|
651 |
The sides of a triangle are in the ratio 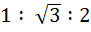 then the angles of the triangle are in the ratio then the angles of the triangle are in the ratio a) 1 : 3 : 5 b) 2 : 3 : 4 c) 3 : 2 : 1 d) 1 : 2 : 3
The sides of a triangle are in the ratio 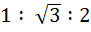 then the angles of the triangle are in the ratio then the angles of the triangle are in the ratio a) 1 : 3 : 5 b) 2 : 3 : 4 c) 3 : 2 : 1 d) 1 : 2 : 3
|
IIT 2004 |
02:52 min
|
|
652 |
Subjective problem Let y = 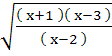 Find all real values of x for which y takes real values a) for x ≥ 3, y is real b) for 2 < x < 3, y is imaginary c) for – 1 ≤ x < 2, y is real d) for x < – 1, y is imaginary
Subjective problem Let y = 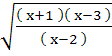 Find all real values of x for which y takes real values a) for x ≥ 3, y is real b) for 2 < x < 3, y is imaginary c) for – 1 ≤ x < 2, y is real d) for x < – 1, y is imaginary
|
IIT 1990 |
03:41 min
|
|
653 |
If f(x) is differentiable and strictly increasing function then the value of 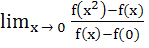 is is a) 1 b) 0 c) – 1 d) 2
If f(x) is differentiable and strictly increasing function then the value of 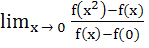 is is a) 1 b) 0 c) – 1 d) 2
|
IIT 2004 |
03:20 min
|
|
654 |
Let R be the set of real numbers and f : R 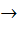 R such that for all x, y ε R, |f (x) – f (y)| ≤ | x – y |2. Then R such that for all x, y ε R, |f (x) – f (y)| ≤ | x – y |2. Then a) 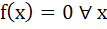 b) f (x) is a constant c) none of the above
Let R be the set of real numbers and f : R 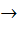 R such that for all x, y ε R, |f (x) – f (y)| ≤ | x – y |2. Then R such that for all x, y ε R, |f (x) – f (y)| ≤ | x – y |2. Then a) 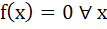 b) f (x) is a constant c) none of the above
|
IIT 1988 |
02:07 min
|
|
655 |
If 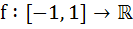 and and 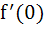 = = and f(0) = 0. Find the value of and f(0) = 0. Find the value of  . Given that 0 < . Given that 0 <  < <  a)  b) 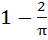 c) 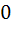 d) 1
|
IIT 2004 |
03:29 min
|
|
656 |
The area bounded by the curves y = (x + 1)2 y = (x – 1)2 and the line 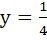 is is a)  b)  c)  d) 
The area bounded by the curves y = (x + 1)2 y = (x – 1)2 and the line 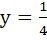 is is a)  b)  c)  d) 
|
IIT 2005 |
06:30 min
|
|
657 |
If 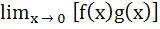 exists then both the limits exists then both the limits 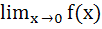 and and 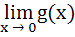 exist exist a) True b) False
If 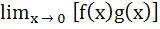 exists then both the limits exists then both the limits 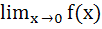 and and 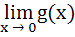 exist exist a) True b) False
|
IIT 1981 |
03:33 min
|
|
658 |
Total number of ways in which six ‘+’ and four ‘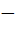 ’ signs can be arranged in a line so that no two ‘ ’ signs can be arranged in a line so that no two ‘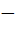 ’signs occur together is ….. ’signs occur together is …..
Total number of ways in which six ‘+’ and four ‘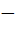 ’ signs can be arranged in a line so that no two ‘ ’ signs can be arranged in a line so that no two ‘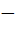 ’signs occur together is ….. ’signs occur together is …..
|
IIT 1988 |
01:55 min
|
|
659 |
Multiple choice The function 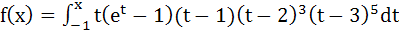 has local minimum at x = a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
Multiple choice The function 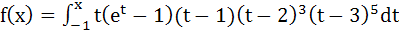 has local minimum at x = a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 1999 |
07:03 min
|
|
660 |
Let 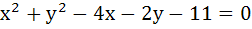 be a circle. A pair of tangents from (4, 5) and a pair of radii form a quadrilateral of area . . . . . be a circle. A pair of tangents from (4, 5) and a pair of radii form a quadrilateral of area . . . . .
Let 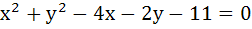 be a circle. A pair of tangents from (4, 5) and a pair of radii form a quadrilateral of area . . . . . be a circle. A pair of tangents from (4, 5) and a pair of radii form a quadrilateral of area . . . . .
|
IIT 1985 |
03:15 min
|
|
661 |
Identify a discontinuous function y = f(x) satisfying 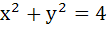
Identify a discontinuous function y = f(x) satisfying 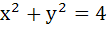
|
IIT 1982 |
02:05 min
|
|
662 |
If 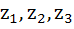 are complex numbers such that are complex numbers such that 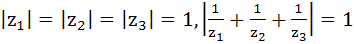 then then 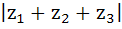 is is a) Equal to 1 b) Less than 1 c) Greater than 3 d) Equal to 3
If 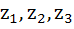 are complex numbers such that are complex numbers such that 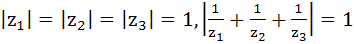 then then 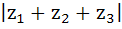 is is a) Equal to 1 b) Less than 1 c) Greater than 3 d) Equal to 3
|
IIT 2000 |
02:36 min
|
|
663 |
A polygon of nine sides, each of length 2, is inscribed in a circle. The radius of the circle is . . . . .
