 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1981 |
|
|
827 |
2sinx + tanx > 3x where 0 ≤ x ≤  a) True b) False
2sinx + tanx > 3x where 0 ≤ x ≤  a) True b) False
|
IIT 1990 |
|
|
828 |
Let f(x) = (x + 1)2 – 1, x ≥ −1 then the set {x : f(x) = f-1(x)} is a) 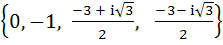 b) { 0, 1, −1} c) {0, −1} d) Ф
Let f(x) = (x + 1)2 – 1, x ≥ −1 then the set {x : f(x) = f-1(x)} is a) 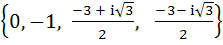 b) { 0, 1, −1} c) {0, −1} d) Ф
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
829 |
Suppose f (x) = (x + 1)2 for x ≥ 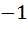 . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals a) 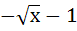 , , 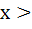 0 0 b) 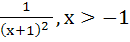 c) 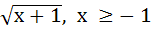 d) 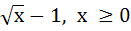
Suppose f (x) = (x + 1)2 for x ≥ 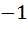 . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals a) 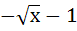 , , 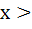 0 0 b) 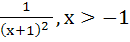 c) 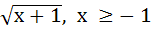 d) 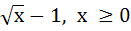
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
830 |
Let a, b, c be three positive real numbers and
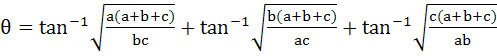
Then tan θ = ……….. a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
Let a, b, c be three positive real numbers and
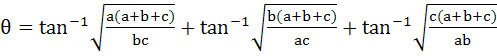
Then tan θ = ……….. a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 1981 |
|
|
831 |
If X and Y are two sets and f : X  Y Y
If { f (c) = y, c ⊂ x, y ⊂ Y } then the true statement is a) 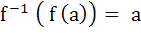 b) 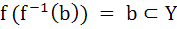 c) 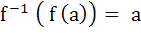 , a ⊂ X , a ⊂ X d) 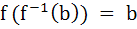
If X and Y are two sets and f : X 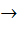 Y Y
If { f (c) = y, c ⊂ x, y ⊂ Y } then the true statement is a) 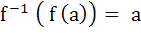 b) 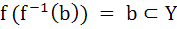 c) 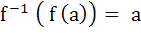 , a ⊂ X , a ⊂ X d) 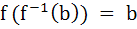
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
832 |
Let O (0, 0), P (3, 4), Q (6, 0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point inside the triangle OPQ is such that OPR, PQR, OQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are a) 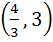 b) 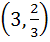 c) 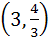 d) 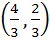
Let O (0, 0), P (3, 4), Q (6, 0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point inside the triangle OPQ is such that OPR, PQR, OQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are a) 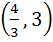 b) 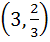 c) 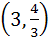 d) 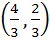
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
833 |
If f be a one–one function with domain { x, y, z}and range { 1, 2, 3}. It is given that exactly one of the following statements is true and the remaining statements are false. Determine 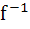 (1) (1) 1. f(x) = 1 2. f(y) ≠ 1 3. f(z) ≠ 2 a) {0} b) {1} c) {y} d) none of the above
If f be a one–one function with domain { x, y, z}and range { 1, 2, 3}. It is given that exactly one of the following statements is true and the remaining statements are false. Determine 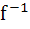 (1) (1) 1. f(x) = 1 2. f(y) ≠ 1 3. f(z) ≠ 2 a) {0} b) {1} c) {y} d) none of the above
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
834 |
One or more correct answers
In triangle ABC the internal angle bisector of ∠A meets the side BC in D. DE is a perpendicular to AD which meets AC in E and AB in F. Then a) AE is harmonic mean of b and c b) AD 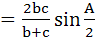 c) 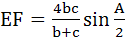 d) Δ AEF is isosceles
One or more correct answers
