|
376 |
The expression 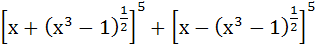 is a polynomial of degree is a polynomial of degree a) 5 b) 6 c) 7 d) 8
The expression 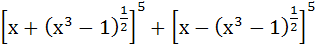 is a polynomial of degree is a polynomial of degree a) 5 b) 6 c) 7 d) 8
|
IIT 1992 |
03:38 min
|
|
377 |
If f(x) = 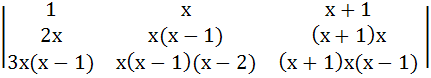
then f(100) equals a) 0 b) 1 c) 100 d) −100
If f(x) = 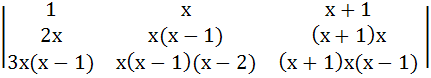
then f(100) equals a) 0 b) 1 c) 100 d) −100
|
IIT 1999 |
02:18 min
|
|
378 |
Show that the area of the triangle on the argand diagram formed by the complex numbers z, iz, z + iz is 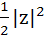 . .
Show that the area of the triangle on the argand diagram formed by the complex numbers z, iz, z + iz is 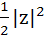 . .
|
IIT 1986 |
03:10 min
|
|
379 |
The angle between the tangents drawn from the point (1, 4) to the parabola 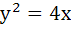 is is a)  b) 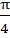 c)  d) 
The angle between the tangents drawn from the point (1, 4) to the parabola 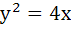 is is a)  b) 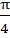 c)  d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
02:56 min
|
|
380 |
The equation 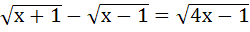 has has a) No solution b) One solution c) Two solutions d) More than two solutions
The equation 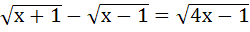 has has a) No solution b) One solution c) Two solutions d) More than two solutions
|
IIT 1997 |
03:20 min
|
|
381 |
If the system of equations x + ay = 0 az + y = 0 ax + z = 0 has infinite solutions then the value of a is a) −1 b) 1 c) 0 d) No real values
If the system of equations x + ay = 0 az + y = 0 ax + z = 0 has infinite solutions then the value of a is a) −1 b) 1 c) 0 d) No real values
|
IIT 2003 |
04:39 min
|
|
382 |
Let z and ω be two complex numbers such that |z| ≤ 1 and |w| ≤ 1 then show that 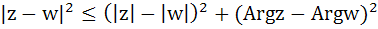 . .
Let z and ω be two complex numbers such that |z| ≤ 1 and |w| ≤ 1 then show that 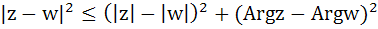 . .
|
IIT 1995 |
06:01 min
|
|
383 |
A is a point on the parabola 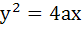 . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB. . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB.
A is a point on the parabola 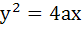 . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB. . The normal at A cuts the parabola again at B. If AB subtends a right angle at the vertex of the parabola, find the slope of AB.
|
IIT 1982 |
06:08 min
|
|
384 |
If a, b, c, d are positive real numbers such that a + b + c + d = 2 then M = ( a + b ) ( c + d ) satisfies a) 0 ≤ M ≤ 1 b) 1 ≤ M ≤ 2 c) 2 ≤ M ≤ 3 d) 3 ≤ M ≤ 4
If a, b, c, d are positive real numbers such that a + b + c + d = 2 then M = ( a + b ) ( c + d ) satisfies a) 0 ≤ M ≤ 1 b) 1 ≤ M ≤ 2 c) 2 ≤ M ≤ 3 d) 3 ≤ M ≤ 4
|
IIT 2000 |
01:54 min
|
|
385 |
Show that the locus of a point that divides a chord of slope 2 of the parabola 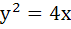 internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex. internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex.
Show that the locus of a point that divides a chord of slope 2 of the parabola 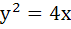 internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex. internally in the ratio 1:2 is a parabola. Find its vertex.
|
IIT 1995 |
06:25 min
|
|
386 |
Let α, β be the roots of 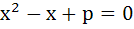 and γ, δ roots of and γ, δ roots of 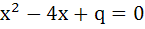 . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are a) −2, −32 b) −2, 3 c) −6, 3 d) −6, −32
Let α, β be the roots of 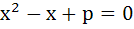 and γ, δ roots of and γ, δ roots of 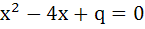 . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are . If α, β, γ, δ are in geometric progression then the integral values of p and q respectively are a) −2, −32 b) −2, 3 c) −6, 3 d) −6, −32
|
IIT 2001 |
05:16 min
|
|
387 |
For what values of k does the following system of equations possess a non-trivial solution over the set of rationals? Find all the solutions. x + y – 2z = 0 2x – 3y + z = 0 x – 5y + 4z = k
For what values of k does the following system of equations possess a non-trivial solution over the set of rationals? Find all the solutions. x + y – 2z = 0 2x – 3y + z = 0 x – 5y + 4z = k
|
IIT 1979 |
05:23 min
|
|
388 |
Prove that there exists no complex number z such that 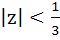 and and 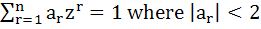 . .
