|
501 |
The largest interval for which 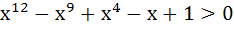 is is a) 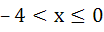 b) 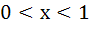 c) 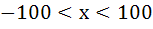 d) 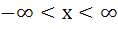
The largest interval for which 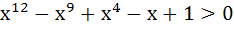 is is a) 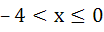 b) 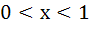 c) 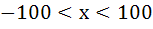 d) 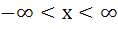
|
IIT 1982 |
04:35 min
|
|
502 |
Find the tangents to the curve
y = cos(x + y), − 2π ≤ x ≤ 2π
that are parallel to the line x + 2y = 0
Find the tangents to the curve
y = cos(x + y), − 2π ≤ x ≤ 2π
that are parallel to the line x + 2y = 0
|
IIT 1985 |
07:32 min
|
|
503 |
The equation 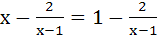 has has a) No root b) One root c) Two equal roots d) Infinitely many roots
The equation 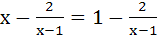 has has a) No root b) One root c) Two equal roots d) Infinitely many roots
|
IIT 1984 |
01:04 min
|
|
504 |
If w ( ≠1 ) is cube root of unity, then
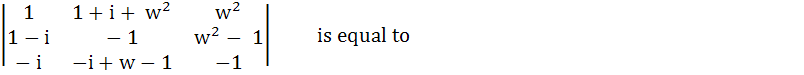 a) 0 b) 1 c) - 1 d) w
If w ( ≠1 ) is cube root of unity, then
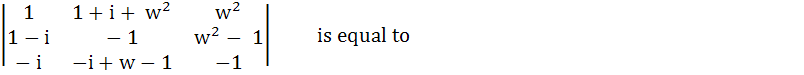 a) 0 b) 1 c) - 1 d) w
|
IIT 1995 |
01:46 min
|
|
505 |
Let a, b, c be real numbers, a ≠ 0. If α is a root of 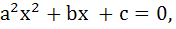 β is a root of β is a root of 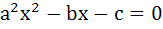 and 0 < α < β then the equation and 0 < α < β then the equation 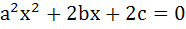 has a root γ that always satisfies has a root γ that always satisfies a) γ = 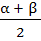 b) γ = 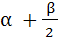 c) γ = α d) α < γ < β
Let a, b, c be real numbers, a ≠ 0. If α is a root of 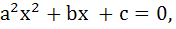 β is a root of β is a root of 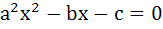 and 0 < α < β then the equation and 0 < α < β then the equation 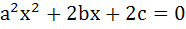 has a root γ that always satisfies has a root γ that always satisfies a) γ = 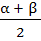 b) γ = 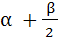 c) γ = α d) α < γ < β
|
IIT 1989 |
03:43 min
|
|
506 |
The determinant
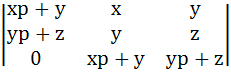 = 0 if = 0 if a) x, y, z are in arithmetic progression b) x, y, z are in geometric progression c) x, y, z are in harmonic progression d) xy, yz, zx are in arithmetic progression
The determinant
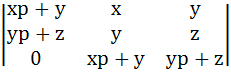 = 0 if = 0 if a) x, y, z are in arithmetic progression b) x, y, z are in geometric progression c) x, y, z are in harmonic progression d) xy, yz, zx are in arithmetic progression
|
IIT 1997 |
02:44 min
|
|
507 |
If 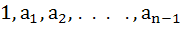 are the n roots of unity then show that are the n roots of unity then show that 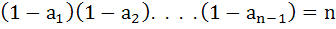 . .
If 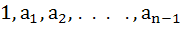 are the n roots of unity then show that are the n roots of unity then show that 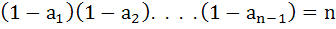 . .
