|
326 |
A circle passes through the point of intersection of the coordinate axes with the lines 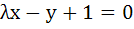 and x and x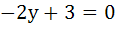 , then λ = . . . . . , then λ = . . . . .
A circle passes through the point of intersection of the coordinate axes with the lines 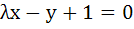 and x and x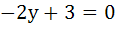 , then λ = . . . . . , then λ = . . . . .
|
IIT 1991 |
04:24 min
|
|
327 |
If x, y, z are real and distinct then
8u = 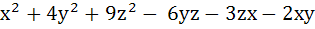
is always a) Non–negative b) Non–positive c) Zero d) None of these
If x, y, z are real and distinct then
8u = 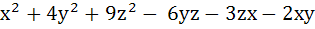
is always a) Non–negative b) Non–positive c) Zero d) None of these
|
IIT 1979 |
02:14 min
|
|
328 |
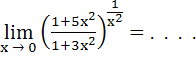
a) 0 b) 1 c) e d) e2
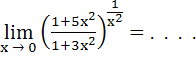
a) 0 b) 1 c) e d) e2
|
IIT 1996 |
01:19 min
|
|
329 |
Show that 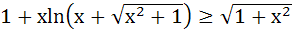 for all x ≥ 0. for all x ≥ 0.
Show that 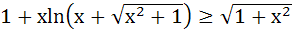 for all x ≥ 0. for all x ≥ 0.
|
IIT 1983 |
04:21 min
|
|
330 |
For each natural number k, let Ck denote the circle with radius k centimeters and center at the origin. On the circle Ck, a particle moves k centimeters in the counterclockwise direction. After completing its motion on Ck the particle moves to Ck + 1 in the radial direction. The motion of the particle continues in this manner. The particle starts at ( 1, 0 ). If the particle crosses the positive direction of the X–axis for the first time on the circle Cn then n = . . . . .
For each natural number k, let Ck denote the circle with radius k centimeters and center at the origin. On the circle Ck, a particle moves k centimeters in the counterclockwise direction. After completing its motion on Ck the particle moves to Ck + 1 in the radial direction. The motion of the particle continues in this manner. The particle starts at ( 1, 0 ). If the particle crosses the positive direction of the X–axis for the first time on the circle Cn then n = . . . . .
|
IIT 1997 |
04:26 min
|
|
331 |
If 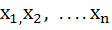 are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then a) 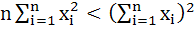 b) 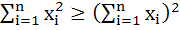 c) 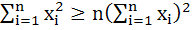 d) none of these
If 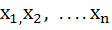 are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then are any real numbers and n is any positive integer then a) 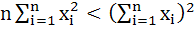 b) 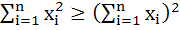 c) 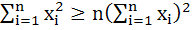 d) none of these
|
IIT 1982 |
01:04 min
|
|
332 |
If |z| = 1 and z ≠ ±1 then the value of 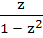 lie on lie on a) a line not passing through the origin b) 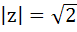 c) the X – axis d) the Y axis
If |z| = 1 and z ≠ ±1 then the value of 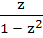 lie on lie on a) a line not passing through the origin b) 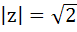 c) the X – axis d) the Y axis
|
IIT 2007 |
02:46 min
|
|
333 |
Let a + b + c = 0, then the quadratic equation 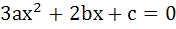 has has a) at least one root in (0, 1) b) one root in (2, 3) and the other in 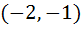 c) imaginary roots d) none of these
Let a + b + c = 0, then the quadratic equation 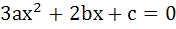 has has a) at least one root in (0, 1) b) one root in (2, 3) and the other in 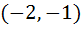 c) imaginary roots d) none of these
|
IIT 1983 |
02:32 min
|
|
334 |
If x = a + b, y = aα + bβ, z = aβ + bα where α, β are cube roots of unity show that  . .
