|
251 |
The equation 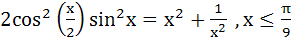 has has a) No solution b) One solution c) More than one real solution d) Cannot be said
The equation 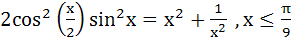 has has a) No solution b) One solution c) More than one real solution d) Cannot be said
|
IIT 1980 |
01:57 min
|
|
252 |
The value of 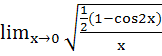 is is a) 1 b) – 1 c) 0 d) None of these
The value of 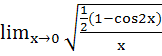 is is a) 1 b) – 1 c) 0 d) None of these
|
IIT 1991 |
02:34 min
|
|
253 |
Evaluate 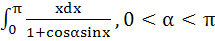 a) 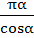 b) 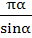 c) 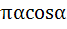 d) 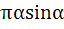
|
IIT 1986 |
05:55 min
|
|
254 |
The number of solutions of the equation 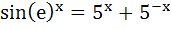 a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) Infinitely many
The number of solutions of the equation 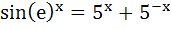 a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) Infinitely many
|
IIT 1990 |
01:46 min
|
|
255 |
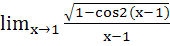
a) exists and equals 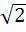 b) exists and equals 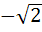 c) does not exist because x – 1 → 0 d) does not exist because the left hand limit is not equal to the right hand limit.
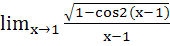
a) exists and equals 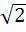 b) exists and equals 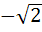 c) does not exist because x – 1 → 0 d) does not exist because the left hand limit is not equal to the right hand limit.
|
IIT 1998 |
03:32 min
|
|
256 |
The number of values of x in the interval (0, 5π) satisfying the equation 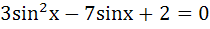 is is a) 0 b) 5 c) 6 d) 10
The number of values of x in the interval (0, 5π) satisfying the equation 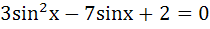 is is a) 0 b) 5 c) 6 d) 10
|
IIT 1998 |
03:17 min
|
|
257 |
Find the natural number a for which
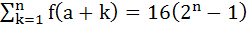
where the function f satisfies the relation f (x + y) = f (x).f(y)for all natural numbers x and y and further f (1) = 2
Find the natural number a for which
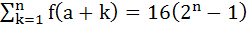
where the function f satisfies the relation f (x + y) = f (x).f(y)for all natural numbers x and y and further f (1) = 2
|
IIT 1992 |
06:01 min
|
|
258 |
The lines 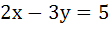 and and 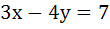 are diameters of a circle of area 154 square units. Then the equation of the circle is are diameters of a circle of area 154 square units. Then the equation of the circle is a) 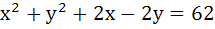 b) 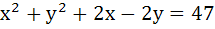 c) 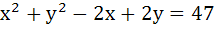 d) 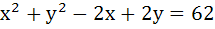
The lines 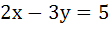 and and 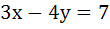 are diameters of a circle of area 154 square units. Then the equation of the circle is are diameters of a circle of area 154 square units. Then the equation of the circle is a) 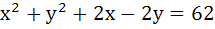 b) 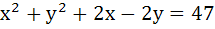 c) 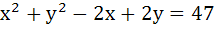 d) 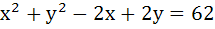
|
IIT 1989 |
03:02 min
|
|
259 |
If α + β =  and β + γ = α, then tanα equals and β + γ = α, then tanα equals a) 2(tanβ + tanγ) b) tanβ + tanγ c) tanβ + 2tanγ d) 2tanβ + tanγ
