|
701 |
The unit vector perpendicular to the plane determined by
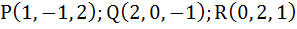 is. is.
The unit vector perpendicular to the plane determined by
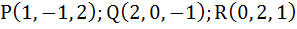 is. is.
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
702 |
Consider the lines 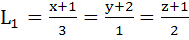 ; ;
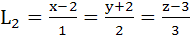
The shortest distance between L1 and L2 is
a) 0 b) 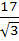 c) 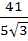 d) 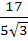
Consider the lines 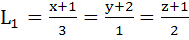 ; ;
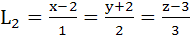
The shortest distance between L1 and L2 is
a) 0 b) 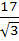 c) 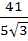 d) 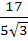
|
IIT 2008 |
|
|
703 |
Let ABCD is the base of parallelopiped T and Aʹ.BʹCʹDʹ be the upper face. The parallelopiped is compressed so that the vertex Aʹ shifts to Aʹʹ on a parallelepiped S. If the volume of the new parallelopiped is 90% of the parallelopiped T, prove that the locus of Aʹʹ is a plane.
Let ABCD is the base of parallelopiped T and Aʹ.BʹCʹDʹ be the upper face. The parallelopiped is compressed so that the vertex Aʹ shifts to Aʹʹ on a parallelepiped S. If the volume of the new parallelopiped is 90% of the parallelopiped T, prove that the locus of Aʹʹ is a plane.
|
IIT 2004 |
|
|
704 |
Show that 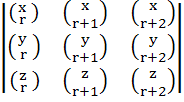 = = 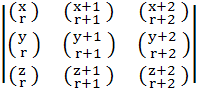
Show that 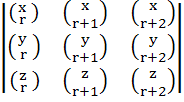 = = 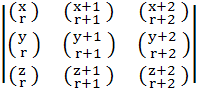
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
705 |
For all A, B, C, P, Q, R show that
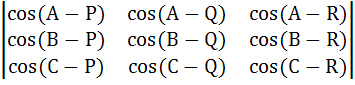 = 0 = 0
For all A, B, C, P, Q, R show that
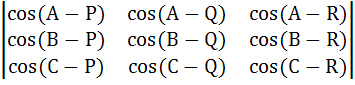 = 0 = 0
|
IIT 1996 |
|
|
706 |
Let f(x) = |x – 1|, then a) 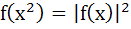 b) 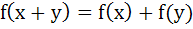 c) 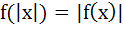 d) None of these
Let f(x) = |x – 1|, then a) 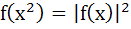 b) 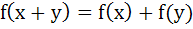 c) 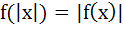 d) None of these
|
IIT 1983 |
|
|
707 |
The differential equation representing the family of curves 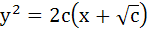 where c is a positive parameter, is of where c is a positive parameter, is of a) Order 1 b) Order 2 c) Degree 3 d) Degree 4
The differential equation representing the family of curves 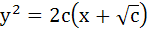 where c is a positive parameter, is of where c is a positive parameter, is of a) Order 1 b) Order 2 c) Degree 3 d) Degree 4
|
IIT 1999 |
|
|
708 |
Let a, b, c be real numbers with a2 + b2 + c2 = 1. Show that the equation represents a straight line
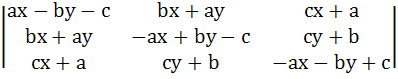 = 0 = 0
Let a, b, c be real numbers with a2 + b2 + c2 = 1. Show that the equation represents a straight line
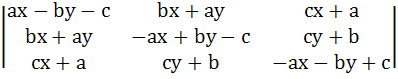 = 0 = 0
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
709 |
Let 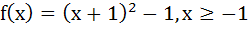 , then the set , then the set 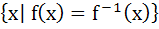 is is a) 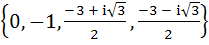 b) 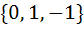 c) 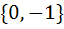 d) ϕ
Let 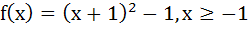 , then the set , then the set 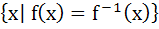 is is a) 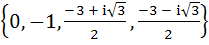 b) 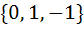 c) 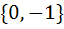 d) ϕ
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
710 |
A normal is drawn at a point 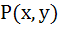 of a curve meeting X-axis at Q. If PQ is of constant length k, then show that the differential equation of the curve is of a curve meeting X-axis at Q. If PQ is of constant length k, then show that the differential equation of the curve is 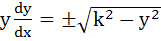
A normal is drawn at a point 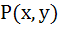 of a curve meeting X-axis at Q. If PQ is of constant length k, then show that the differential equation of the curve is of a curve meeting X-axis at Q. If PQ is of constant length k, then show that the differential equation of the curve is 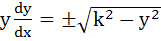
|
IIT 1994 |
|
|
711 |
If f(x) = 3x – 5 then 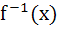 a) is given by 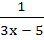 b) is given by 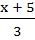 c) does not exist because f is not one-one d) does not exist because f is not onto
If f(x) = 3x – 5 then 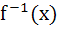 a) is given by 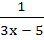 b) is given by 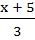 c) does not exist because f is not one-one d) does not exist because f is not onto
|
IIT 1998 |
|
|
712 |
Find the integral solutions of the following system of inequality
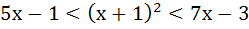 a) x = 1 b) x = 2 c) x = 3 d) x = 4
Find the integral solutions of the following system of inequality
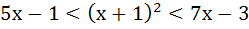 a) x = 1 b) x = 2 c) x = 3 d) x = 4
|
IIT 1979 |
|
|
713 |
Area bounded by 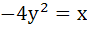 and and 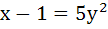
Area bounded by 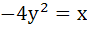 and and 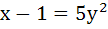
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
714 |
mn squares of equal size are arranged to form a rectangle of dimension m by n, where m and n are natural numbers. Two squares will be called neighbours if they have exactly one common side. A natural number is written in each square such that the number written in any square is the arithmetic mean of the numbers written in the neighbouring squares. Show that this is possible only if all the numbers used are equal.