If x = a + b, y = aα + bβ, z = aβ + bα where α, β are cube roots of unity show that  . .
|
IIT 1979 |
02:39 min
|
|
335 |
If 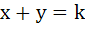 is a normal to is a normal to 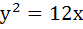 then k is then k is a) 3 b) 9 c) – 9 d) – 3
If 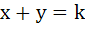 is a normal to is a normal to 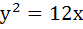 then k is then k is a) 3 b) 9 c) – 9 d) – 3
|
IIT 2000 |
02:47 min
|
|
336 |
If α and β are roots of 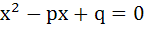 and and 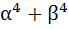 are roots of are roots of 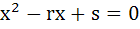 then the equation then the equation 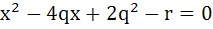 has always has always a) Two real roots b) Two positive roots c) Two negative roots d) One positive and one negative root
If α and β are roots of 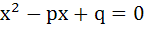 and and 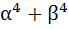 are roots of are roots of 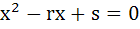 then the equation then the equation 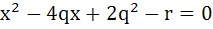 has always has always a) Two real roots b) Two positive roots c) Two negative roots d) One positive and one negative root
|
IIT 1989 |
04:41 min
|
|
337 |
The number of points of intersection of the two curves y = 2sinx and y = 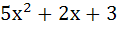 is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 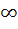
The number of points of intersection of the two curves y = 2sinx and y = 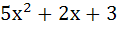 is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 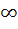
|
IIT 1994 |
01:51 min
|
|
338 |
If the system of equations x – ky – z = 0 kx – y –z = 0 x + y –z = 0 has a non zero solution then possible values of k are a) −1, 2 b) 1, 2 c) 0, 1 d) −1, 1
If the system of equations x – ky – z = 0 kx – y –z = 0 x + y –z = 0 has a non zero solution then possible values of k are a) −1, 2 b) 1, 2 c) 0, 1 d) −1, 1
|
IIT 2000 |
02:26 min
|
|
339 |
The axis of the parabola is along the line 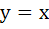 and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are 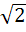 and and 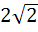 respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is a) 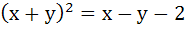 b) 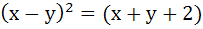 c) 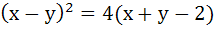 d) 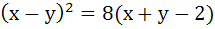
The axis of the parabola is along the line 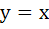 and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are and the distance of the vertex and focus from origin are 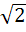 and and 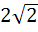 respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is respectively. If vertex and focus both lie in the first quadrant, then the equation of the parabola is a) 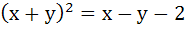 b) 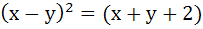 c) 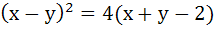 d) 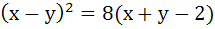
|
IIT 2006 |
05:21 min
|
|
340 |
The roots of the equation 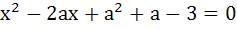 are real and less than 3, then are real and less than 3, then a) a < 2 b) 2 < a < 3 c) 3 ≤ a ≤ 4 d) a > 4
The roots of the equation 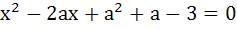 are real and less than 3, then are real and less than 3, then a) a < 2 b) 2 < a < 3 c) 3 ≤ a ≤ 4 d) a > 4
|
IIT 1999 |
02:39 min
|
|
341 |
Given 2x – y – z = 2, x – 2y + z = − 4, x + y + λz = 4 then the value of λ such that the given system of equations has no solution is a) 3 b) −2 c) 0 d) −3
Given 2x – y – z = 2, x – 2y + z = − 4, x + y + λz = 4 then the value of λ such that the given system of equations has no solution is a) 3 b) −2 c) 0 d) −3
|
IIT 2004 |
03:35 min
|
|
342 |
Find all non zero complex numbers satisfying  . .
Find all non zero complex numbers satisfying  . .
|
IIT 1996 |
04:39 min
|
|
343 |
Sketch the region bounded by the curves y = x2 and 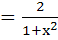 . Find the area. . Find the area. a)  b)  c) 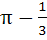 d) 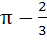
Sketch the region bounded by the curves y = x2 and 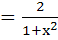 . Find the area. . Find the area. a)  b)  c) 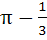 d) 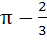
|
IIT 1992 |
06:17 min
|
|
344 |
Find the equation of the normal to the curve 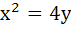 which passes through the point (1, 2). which passes through the point (1, 2).
