|
776 |
Let 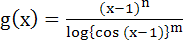 , 0 < x < 2 are integers m ≠ 0, n > 0 and let p be the left hand derivative of |x − 1| at x = 1. If , 0 < x < 2 are integers m ≠ 0, n > 0 and let p be the left hand derivative of |x − 1| at x = 1. If 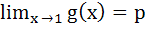 , then , then a) n = −1, m = 1 b) n = 1, m = −1 c) n = 2, m = 2 d) n > 2, n = m
Let 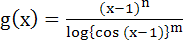 , 0 < x < 2 are integers m ≠ 0, n > 0 and let p be the left hand derivative of |x − 1| at x = 1. If , 0 < x < 2 are integers m ≠ 0, n > 0 and let p be the left hand derivative of |x − 1| at x = 1. If 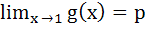 , then , then a) n = −1, m = 1 b) n = 1, m = −1 c) n = 2, m = 2 d) n > 2, n = m
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
777 |
For three vectors 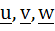 which of the following expressions is not equal to any of the remaining three which of the following expressions is not equal to any of the remaining three a) 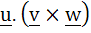 b) 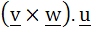 c) 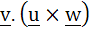 d) 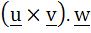
For three vectors 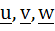 which of the following expressions is not equal to any of the remaining three which of the following expressions is not equal to any of the remaining three a) 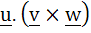 b) 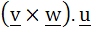 c) 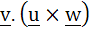 d) 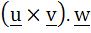
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
778 |
If total number of runs scored in n matches is
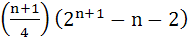 where n > 1 and the runs scored in the kth match are given by k.2n + 1 – k where 1 ≤ k ≤ n. Find n. where n > 1 and the runs scored in the kth match are given by k.2n + 1 – k where 1 ≤ k ≤ n. Find n.
If total number of runs scored in n matches is
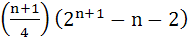 where n > 1 and the runs scored in the kth match are given by k.2n + 1 – k where 1 ≤ k ≤ n. Find n. where n > 1 and the runs scored in the kth match are given by k.2n + 1 – k where 1 ≤ k ≤ n. Find n.
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
779 |
In a triangle ABC if cotA, cotB, cotC are in Arithmetic Progression then a, b, c are in . . . . . Progression.
In a triangle ABC if cotA, cotB, cotC are in Arithmetic Progression then a, b, c are in . . . . . Progression.
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
780 |
For any odd integer n ≥ 1,
n3 – (n – 1)3 + . . . + (−)n – 1 13 = . . .
For any odd integer n ≥ 1,
n3 – (n – 1)3 + . . . + (−)n – 1 13 = . . .
