|
726 |
If f (x) = 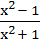 for every real x then the minimum value of f for every real x then the minimum value of f a) does not exist because f is unbounded b) is not attained even though f is bounded c) is equal to 1 d) is equal to −1
If f (x) = 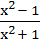 for every real x then the minimum value of f for every real x then the minimum value of f a) does not exist because f is unbounded b) is not attained even though f is bounded c) is equal to 1 d) is equal to −1
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
727 |
Find the larger of cos(lnθ) and ln(cosθ) if 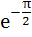 < θ < < θ <  . . a) cos(lnθ) b) ln(cosθ) c) Neither is larger throughout the interval
Find the larger of cos(lnθ) and ln(cosθ) if 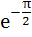 < θ < < θ <  . . a) cos(lnθ) b) ln(cosθ) c) Neither is larger throughout the interval
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
728 |
If the function f : [ 1, 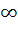 ) → [ 1, ) → [ 1, 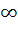 ) is defined by f (x) = 2x(x – 1) then ) is defined by f (x) = 2x(x – 1) then
f -1(x) is a) 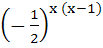 b)  ( (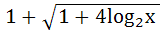 ) ) c)  ( (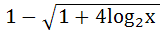 ) ) d) 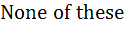
|
IIT 1999 |
|
|
729 |
If 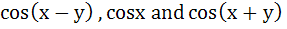 are in harmonic progression then are in harmonic progression then 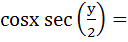 ………… ………… a) 1 b) 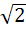 c) 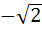 d) 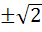
If 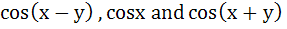 are in harmonic progression then are in harmonic progression then 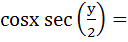 ………… ………… a) 1 b) 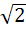 c) 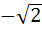 d) 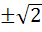
|
IIT 1997 |
|
|
730 |
If 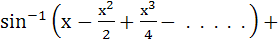 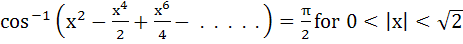
then x equals a)  b) 1 c) 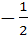 d) –1
If 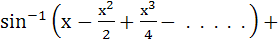 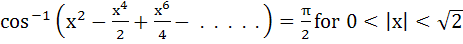
then x equals a)  b) 1 c) 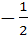 d) –1
|
IIT 1999 |
|
|
731 |
Let f ( x ) = 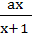 , x ≠ , x ≠ 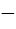 1 then for what value of a is f ( f (x)) = x 1 then for what value of a is f ( f (x)) = x a) 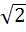 b) 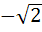 c) 1 d) 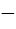 1 1
Let f ( x ) = 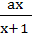 , x ≠ , x ≠ 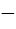 1 then for what value of a is f ( f (x)) = x 1 then for what value of a is f ( f (x)) = x a) 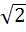 b) 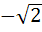 c) 1 d) 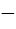 1 1
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
732 |
If f : [ 0, 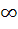 ) ) 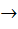 [ 0, [ 0, 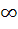 ) and f (x) = ) and f (x) = 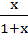 then f is then f is a) one-one and onto b) one-one but not onto c) onto but not one-one d) neither one-one nor onto
If f : [ 0, 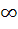 ) ) 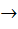 [ 0, [ 0, 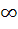 ) and f (x) = ) and f (x) = 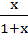 then f is then f is a) one-one and onto b) one-one but not onto c) onto but not one-one d) neither one-one nor onto
|
IIT 2003 |
|
|
733 |
Match the following Let (x, y) be such that 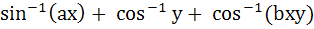 = = 
| Column 1 | Column 2 | | i) If a=1 and b=0 then (x, y) | A)Lies on the circle
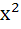 + +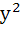 =1 =1 | | ii) If a=1 and b=1 then (x, y) | B)Lies on
(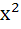 −1)( −1)(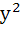 −1) = 0 −1) = 0 | | iii) If a=1 and b=2 then (x, y) | C)Lies on y = x | | iv) If a=2 and b=2 then (x, y) | D)Lies on
(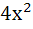 −1)( −1)(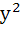 −1) = 0 −1) = 0 |
Match the following Let (x, y) be such that 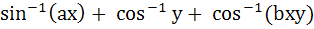 = = 
| Column 1 | Column 2 | | i) If a=1 and b=0 then (x, y) | A)Lies on the circle
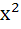 + +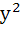 =1 =1 | | ii) If a=1 and b=1 then (x, y) | B)Lies on
(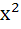 −1)( −1)(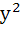 −1) = 0 −1) = 0 | | iii) If a=1 and b=2 then (x, y) | C)Lies on y = x | | iv) If a=2 and b=2 then (x, y) | D)Lies on
(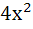 −1)( −1)(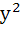 −1) = 0 −1) = 0 |
|
IIT 2007 |
|
|
734 |
f (x) = 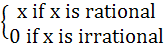
and g (x) = 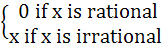
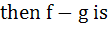 a) neither one-one nor onto b) one-one and onto c) one-one and into d) many one and onto
f (x) = 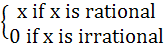
and g (x) = 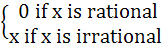
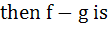 a) neither one-one nor onto b) one-one and onto c) one-one and into d) many one and onto
|
IIT 2005 |
|
|
735 |
One angle of an isosceles triangle is 120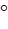 and the radius of its incircle = and the radius of its incircle = 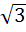 . Then the area of the triangle in square units is . Then the area of the triangle in square units is a) 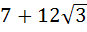 b) 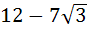 c) 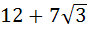 d) 2π