Find the equation of the normal to the curve 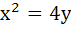 which passes through the point (1, 2). which passes through the point (1, 2).
|
IIT 1984 |
03:23 min
|
|
345 |
(Multiple choices)
The determinant
 is equal to zero if is equal to zero if a) a, b, c are in arithmetic progression b) a, b, c are in geometric progression c) a, b, c are in harmonic progression d) α is a root of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 e) x – α is a factor of ax2 + 2bx + c
(Multiple choices)
The determinant
 is equal to zero if is equal to zero if a) a, b, c are in arithmetic progression b) a, b, c are in geometric progression c) a, b, c are in harmonic progression d) α is a root of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 e) x – α is a factor of ax2 + 2bx + c
|
IIT 1986 |
03:09 min
|
|
346 |
Let f(x) = 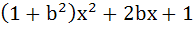 and m(b) be the minimum value of f(x). As b varies, range of m(b) is and m(b) be the minimum value of f(x). As b varies, range of m(b) is a) 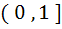 b) [ 0, 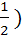 c) [ 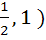 d) 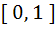
Let f(x) = 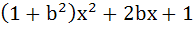 and m(b) be the minimum value of f(x). As b varies, range of m(b) is and m(b) be the minimum value of f(x). As b varies, range of m(b) is a) 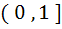 b) [ 0, 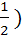 c) [ 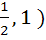 d) 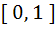
|
IIT 2001 |
03:22 min
|
|
347 |
At any point P on the parabola 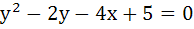 , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio 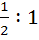 . .
At any point P on the parabola 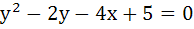 , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio , a tangent is drawn which meets the directrix at Q. Find the locus of the point R which divides QP externally in the ratio 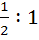 . .
|
IIT 2004 |
06:48 min
|
|
348 |
The set of all real numbers x for which 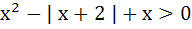 is is a) 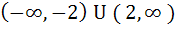 b) 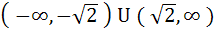 c) 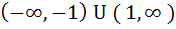 d) 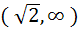
The set of all real numbers x for which 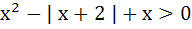 is is a) 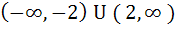 b) 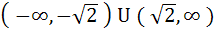 c) 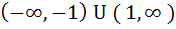 d) 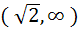
|
IIT 2002 |
03:01 min
|
|
349 |
If the expression 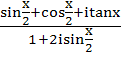 is real then the set of all possible values of x is . . . . is real then the set of all possible values of x is . . . . a) x = 2nπ or mπ + π/4 b) x = nπ or mπ + π/4 c) x = 2nπ or 2mπ + π/4 d) x = nπ or 2mπ + π/4
If the expression 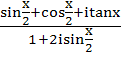 is real then the set of all possible values of x is . . . . is real then the set of all possible values of x is . . . . a) x = 2nπ or mπ + π/4 b) x = nπ or mπ + π/4 c) x = 2nπ or 2mπ + π/4 d) x = nπ or 2mπ + π/4
|
IIT 1987 |
06:12 min
|
|
350 |
(Assertion and reason) The question contains statement – 1 (assertion) and statement 2 (reason). Of these statements mark correct choice if a) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1. b) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1. c) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false. d) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true Statement 1 – The curve 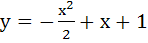 is symmetric with respect to the line x = 1 is symmetric with respect to the line x = 1 Statement 2 – The parabola is symmetric about its axis.
(Assertion and reason) The question contains statement – 1 (assertion) and statement 2 (reason). Of these statements mark correct choice if a) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1. b) Statement 1 and 2 are true. Statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1. c) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false. d) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true Statement 1 – The curve 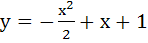 is symmetric with respect to the line x = 1 is symmetric with respect to the line x = 1 Statement 2 – The parabola is symmetric about its axis.
|
IIT 2007 |
01:47 min
|