Prove that there exists no complex number z such that 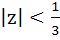 and and 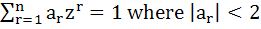 . .
|
IIT 2003 |
04:27 min
|
|
389 |
Three normals with slopes 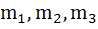 are drawn from a point P not on the axis of the parabola are drawn from a point P not on the axis of the parabola 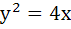 . If . If 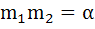 results in the locus of P being a part of the parabola, find the value of α. results in the locus of P being a part of the parabola, find the value of α.
|
IIT 2003 |
05:59 min
|
|
390 |
Find the value of the expression 1.(2−ω)(2−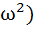 + 2.(3−ω)(3− + 2.(3−ω)(3−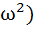 + … (n−1).(n−ω)(n− + … (n−1).(n−ω)(n−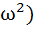 where ω is an imaginary cube root of unity. a)  n(n−1)( n(n−1)(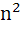 +3n+4) +3n+4) b)  n(n+1)( n(n+1)(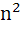 +3n+4) +3n+4) c)  n(n−1)( n(n−1)(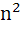 +n+1) +n+1) d)  n(n+1)( n(n+1)(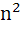 +n+1) +n+1)
|
IIT 1996 |
05:00 min
|
|
391 |
If  are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of 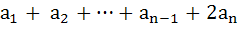 is is a) 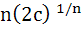 b) 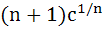 c) 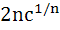 d) 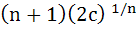
If  are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of are positive real numbers whose product is a fixed number c then the minimum value of 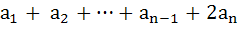 is is a) 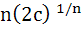 b) 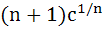 c) 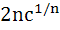 d) 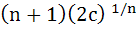
|
IIT 2002 |
02:06 min
|
|
392 |
If three complex numbers are in arithmetic progression then they lie on a circle in the complex plane. a) True b) False
If three complex numbers are in arithmetic progression then they lie on a circle in the complex plane. a) True b) False
|
IIT 1985 |
01:13 min
|
|
393 |
A solution of the differential equation 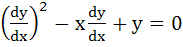 is is a) y = 2 b) y = 2x c) 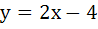 d) 2
A solution of the differential equation 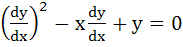 is is a) y = 2 b) y = 2x c) 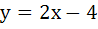 d) 2
|
IIT 1999 |
01:47 min
|
|
394 |
For all x, 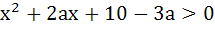 then the interval in which a lies is then the interval in which a lies is a) a < 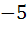 b) 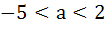 c) 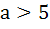 d) 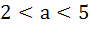
For all x, 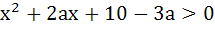 then the interval in which a lies is then the interval in which a lies is a) a < 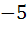 b) 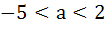 c) 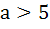 d) 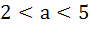
|
IIT 2004 |
01:45 min
|
|
395 |
Let the three digit numbers A28, 3B9 and 62C where A, B, C are integers between 0 and 9, be divisible by a fixed number k. Show that the determinant
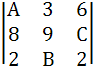 is divisible by k.
Let the three digit numbers A28, 3B9 and 62C where A, B, C are integers between 0 and 9, be divisible by a fixed number k. Show that the determinant
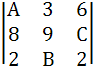 is divisible by k.
|
IIT 1990 |
04:45 min
|
|
396 |
If a and b are real numbers between 0 and 1 such that the points 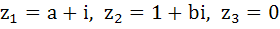 form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . a) 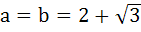 b) 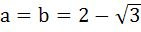 c) 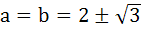 d) 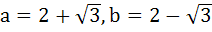
If a and b are real numbers between 0 and 1 such that the points 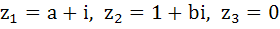 form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . form an equilateral triangle then a is equal to . . . . a) 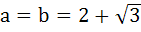 b) 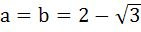 c) 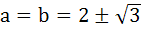 d) 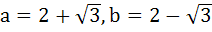
|
IIT 1989 |
03:07 min
|
|
397 |
Let E be the ellipse 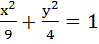 and C be the circle and C be the circle 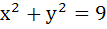 . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then a) Q lies inside C but outside E b) Q lies outside both C and E c) P lies inside both C and E d) P lies inside C but outside E
Let E be the ellipse 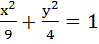 and C be the circle and C be the circle 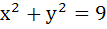 . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then . Let P and Q be the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) respectively. Then a) Q lies inside C but outside E b) Q lies outside both C and E c) P lies inside both C and E d) P lies inside C but outside E
|
IIT 1994 |
04:15 min
|
|
398 |
Let a, b, c be the sides of a triangle where a ≠ c and λ ε R. If roots of the equation 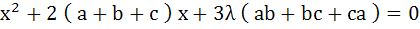 are real then are real then a) 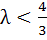 b) 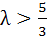 c) 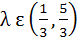 d) 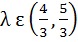
Let a, b, c be the sides of a triangle where a ≠ c and λ ε R. If roots of the equation 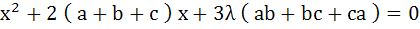 are real then are real then a) 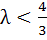 b) 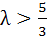 c) 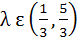 d) 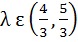
|
IIT 2006 |
04:47 min
|
|
399 |
Find the value of the determinant
 where a, b, c are respectively pth, qth and rth term of a harmonic progression. a) 0 b) 1 c) ½ d) None of the above
Find the value of the determinant
 where a, b, c are respectively pth, qth and rth term of a harmonic progression. a) 0 b) 1 c) ½ d) None of the above
|
IIT 1997 |
04:23 min
|
|
400 |
If tangents are drawn to the ellipse 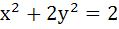 then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is a) 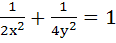 b) 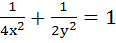 c) 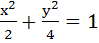 d) 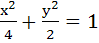
If tangents are drawn to the ellipse 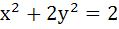 then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is then the locus of the mid-points of the intercepts made by the tangents between the coordinate axes is a) 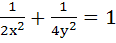 b) 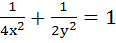 c) 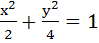 d) 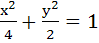
|
IIT 2004 |
03:11 min
|