A polygon of nine sides, each of length 2, is inscribed in a circle. The radius of the circle is . . . . .
|
IIT 1987 |
01:45 min
|
|
664 |
Fill in the blank
If f (x) = sin ln 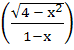 then the domain of f (x) is …………. then the domain of f (x) is …………. a) (−2, −1) b) (−2, 1) c) (0, 1) d) (1, ∞)
Fill in the blank
If f (x) = sin ln 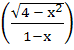 then the domain of f (x) is …………. then the domain of f (x) is …………. a) (−2, −1) b) (−2, 1) c) (0, 1) d) (1, ∞)
|
IIT 1985 |
01:25 min
|
|
665 |
If f(9) = 9, 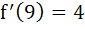 then then 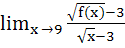 equals equals a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
If f(9) = 9, 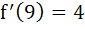 then then 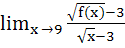 equals equals a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
|
IIT 1988 |
02:24 min
|
|
666 |
A circle passes through the point of intersection of the coordinate axes with the lines 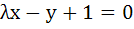 and x and x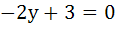 , then λ = . . . . . , then λ = . . . . .
A circle passes through the point of intersection of the coordinate axes with the lines 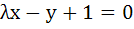 and x and x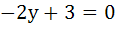 , then λ = . . . . . , then λ = . . . . .
|
IIT 1991 |
04:24 min
|
|
667 |
If x, y, z are real and distinct then
8u = 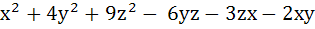
is always a) Non–negative b) Non–positive c) Zero d) None of these
If x, y, z are real and distinct then
8u = 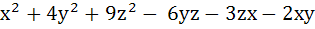
is always a) Non–negative b) Non–positive c) Zero d) None of these
|
IIT 1979 |
02:14 min
|
|
668 |
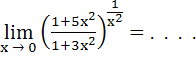
a) 0 b) 1 c) e d) e2
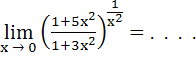
a) 0 b) 1 c) e d) e2
|
IIT 1996 |
01:19 min
|
|
669 |
Show that 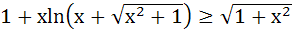 for all x ≥ 0. for all x ≥ 0.
Show that 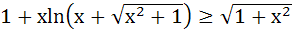 for all x ≥ 0. for all x ≥ 0.
|
IIT 1983 |
04:21 min
|
|
670 |
For each natural number k, let Ck denote the circle with radius k centimeters and center at the origin. On the circle Ck, a particle moves k centimeters in the counterclockwise direction. After completing its motion on Ck the particle moves to Ck + 1 in the radial direction. The motion of the particle continues in this manner. The particle starts at ( 1, 0 ). If the particle crosses the positive direction of the X–axis for the first time on the circle Cn then n = . . . . .
For each natural number k, let Ck denote the circle with radius k centimeters and center at the origin. On the circle Ck, a particle moves k centimeters in the counterclockwise direction. After completing its motion on Ck the particle moves to Ck + 1 in the radial direction. The motion of the particle continues in this manner. The particle starts at ( 1, 0 ). If the particle crosses the positive direction of the X–axis for the first time on the circle Cn then n = . . . . .
|
IIT 1997 |
04:26 min
|
|
671 |
If 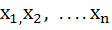 are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then a) 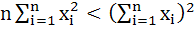 b) 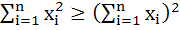 c) 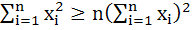 d) none of these
If 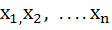 are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then a) 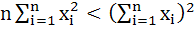 b) 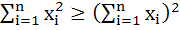 c) 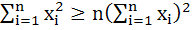 d) none of these
|
IIT 1982 |
01:04 min
|
|
672 |
If |z| = 1 and z ≠ ±1 then the value of 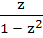 lie on lie on a) a line not passing through the origin b) 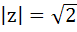 c) the X – axis d) the Y axis
If |z| = 1 and z ≠ ±1 then the value of 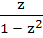 lie on lie on a) a line not passing through the origin b) 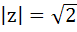 c) the X – axis d) the Y axis
|
IIT 2007 |
02:46 min
|
|
673 |
Let a + b + c = 0, then the quadratic equation 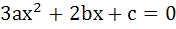 has has a) at least one root in (0, 1) b) one root in (2, 3) and the other in 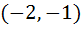 c) imaginary roots d) none of these
Let a + b + c = 0, then the quadratic equation 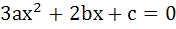 has has a) at least one root in (0, 1) b) one root in (2, 3) and the other in 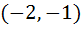 c) imaginary roots d) none of these
|
IIT 1983 |
02:32 min
|
|
674 |
If x = a + b, y = aα + bβ, z = aβ + bα where α, β are cube roots of unity show that  . .
If x = a + b, y = aα + bβ, z = aβ + bα where α, β are cube roots of unity show that  . .
|
IIT 1979 |
02:39 min
|
|
675 |
If 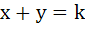 is a normal to is a normal to 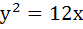 then k is then k is a) 3 b) 9 c) – 9 d) – 3
If 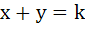 is a normal to is a normal to 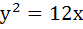 then k is then k is a) 3 b) 9 c) – 9 d) – 3
|
IIT 2000 |
02:47 min
|