|
551 |
Let f(x) = ∫ex (x – 1) (x − 2) dx, then f(x) decreases in the interval a) (−∞, −2) b) (−2, −1) c) (1, 2) d) (2, ∞)
Let f(x) = ∫ex (x – 1) (x − 2) dx, then f(x) decreases in the interval a) (−∞, −2) b) (−2, −1) c) (1, 2) d) (2, ∞)
|
IIT 2000 |
00:47 min
|
|
552 |
The harmonic means of the roots of the equation
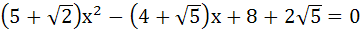 is is a) 2 b) 4 c) 6 d) 8
The harmonic means of the roots of the equation
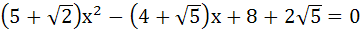 is is a) 2 b) 4 c) 6 d) 8
|
IIT 1999 |
01:43 min
|
|
553 |
Find the integral of 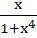 a) tan−1x2 + c b) 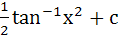 c) 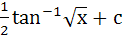 d) 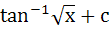
Find the integral of 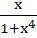 a) tan−1x2 + c b) 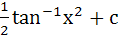 c) 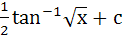 d) 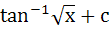
|
IIT 1978 |
00:32 min
|
|
554 |
Consider the two curves 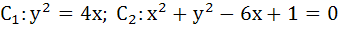 then then a) 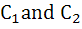 touch each other at only one point touch each other at only one point b) 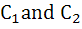 touch each other exactly at two points touch each other exactly at two points c) 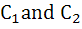 intersect(but not touch) at exactly two points intersect(but not touch) at exactly two points d) 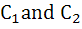 neither intersect nor touch each other neither intersect nor touch each other
Consider the two curves 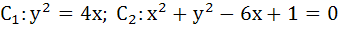 then then a) 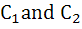 touch each other at only one point touch each other at only one point b) 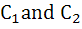 touch each other exactly at two points touch each other exactly at two points c) 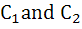 intersect(but not touch) at exactly two points intersect(but not touch) at exactly two points d) 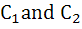 neither intersect nor touch each other neither intersect nor touch each other
|
IIT 2008 |
04:50 min
|
|
555 |
Suppose p(x) = 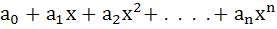
If 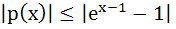 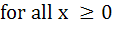 prove that prove that
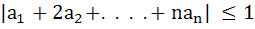
|
IIT 2000 |
05:19 min
|
|
556 |
The sum of the first 2n terms of the Arithmetic Progression 2, 5, 8, . . . . is equal to the sum of the first n terms of the Arithmetic Progression 57, 59, 61, . . . . then n equals a) 100 b) 12 c) 11 d) 13
The sum of the first 2n terms of the Arithmetic Progression 2, 5, 8, . . . . is equal to the sum of the first n terms of the Arithmetic Progression 57, 59, 61, . . . . then n equals a) 100 b) 12 c) 11 d) 13
|
IIT 2001 |
01:42 min
|
|
557 |
Show that 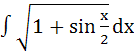 = = 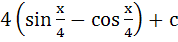
Show that 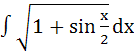 = = 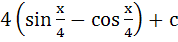
|
IIT 1980 |
01:51 min
|
|
558 |
Seven white balls and three black balls are randomly placed in a row. The possibility that no two black balls are placed adjacently equals a)  b) 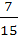 c) 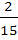 d) 
Seven white balls and three black balls are randomly placed in a row. The possibility that no two black balls are placed adjacently equals a)  b) 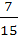 c) 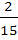 d) 
|
IIT 1998 |
03:25 min
|
|
559 |
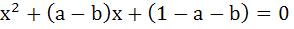 where a, b ε R then find the value of a for which equation has unequal roots for all values of b. where a, b ε R then find the value of a for which equation has unequal roots for all values of b.
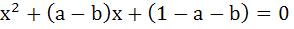 where a, b ε R then find the value of a for which equation has unequal roots for all values of b. where a, b ε R then find the value of a for which equation has unequal roots for all values of b.