If α + β =  and β + γ = α, then tanα equals and β + γ = α, then tanα equals a) 2(tanβ + tanγ) b) tanβ + tanγ c) tanβ + 2tanγ d) 2tanβ + tanγ
|
IIT 2001 |
02:03 min
|
|
260 |
Let n be a positive integer and
(1 + x + x2)n = a0 + a1x + a2x + a2x2 + . . . + a2nx2n then prove that
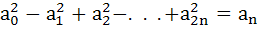
Let n be a positive integer and
(1 + x + x2)n = a0 + a1x + a2x + a2x2 + . . . + a2nx2n then prove that
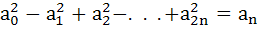
|
IIT 1994 |
06:48 min
|
|
261 |
Evaluate 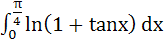 a) πln2 b) 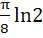 c) 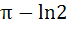 d) 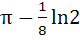
Evaluate 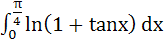 a) πln2 b) 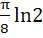 c) 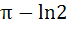 d) 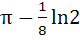
|
IIT 1997 |
02:50 min
|
|
262 |
The angle between a pair of tangents drawn from a point P to the circle 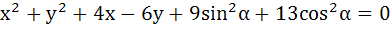 is 2α. Then the locus of P is is 2α. Then the locus of P is a) 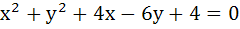 b) 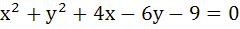 c) 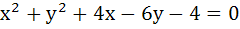 d) 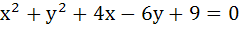
The angle between a pair of tangents drawn from a point P to the circle 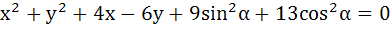 is 2α. Then the locus of P is is 2α. Then the locus of P is a) 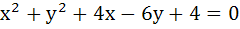 b) 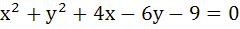 c) 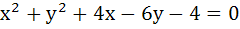 d) 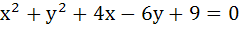
|
IIT 1996 |
05:15 min
|
|
263 |
If 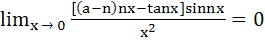 where n is a non–zero real number, then a is equal to where n is a non–zero real number, then a is equal to a) 0 b) 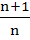 c) n d) 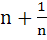
If 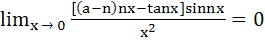 where n is a non–zero real number, then a is equal to where n is a non–zero real number, then a is equal to a) 0 b) 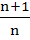 c) n d) 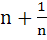
|
IIT 2003 |
02:22 min
|
|
264 |
If f (x) is an even function then prove that
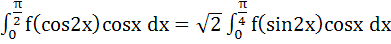 . .
If f (x) is an even function then prove that
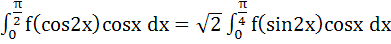 . .
|
IIT 2003 |
07:55 min
|
|
265 |
If A, B, C are three non-coplanar vectors then
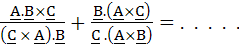
If A, B, C are three non-coplanar vectors then
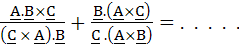
|
IIT 1985 |
02:22 min
|
|
266 |
The triangle PQR is inscribed in the circle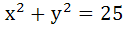 . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to a)  b)  c) 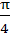 d) 
The triangle PQR is inscribed in the circle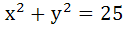 . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to . If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (-4, 3) respectively, then the ∠QPR is equal to a)  b)  c) 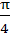 d) 
|
IIT 2000 |
02:46 min
|
|
267 |
The larger of 9950 + 10050 and 10150 is
The larger of 9950 + 10050 and 10150 is
|
IIT 1982 |
04:38 min
|
|
268 |
The projection of a vector a along and perpendicular to a non-zero vector 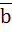 are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively. are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively.
The projection of a vector a along and perpendicular to a non-zero vector 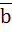 are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively. are . . . . . and . . . . . respectively.