|
IIT 1996 |
|
|
781 |
A unit vector which is orthogonal to the vectors 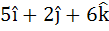 and and coplanar with the vectors 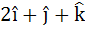 and and 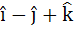 is is a) 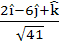 b) 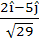 c) 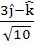 d) 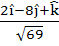
A unit vector which is orthogonal to the vectors 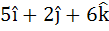 and and coplanar with the vectors 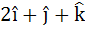 and and 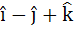 is is a) 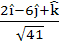 b) 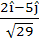 c) 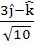 d) 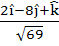
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
782 |
The area of the equilateral triangle which contains three coins of unit radius is a) 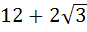 square units square units b) 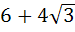 square units square units c) 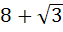 square units square units d) 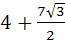 square units square units
The area of the equilateral triangle which contains three coins of unit radius is a) 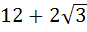 square units square units b) 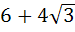 square units square units c) 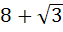 square units square units d) 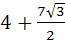 square units square units
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
783 |
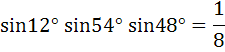
a) True b) False
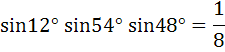
a) True b) False
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
784 |
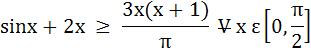
a) True b) False
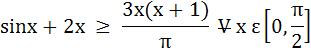
a) True b) False
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
785 |
Match the following 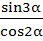 is is | Column 1 | Column 2 | | i) Positive | A) (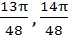 ) ) | | ii) Negative | B) (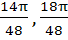 ) ) | | | C) (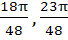 ) ) | | | D) (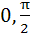 ) ) |
Match the following 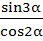 is is | Column 1 | Column 2 | | i) Positive | A) (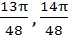 ) ) | | ii) Negative | B) (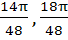 ) ) | | | C) (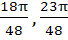 ) ) | | | D) (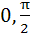 ) ) |
|
IIT 1992 |
|
|
786 |
If the vectors b, c, d, are not coplanar then prove that a is parallel to the vector 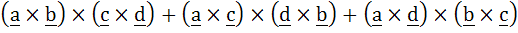
If the vectors b, c, d, are not coplanar then prove that a is parallel to the vector 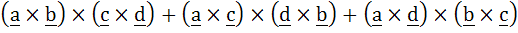
|
IIT 1994 |
|
|
787 |
Prove by vector method or otherwise, that the point of intersection of the diagonals of a trapezium lies on the line passing through the mid points of the parallel sides (you may assume that the trapezium is not a parallelogram)
Prove by vector method or otherwise, that the point of intersection of the diagonals of a trapezium lies on the line passing through the mid points of the parallel sides (you may assume that the trapezium is not a parallelogram)
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
788 |
True / False Let 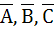 are unit vectors. Suppose that are unit vectors. Suppose that 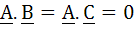 and the angle between B and and the angle between B and 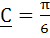 then then 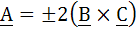 a) True b) False
True / False Let 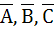 are unit vectors. Suppose that are unit vectors. Suppose that 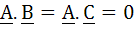 and the angle between B and and the angle between B and 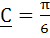 then then 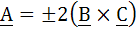 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1981 |
|
|
789 |
2sinx + tanx > 3x where 0 ≤ x ≤  a) True b) False
2sinx + tanx > 3x where 0 ≤ x ≤  a) True b) False
|
IIT 1990 |
|
|
790 |
Let f(x) = (x + 1)2 – 1, x ≥ −1 then the set {x : f(x) = f-1(x)} is a) 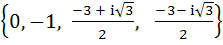 b) { 0, 1, −1} c) {0, −1} d) Ф
Let f(x) = (x + 1)2 – 1, x ≥ −1 then the set {x : f(x) = f-1(x)} is a) 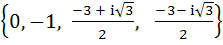 b) { 0, 1, −1} c) {0, −1} d) Ф
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
791 |
Suppose f (x) = (x + 1)2 for x ≥ 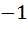 . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals a) 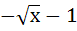 , , 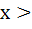 0 0 b) 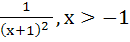 c) 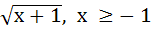 d) 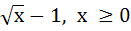