|
IIT 1984 |
02:49 min
|
|
508 |
The equation of the common tangent to the curves 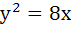 and and 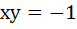 is is a) 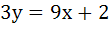 b) 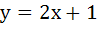 c) 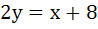 d) 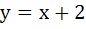
The equation of the common tangent to the curves 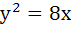 and and 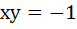 is is a) 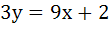 b) 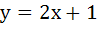 c) 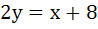 d) 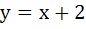
|
IIT 2002 |
03:51 min
|
|
509 |
If p, q, r are positive and are in arithmetic progression the roots of the quadratic 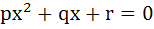 are all real for are all real for a) 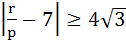 b) 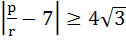 c) 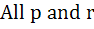 d) 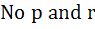
If p, q, r are positive and are in arithmetic progression the roots of the quadratic 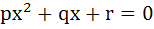 are all real for are all real for a) 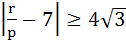 b) 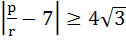 c)  d) 
|
IIT 1994 |
02:34 min
|
|
510 |
The number of distinct roots of
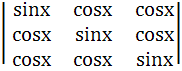 = 0 = 0
in the interval 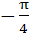 ≤ x ≤ ≤ x ≤ 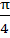 is is a) 0 b) 2 c) 1 d) 3
The number of distinct roots of
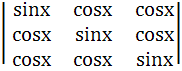 = 0 = 0
in the interval 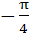 ≤ x ≤ ≤ x ≤ 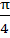 is is a) 0 b) 2 c) 1 d) 3
|
IIT 2001 |
04:03 min
|
|
511 |
(Multiple choice) The equation of common tangent to the parabolas 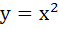 and and 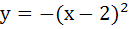 is/are is/are a) 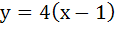 b) 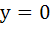 c) 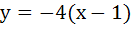 d) 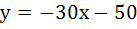
(Multiple choice) The equation of common tangent to the parabolas 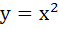 and and 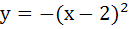 is/are is/are a) 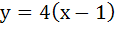 b) 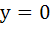 c) 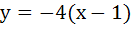 d) 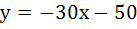
|
IIT 2006 |
04:15 min
|
|
512 |
If α and β (α < β) are roots of the equation 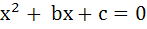 where c < 0 < b then where c < 0 < b then a) 0 < α < β b) α < 0 < β < | α | c) α < β < 0 d) α < 0 < | α | < β
If α and β (α < β) are roots of the equation 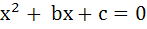 where c < 0 < b then where c < 0 < b then a) 0 < α < β b) α < 0 < β < | α | c) α < β < 0 d) α < 0 < | α | < β
|
IIT 2000 |
02:20 min
|
|
513 |
If A = 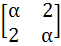 and | A3| = 125 then the value of α is and | A3| = 125 then the value of α is a) ± 1 b) ±2 c) ± 3 d) ± 5
If A = 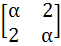 and | A3| = 125 then the value of α is and | A3| = 125 then the value of α is a) ± 1 b) ±2 c) ± 3 d) ± 5
|
IIT 2004 |
00:46 min
|
|
514 |
Let 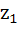 and and 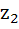 be the roots of the equation be the roots of the equation 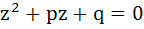 where the coefficients p and q may be complex numbers. Let A and B represent where the coefficients p and q may be complex numbers. Let A and B represent 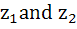 in the complex plane. If in the complex plane. If 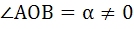 and OB = OA where O is the origin, prove that and OB = OA where O is the origin, prove that 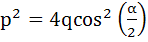 . .
|
IIT 1997 |
04:53 min
|
|
515 |
Three normals are drawn from the point (c, 0) to the curve 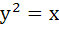 . Show that c must be greater than . Show that c must be greater than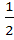 . One normal is always the X-axis. Find c for which the other two normals are perpendicular. . One normal is always the X-axis. Find c for which the other two normals are perpendicular.
Three normals are drawn from the point (c, 0) to the curve 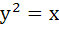 . Show that c must be greater than . Show that c must be greater than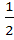 . One normal is always the X-axis. Find c for which the other two normals are perpendicular. . One normal is always the X-axis. Find c for which the other two normals are perpendicular.
|
IIT 1991 |
05:44 min
|
|
516 |
For the equation 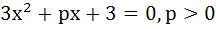 if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to a)  b) 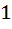 c) 3 d) 
For the equation 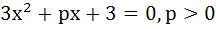 if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to if one of the roots is square of the other then p is equal to a)  b) 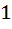 c) 3 d) 
|
IIT 2000 |
03:13 min
|
|
517 |
The number of solutions of 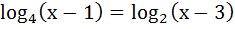 is is a) 3 b) 1 c) 2 d) 0
The number of solutions of 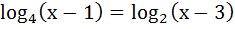 is is a) 3 b) 1 c) 2 d) 0
|
IIT 2001 |
02:44 min
|
|
518 |
If a, b, c be positive and not all equal, show that the value of the determinant 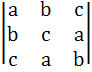 is negative. is negative.