In triangle ABC the internal angle bisector of ∠A meets the side BC in D. DE is a perpendicular to AD which meets AC in E and AB in F. Then a) AE is harmonic mean of b and c b) AD 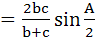 c) 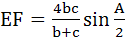 d) Δ AEF is isosceles
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
835 |
For a triangle ABC it is given that 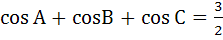 , then Δ ABC is equilateral. , then Δ ABC is equilateral. a) True b) False
For a triangle ABC it is given that 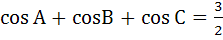 , then Δ ABC is equilateral. , then Δ ABC is equilateral. a) True b) False
|
IIT 1984 |
|
|
836 |
True / False The function f (x) = 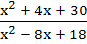 is not one to one. is not one to one. a) True b) False
True / False The function f (x) = 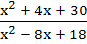 is not one to one. is not one to one. a) True b) False
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
837 |
Find the set of all values of a such that 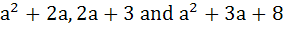 are sides of a triangle. are sides of a triangle. a) (0, 3) b) (3, ∞) c) (0, 5) d) (5, ∞)
Find the set of all values of a such that 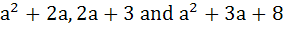 are sides of a triangle. are sides of a triangle. a) (0, 3) b) (3, ∞) c) (0, 5) d) (5, ∞)
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
838 |
Fill in the blank Let A be the set of n distinct elements then the total number of distinct functions from A to A is ……… and out of these …… are onto a) n!, 1 b) nn, n! c) nn, 1 d) none of the above
Fill in the blank Let A be the set of n distinct elements then the total number of distinct functions from A to A is ……… and out of these …… are onto a) n!, 1 b) nn, n! c) nn, 1 d) none of the above
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
839 |
In a triangle of base a the ratio of the other two sides is r (< 1). Then the altitude of the triangle is less than or equal to 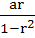 . . a) True b) False
In a triangle of base a the ratio of the other two sides is r (< 1). Then the altitude of the triangle is less than or equal to 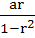 . . a) True b) False
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
840 |
The value of k such that 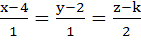 lies in the plane lies in the plane
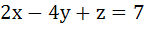 is is a) 7 b) – 7 c) No real value d) 4
The value of k such that 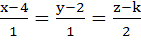 lies in the plane lies in the plane
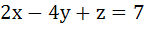 is is a) 7 b) – 7 c) No real value d) 4
|
IIT 2003 |
|
|
841 |
If ABCD are four points in a space, prove that
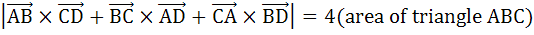
If ABCD are four points in a space, prove that
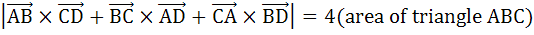
|
IIT 1987 |
|
|
842 |
If a, b, c are distinct positive numbers then the expression
( b + c – a ) ( c + a – b ) ( a + b – c ) –abc is a) Positive b) Negative c) Non–positive d) None of these
If a, b, c are distinct positive numbers then the expression
( b + c – a ) ( c + a – b ) ( a + b – c ) –abc is a) Positive b) Negative c) Non–positive d) None of these
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
843 |
Let A and B be square matrices of equal degree, then which one is correct amongst the following a) A + B = B + A b) A + B = A – B c) A – B = B – A d) AB = BA
Let A and B be square matrices of equal degree, then which one is correct amongst the following a) A + B = B + A b) A + B = A – B c) A – B = B – A d) AB = BA
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
844 |
The edges of a parallelepiped are of unit length and are parallel to non-coplanar unit vectors 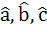 such that such that 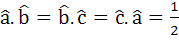 . Then the volume of the parallelepiped is . Then the volume of the parallelepiped is a) 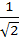 b) 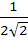 c) 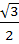 d) 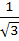