mn squares of equal size are arranged to form a rectangle of dimension m by n, where m and n are natural numbers. Two squares will be called neighbours if they have exactly one common side. A natural number is written in each square such that the number written in any square is the arithmetic mean of the numbers written in the neighbouring squares. Show that this is possible only if all the numbers used are equal.
|
IIT 1982 |
|
|
715 |
Let A = 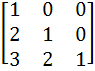
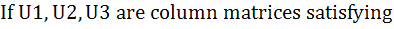
AU1 = 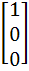 , AU2 = , AU2 = 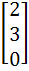 and AU3 = and AU3 = 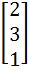
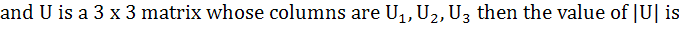 a) 3 b) −3 c)  d) 2
Let A = 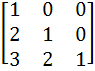
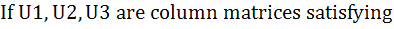
AU1 = 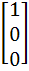 , AU2 = , AU2 = 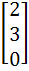 and AU3 = and AU3 = 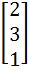
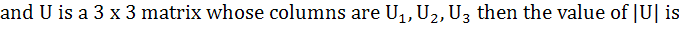 a) 3 b) −3 c)  d) 2
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
716 |
The domain of definition of 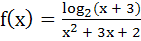 is is a) 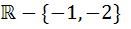 b) 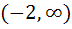 c) 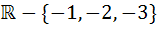 d) 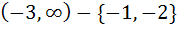
The domain of definition of 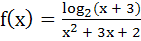 is is a) 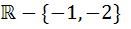 b) 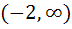 c) 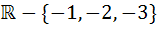 d) 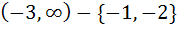
|
IIT 2001 |
|
|
717 |
Let f : ℝ → ℝ be defined by f(x) = 2x + sinx for all x 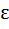 ℝ. Then f is ℝ. Then f is a) One to one and onto b) One to one but not onto c) Onto but not one to one d) Neither one to one nor onto
Let f : ℝ → ℝ be defined by f(x) = 2x + sinx for all x 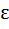 ℝ. Then f is ℝ. Then f is a) One to one and onto b) One to one but not onto c) Onto but not one to one d) Neither one to one nor onto
|
IIT 2002 |
|
|
718 |
Range of 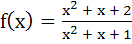 ; x ; x 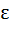 ℝ is ℝ is a) (1, ∞) b) 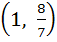 c) 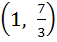 d) 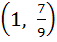
Range of 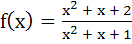 ; x ; x 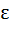 ℝ is ℝ is a) (1, ∞) b) 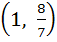 c) 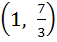 d) 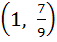
|
IIT 2003 |
|
|
719 |
Let a, b, c, ε R and α, β be roots of 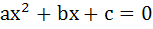 such that such that 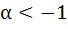 and and 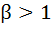 then show that then show that 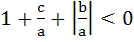 . .
|
IIT 1995 |
|
|
720 |
If 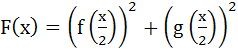 where where 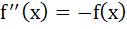
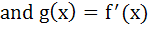 . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to a) 5 b) 10 c) 0 d) 15
If 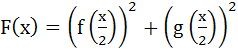 where where 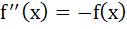
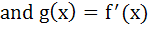 . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to . Given F(5) = 5, then f(10) is equal to a) 5 b) 10 c) 0 d) 15
|
IIT 2006 |
|
|
721 |
Subjective problems
Let 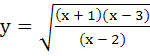 . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. a) [− 1, 2) b) [3, ∞) c) [− 1, 2) ∪ [3, ∞) d) None of the above
Subjective problems
Let 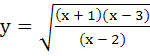 . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. . Find all real values of x for which y takes real values. a) [− 1, 2) b) [3, ∞) c) [− 1, 2) ∪ [3, ∞) d) None of the above
|
IIT 1980 |
|
|
722 |
Let R be the set of real numbers and f : R → R be such that for all x and y in R, 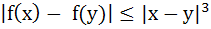 . Prove that f(x) is constant. . Prove that f(x) is constant.
Let R be the set of real numbers and f : R → R be such that for all x and y in R, 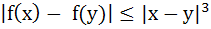 . Prove that f(x) is constant. . Prove that f(x) is constant.
|
IIT 1988 |
|
|
723 |
If f1(x) and f2(x) are defined by domains D1 and D2 respectively then f1(x) + f2(x) is defined as on D1 ⋂ D2 a) True b) False
If f1(x) and f2(x) are defined by domains D1 and D2 respectively then f1(x) + f2(x) is defined as on D1 ⋂ D2 a) True b) False
|
IIT 1988 |
|
|
724 |
If 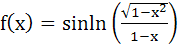 then the domain of f(x) is then the domain of f(x) is
If 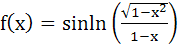 then the domain of f(x) is then the domain of f(x) is
|
IIT 1985 |
|
|
725 |
The real numbers x1, x2, x3 satisfying the equation x3 – x2 + βx + γ = 0 are in Arithmetic Progression. Find the interval in which β and γ lie.
The real numbers x1, x2, x3 satisfying the equation x3 – x2 + βx + γ = 0 are in Arithmetic Progression. Find the interval in which β and γ lie.
|
IIT 1996 |
|