If a, b, c be positive and not all equal, show that the value of the determinant 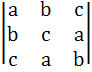 is negative. is negative.
|
IIT 1981 |
04:21 min
|
|
519 |
Match the following Normals are drawn at the points P, Q and R lying on the parabola 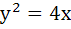 which intersect at (3, 0) then which intersect at (3, 0) then | Column 1 | Column 2 | | i) Area of ΔPQR | A. 2 | | ii) Radius of circumcircle of ΔPQR | B.  | | iii) Centroid of ΔPQR | C. 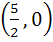 | | iv) Circumcentre of ΔPQR | D. 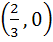 |
Match the following Normals are drawn at the points P, Q and R lying on the parabola 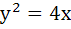 which intersect at (3, 0) then which intersect at (3, 0) then | Column 1 | Column 2 | | i) Area of ΔPQR | A. 2 | | ii) Radius of circumcircle of ΔPQR | B.  | | iii) Centroid of ΔPQR | C. 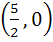 | | iv) Circumcentre of ΔPQR | D. 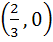 |
|
IIT 2006 |
07:33 min
|
|
520 |
If 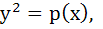 a polynomial of degree 3, then a polynomial of degree 3, then 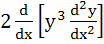 equals equals a) 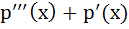 b) 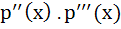 c) 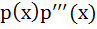 d) a constant
If 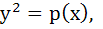 a polynomial of degree 3, then a polynomial of degree 3, then 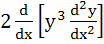 equals equals a) 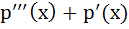 b) 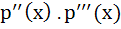 c) 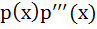 d) a constant
|
IIT 1988 |
05:23 min
|
|
521 |
If 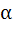 ε ε 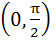 then then 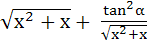 is always greater than or equal to is always greater than or equal to a) 2 tan 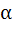 b) 1 c) 2 d) 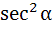
If 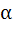 ε ε 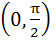 then then 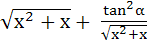 is always greater than or equal to is always greater than or equal to a) 2 tan 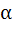 b) 1 c) 2 d) 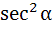
|
IIT 2003 |
02:05 min
|
|
522 |
If f (x) = 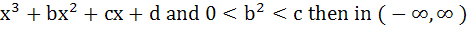 a) f (x) is a strictly increasing function b) f (x) has a local maxima c) f (x) is a strictly decreasing function d) f (x) is bounded
If f (x) = 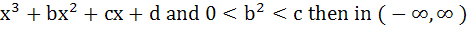 a) f (x) is a strictly increasing function b) f (x) has a local maxima c) f (x) is a strictly decreasing function d) f (x) is bounded
|
IIT 2004 |
02:07 min
|
|
523 |
Let Δa = 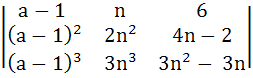
Then show that 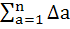 = c, a constant. = c, a constant.
Let Δa = 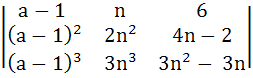
Then show that 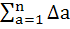 = c, a constant. = c, a constant.
|
IIT 1989 |
05:34 min
|
|
524 |
For any two complex numbers 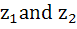 and any real numbers and any real numbers 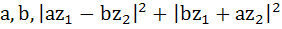 is equal to . . . . is equal to . . . . a) 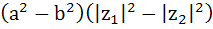 b)  c) 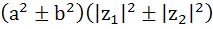 d) 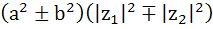
For any two complex numbers 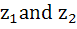 and any real numbers and any real numbers 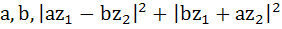 is equal to . . . . is equal to . . . . a) 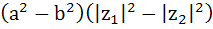 b)  c) 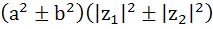 d) 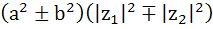
|
IIT 1988 |
02:43 min
|
|
525 |
The locus of a variable point whose distance from 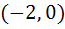 is is  times its distance from the line times its distance from the line 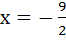 is is a) Ellipse b) Parabola c) Hyperbola d) None of these
The locus of a variable point whose distance from 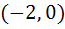 is is  times its distance from the line times its distance from the line 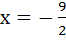 is is a) Ellipse b) Parabola c) Hyperbola d) None of these
|
IIT 1994 |
02:40 min
|