One angle of an isosceles triangle is 120 and the radius of its incircle = and the radius of its incircle = 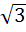 . Then the area of the triangle in square units is . Then the area of the triangle in square units is a) 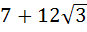 b) 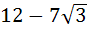 c) 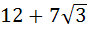 d) 2π
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
736 |
The sides of a triangle are three consecutive natural numbers and its largest angle is twice the smallest one. Determine the sides of triangle. a) 3, 4, 5 b) 4, 5, 6 c) 4, 5, 7 d) 5, 6, 7
The sides of a triangle are three consecutive natural numbers and its largest angle is twice the smallest one. Determine the sides of triangle. a) 3, 4, 5 b) 4, 5, 6 c) 4, 5, 7 d) 5, 6, 7
|
IIT 1991 |
|
|
737 |
A plane which is perpendicular to two planes 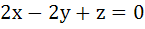 and and 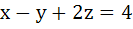 passes through (1, −2, 1). The distance of the plane from the point (1, 2, 2) is passes through (1, −2, 1). The distance of the plane from the point (1, 2, 2) is a) 0 b) 1 c) 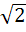 d) 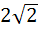
A plane which is perpendicular to two planes 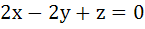 and and 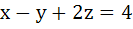 passes through (1, −2, 1). The distance of the plane from the point (1, 2, 2) is passes through (1, −2, 1). The distance of the plane from the point (1, 2, 2) is a) 0 b) 1 c) 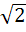 d) 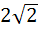
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
738 |
Two lines having direction ratios (1, 0, −1) and (1, −1, 0) are parallel to a plane passing through (1, 1, 1). This plane cuts the coordinate axes at A, B, C. Find the value of the tetrahedron OABC.
Two lines having direction ratios (1, 0, −1) and (1, −1, 0) are parallel to a plane passing through (1, 1, 1). This plane cuts the coordinate axes at A, B, C. Find the value of the tetrahedron OABC.
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
739 |
Let a, b, c be real numbers. Then the following system of equations in x, y, z 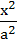 + +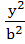 − − 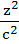 = 1 = 1 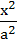 − −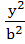 + + 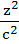 = 1 = 1 − 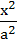 + +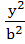 + + 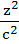 = 1 has = 1 has a) No solution b) Unique solution c) Infinitely many solutions d) Finitely many solutions
Let a, b, c be real numbers. Then the following system of equations in x, y, z 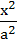 + +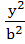 − − 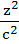 = 1 = 1 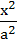 − −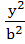 + + 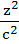 = 1 = 1 − 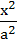 + +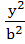 + + 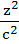 = 1 has = 1 has a) No solution b) Unique solution c) Infinitely many solutions d) Finitely many solutions
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
740 |
Consider the lines 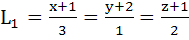 ; ;
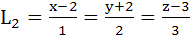
The distance of the point (1, 1, 1) from the plane through the point (−1, −2, −1) and whose normal is perpendicular to both lines L1 and L2 is
a) 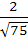 b) 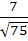 c) 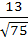 d) 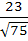
Consider the lines 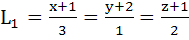 ; ;
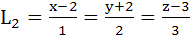
The distance of the point (1, 1, 1) from the plane through the point (−1, −2, −1) and whose normal is perpendicular to both lines L1 and L2 is
a) 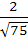 b) 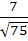 c) 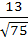 d) 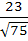
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
741 |
The domain of definition of the function 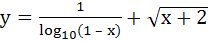 is is a) 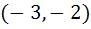 excluding excluding 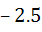 b) [0, 1] excluding 0.5 c) 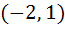 excluding x = 0 excluding x = 0 d) None of these
The domain of definition of the function 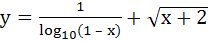 is is a) 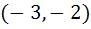 excluding excluding 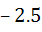 b) [0, 1] excluding 0.5 c) 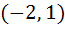 excluding x = 0 excluding x = 0 d) None of these
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
742 |
A curve 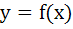 passes through passes through 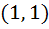 and the tangent at and the tangent at 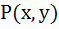 cuts the X-axis and Y-axis at A and B respectively such that cuts the X-axis and Y-axis at A and B respectively such that 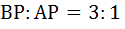 then then a) Equation of the curve is 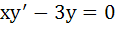 b) Normal at 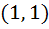 is is 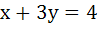 c) Curve passes through 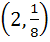 d) Equation of the curve is 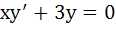
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
743 |
If M is a 3 x 3 matrix where det (M) = 1 and MMT = I, then prove that det (M – I) = 0.