Suppose f (x) = (x + 1)2 for x ≥ 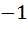 . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals . If g (x) is the function whose graph is the reflection of the graph of f (x) with respect to the line y = x then g (x) equals a) 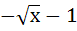 , , 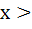 0 0 b) 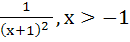 c) 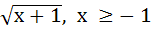 d) 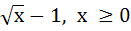
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
792 |
Let a, b, c be three positive real numbers and
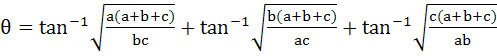
Then tan θ = ……….. a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
Let a, b, c be three positive real numbers and
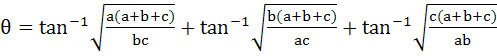
Then tan θ = ……….. a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 1981 |
|
|
793 |
If X and Y are two sets and f : X 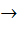 Y Y
If { f (c) = y, c ⊂ x, y ⊂ Y } then the true statement is a) 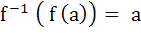 b) 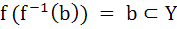 c) 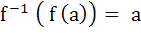 , a ⊂ X , a ⊂ X d) 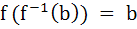
If X and Y are two sets and f : X 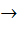 Y Y
If { f (c) = y, c ⊂ x, y ⊂ Y } then the true statement is a) 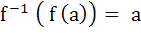 b) 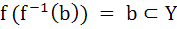 c) 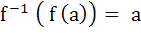 , a ⊂ X , a ⊂ X d) 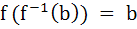
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
794 |
Let O (0, 0), P (3, 4), Q (6, 0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point inside the triangle OPQ is such that OPR, PQR, OQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are a) 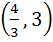 b) 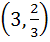 c) 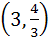 d) 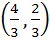
Let O (0, 0), P (3, 4), Q (6, 0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point inside the triangle OPQ is such that OPR, PQR, OQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are a) 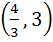 b) 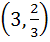 c) 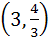 d) 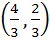
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
795 |
If f be a one–one function with domain { x, y, z}and range { 1, 2, 3}. It is given that exactly one of the following statements is true and the remaining statements are false. Determine 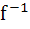 (1) (1) 1. f(x) = 1 2. f(y) ≠ 1 3. f(z) ≠ 2 a) {0} b) {1} c) {y} d) none of the above
If f be a one–one function with domain { x, y, z}and range { 1, 2, 3}. It is given that exactly one of the following statements is true and the remaining statements are false. Determine 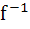 (1) (1) 1. f(x) = 1 2. f(y) ≠ 1 3. f(z) ≠ 2 a) {0} b) {1} c) {y} d) none of the above
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
796 |
One or more correct answers
In triangle ABC the internal angle bisector of ∠A meets the side BC in D. DE is a perpendicular to AD which meets AC in E and AB in F. Then a) AE is harmonic mean of b and c b) AD 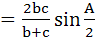 c) 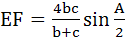 d) Δ AEF is isosceles
One or more correct answers
In triangle ABC the internal angle bisector of ∠A meets the side BC in D. DE is a perpendicular to AD which meets AC in E and AB in F. Then a) AE is harmonic mean of b and c b) AD 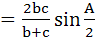 c) 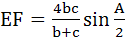 d) Δ AEF is isosceles
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
797 |
With usual notation if in a triangle ABC, 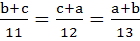 then then 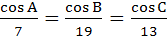 . .
a) True b) False
With usual notation if in a triangle ABC, 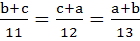 then then 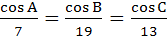 . .
a) True b) False
|
IIT 1984 |
|
|
798 |
If in a triangle ABC, cosA cosB + sinA sinB sin C = 1 then show that a : b : c = 1 : 1 : 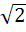 a) True b) False
If in a triangle ABC, cosA cosB + sinA sinB sin C = 1 then show that a : b : c = 1 : 1 : 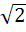 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1986 |
|
|
799 |
If the lines 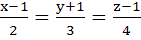 and and 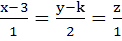 intersect then the value of k is intersect then the value of k is a)  b)  c) 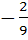 d) 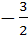
If the lines 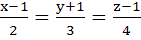 and and 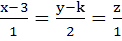 intersect then the value of k is intersect then the value of k is a)  b)  c) 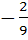 d) 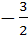
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
800 |
The area of a triangle whose vertices are
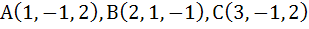 is is
The area of a triangle whose vertices are
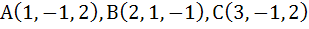 is is
|
IIT 1983 |
|