The edges of a parallelepiped are of unit length and are parallel to non-coplanar unit vectors 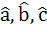 such that such that 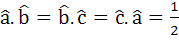 . Then the volume of the parallelepiped is . Then the volume of the parallelepiped is a) 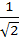 b) 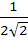 c) 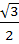 d) 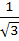
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
845 |
If P = 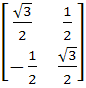 , A = , A = 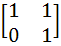 and Q = PAPT and Q = PAPT then PT (Q2005) P is equal to a) 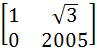 b) 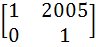 c) 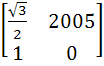 d) 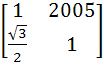
If P = 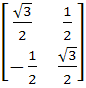 , A = , A = 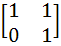 and Q = PAPT and Q = PAPT then PT (Q2005) P is equal to a) 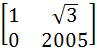 b) 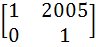 c) 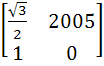 d) 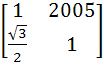
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
846 |
Consider three planes
P1 : x – y + z = 1 P2 : x + y – z = −1 P3 : x – 3y + 3z = 2 Let L1, L2, L3 be lines of intersection of planes P2 and P3, P3 and P1, and P1 and P2 respectively. Statement 1 – At least two of the lines L1, L2, L3 are non parallel Statement 2 – The three planes do not have a common point. a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 2 is a correct explanation of statement 1. b) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation of statement 1. c) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false. d) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
Consider three planes
P1 : x – y + z = 1 P2 : x + y – z = −1 P3 : x – 3y + 3z = 2 Let L1, L2, L3 be lines of intersection of planes P2 and P3, P3 and P1, and P1 and P2 respectively. Statement 1 – At least two of the lines L1, L2, L3 are non parallel Statement 2 – The three planes do not have a common point. a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 2 is a correct explanation of statement 1. b) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation of statement 1. c) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false. d) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
847 |
Show that the system of equations
3x – y + 4z = 3
x + 2y − 3z = −2
6x + 5y + λz = −3
has at least one solution for any real number λ ≠ −5. Find the set of solutions if λ = −5 a) 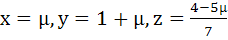 b) 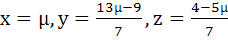 c) 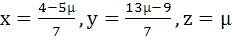 d) 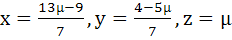
Show that the system of equations
3x – y + 4z = 3
x + 2y − 3z = −2
6x + 5y + λz = −3
has at least one solution for any real number λ ≠ −5. Find the set of solutions if λ = −5 a) 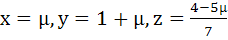 b) 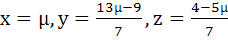 c) 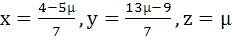 d) 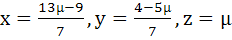
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
848 |
The differential equation 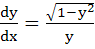 determines a family of circles with determines a family of circles with a) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, 1) b) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, -1) c) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the X-axis d) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the Y-axis
The differential equation 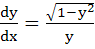 determines a family of circles with determines a family of circles with a) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, 1) b) Variable radii and a fixed centre ( 0, -1) c) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the X-axis d) Fixed radius and a variable centre along the Y-axis
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
849 |
Prove that for all values of θ
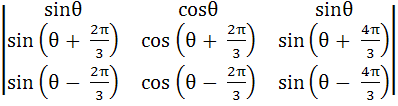 = 0 = 0
Prove that for all values of θ
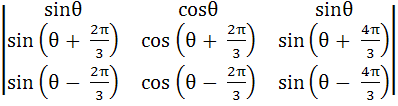 = 0 = 0
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
850 |
If 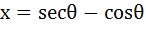 and and 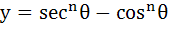 , then show that , then show that
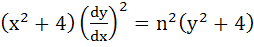
|
IIT 1989 |
|