If M is a 3 x 3 matrix where det (M) = 1 and MMT = I, then prove that det (M – I) = 0.
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
744 |
Let f(x) be defined for all x > 0 and be continuous. If f(x) satisfies 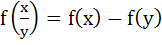 for all x, y and f(e)=1 then for all x, y and f(e)=1 then a) f(x) is bounded b) 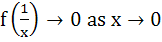 c) x f(x) → 1 as x → 0 d) f(x) = lnx
Let f(x) be defined for all x > 0 and be continuous. If f(x) satisfies 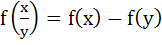 for all x, y and f(e)=1 then for all x, y and f(e)=1 then a) f(x) is bounded b) 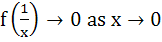 c) x f(x) → 1 as x → 0 d) f(x) = lnx
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
745 |
The number of values of x where the function 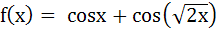 attains its maximum is attains its maximum is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) infinite
The number of values of x where the function 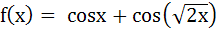 attains its maximum is attains its maximum is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) infinite
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
746 |
The domain of the definition of the function y given by the equation 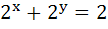 is is a) 0 < x < 1 b) 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 c) 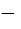 ∞ < x ≤ 0 ∞ < x ≤ 0 d) 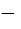 ∞ < x ≤ 1 ∞ < x ≤ 1
The domain of the definition of the function y given by the equation 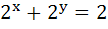 is is a) 0 < x < 1 b) 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 c) 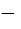 ∞ < x ≤ 0 ∞ < x ≤ 0 d) 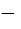 ∞ < x ≤ 1 ∞ < x ≤ 1
|
IIT 2000 |
|
|
747 |
Solution of the differential equation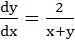 is is
Solution of the differential equation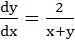 is is
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
748 |
Let A = 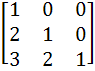 If U1, U2, U3 are column matrices satisfying
AU1 = 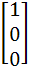 , AU2 = , AU2 = 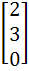 and AU3 = and AU3 = 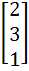 and U is a 3 x 3 matrix whose columns are U1, U2, U3 then the value of [ 3 2 0 ] U 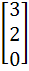 is is a) 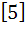 b) 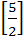 c) 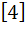 d) 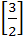
Let A = 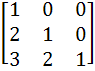 If U1, U2, U3 are column matrices satisfying
AU1 = 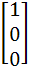 , AU2 = , AU2 = 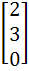 and AU3 = and AU3 = 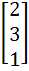 and U is a 3 x 3 matrix whose columns are U1, U2, U3 then the value of [ 3 2 0 ] U 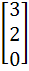 is is a) 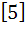 b) 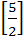 c) 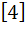 d) 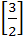
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
749 |
Let f(x) = 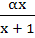 , x ≠ , x ≠ 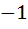 then for what value of α, f(f(x)) = x then for what value of α, f(f(x)) = x a) 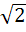 b) 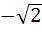 c) 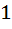 d) 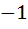
Let f(x) = 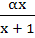 , x ≠ , x ≠ 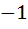 then for what value of α, f(f(x)) = x then for what value of α, f(f(x)) = x a) 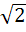 b) 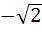 c) 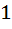 d) 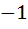
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
750 |
If 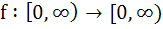 and and 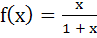 then f is then f is a) One-one and onto b) One-one but not onto c) Onto but not one-one d) Neither one-one nor onto
If 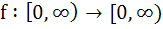 and and 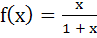 then f is then f is a) One-one and onto b) One-one but not onto c) Onto but not one-one d) Neither one-one nor onto
|
IIT 2003 |
|