|
IIT 2003 |
02:36 min
|
|
560 |
If α, β are roots of 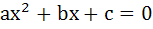 and and 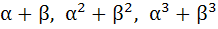 are in Geometric Progression and are in Geometric Progression and 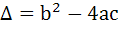 then then a) 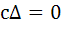 b) 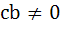 c) 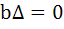 d) 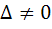
If α, β are roots of 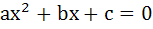 and and 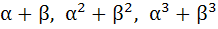 are in Geometric Progression and are in Geometric Progression and 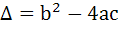 then then a) 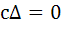 b) 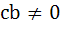 c) 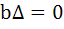 d) 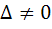
|
IIT 2005 |
02:38 min
|
|
561 |
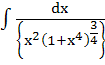 = =
a) 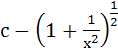 b) 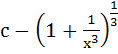 c) 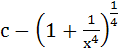 d) 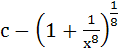
|
IIT 1984 |
02:26 min
|
|
562 |
A fair coin is tossed repeatedly. If the tail appears on first four times, then the probability of the head appearing on in the fifth toss equals a)  b) 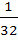 c) 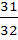 d) 
A fair coin is tossed repeatedly. If the tail appears on first four times, then the probability of the head appearing on in the fifth toss equals a)  b) 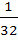 c) 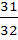 d) 
|
IIT 1998 |
00:47 min
|
|
563 |
If x and y are positive real numbers and m and n are any positive integers then 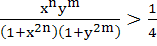
a) True b) False
If x and y are positive real numbers and m and n are any positive integers then 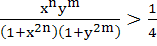
a) True b) False
|
IIT 1989 |
02:49 min
|
|
564 |
If x, y, z are in Harmonic Progression then show that
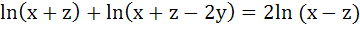
If x, y, z are in Harmonic Progression then show that
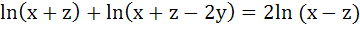
|
IIT 1978 |
02:51 min
|
|
565 |
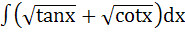 = =
a) 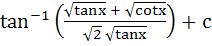 b) 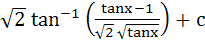 c) 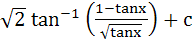 d) 
|
IIT 1989 |
04:05 min
|
|
566 |
The points with position vectors 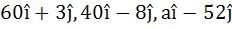 are collinear if are collinear if a) 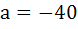 b) 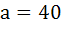 c) 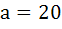 d) 
The points with position vectors 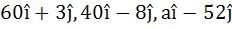 are collinear if are collinear if a) 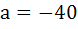 b) 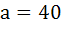 c) 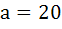 d) 
|
IIT 1983 |
03:14 min
|
|
567 |
If P (B) = 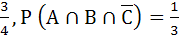 and and 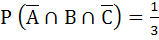 then then P (B ∩ C) is a) 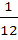 b)  c) 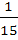 d) 
If P (B) = 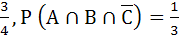 and and 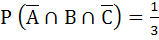 then then P (B ∩ C) is a) 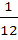 b)  c) 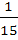 d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
02:56 min
|
|
568 |
Fill in the blank The solution of the equation
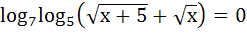 is ………….. is …………..
Fill in the blank The solution of the equation
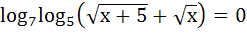 is ………….. is …………..
|
IIT 1986 |
02:04 min
|
|
569 |
If 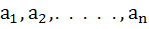 are in Arithmetic Progression where are in Arithmetic Progression where 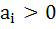 for all i, show that for all i, show that
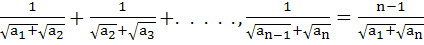
|
IIT 1982 |
04:29 min
|
|
570 |
Show that
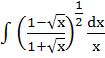 = = 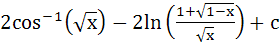
Show that
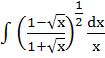 = = 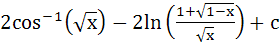
|
IIT 1997 |
04:06 min
|
|
571 |
Let a, b, c be three non co–planar vectors and p, q, r are vectors defined by the relations
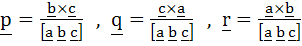
Then the value of the expression
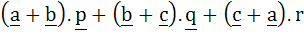 is equal to is equal to a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
Let a, b, c be three non co–planar vectors and p, q, r are vectors defined by the relations
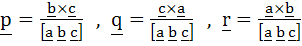
Then the value of the expression
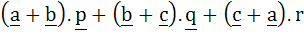 is equal to is equal to a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 1988 |
05:35 min
|
|
572 |
Fill in the blank If x < 0, y < 0, 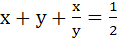 and and 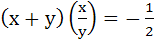 then x then x  ……….. and y ……….. and y  ……….. ………..
|
IIT 1990 |
04:06 min
|
|
573 |
The sum of the squares of three distinct real numbers which are in Geometric Progression is 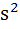 . If their sum is . If their sum is 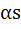 , show that , show that
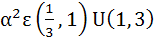
|
IIT 1986 |
06:02 min
|
|
574 |
Show that  = = 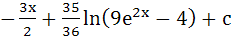
Show that  = = 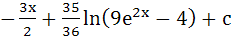
|
IIT 1990 |
07:54 min
|
|
575 |
Let 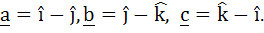 If d is a unit vector such that If d is a unit vector such that 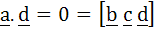 then d equals then d equals a) 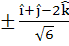 b) 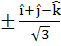 c) 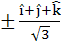 d) 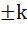
Let 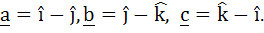 If d is a unit vector such that If d is a unit vector such that 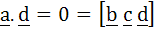 then d equals then d equals a) 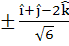 b) 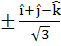 c) 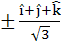 d) 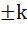
|
IIT 1995 |
04:16 min
|