|
IIT 1988 |
03:53 min
|
|
269 |
If the tangent at the point P on the circle 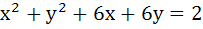 meets the straight line meets the straight line 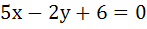 at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is a) 4 b) 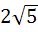 c) 5 d) 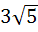
If the tangent at the point P on the circle 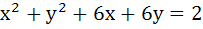 meets the straight line meets the straight line 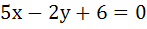 at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is at a point Q on the Y-axis, then the length of PˆQ is a) 4 b) 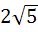 c) 5 d) 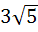
|
IIT 2002 |
01:46 min
|
|
270 |
The integral 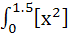 dx where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function equals . . . dx where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function equals . . . a) 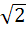 b) 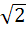 + 1 + 1 c) 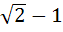 d) 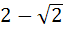
The integral 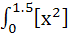 dx where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function equals . . . dx where [ ] denotes the greatest integer function equals . . . a) 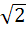 b) 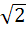 + 1 + 1 c) 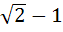 d) 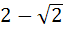
|
IIT 1988 |
02:11 min
|
|
271 |
A non-zero vector a is parallel to the line of intersection of the plane determined by the vectors 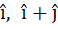 and the plane determined by the vectors and the plane determined by the vectors 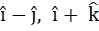 . The angle between a and . The angle between a and 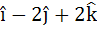 is . . . . . is . . . . .
|
IIT 1996 |
06:39 min
|
|
272 |
A circle is given by 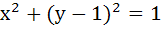 , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is a) 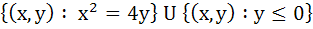 b)  c) 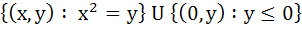 d) 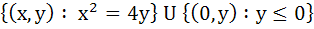
A circle is given by 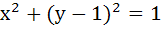 , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is , another circle C touches it externally and also the X-axis, then the locus of the centre of C is a) 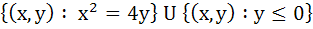 b)  c) 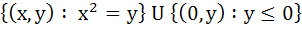 d) 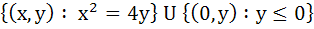
|
IIT 2005 |
05:02 min
|
|
273 |
Find all solutions of
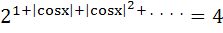 in in 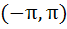 a) 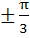 b) 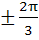 c) 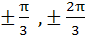 d) 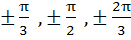
Find all solutions of
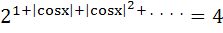 in in 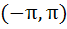 a) 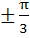 b) 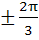 c) 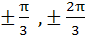 d) 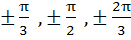
|
IIT 1984 |
03:20 min
|
|
274 |
Let f (x) = sin x and g (x) = ln|x|. If the range of the composition functions fog and gof are R1 and R2 respectively, then a) R1 = [ u : −1 ≤ u < 1], R2 = [ v : −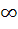 < v < 0 ] < v < 0 ] b) R1 = [ u : −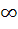 < u < 0 ], R2 = [ v : −1 ≤ v ≤ 0] < u < 0 ], R2 = [ v : −1 ≤ v ≤ 0] c) R1 = [ u : −1 < u < 1], R2 = [ v : −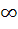 < v < 0 ] < v < 0 ] d) R1 = [ u : −1 ≤ u ≤ 1], R2 = [ v : −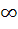 < v ≤ 0 ] < v ≤ 0 ]
Let f (x) = sin x and g (x) = ln|x|. If the range of the composition functions fog and gof are R1 and R2 respectively, then a) R1 = [ u : −1 ≤ u < 1], R2 = [ v : −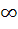 < v < 0 ] < v < 0 ] b) R1 = [ u : −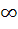 < u < 0 ], R2 = [ v : −1 ≤ v ≤ 0] < u < 0 ], R2 = [ v : −1 ≤ v ≤ 0] c) R1 = [ u : −1 < u < 1], R2 = [ v : −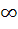 < v < 0 ] < v < 0 ] d) R1 = [ u : −1 ≤ u ≤ 1], R2 = [ v : −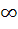 < v ≤ 0 ] < v ≤ 0 ]
|
IIT 1994 |
03:03 min
|
|
275 |
Let f (x) = 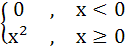 then for all x then for all x a) 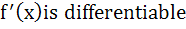 b) f is differentiable c) 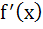 is continuous is continuous d) f is continuous
Let f (x) = 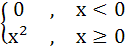 then for all x then for all x a) 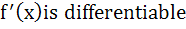 b) f is differentiable c) 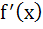 is continuous is continuous d) f is continuous
|
IIT 1994 |
04:05 min
|