|
26 |
Let f : ℝ → ℝ and g : ℝ → ℝ be continuous functions. Then the value of integral 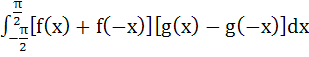 is is a) π b) 1 c) – 1 d) 0
Let f : ℝ → ℝ and g : ℝ → ℝ be continuous functions. Then the value of integral 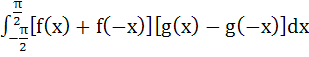 is is a) π b) 1 c) – 1 d) 0
|
IIT 1990 |
01:59 min
|
|
27 |
Let 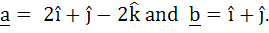 If c is a vector such that If c is a vector such that 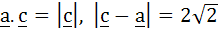 and the angle between and the angle between 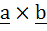 and c is 30° then and c is 30° then 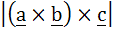 is equal to is equal to a)  b)  c) 2 d) 3
Let 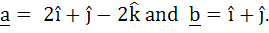 If c is a vector such that If c is a vector such that 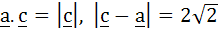 and the angle between and the angle between 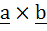 and c is 30° then and c is 30° then 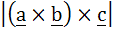 is equal to is equal to a)  b)  c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 1999 |
03:56 min
|
|
28 |
An anti–aircraft gun can take a maximum of 4 shots at an enemy plane moving away from it. The probability of hitting the plane at the first shot, 2nd, 3rd and 4th shots are 0.4, 0.3, 0.2 and 0.1 respectively. What is the probability that the gun hits the plane?
An anti–aircraft gun can take a maximum of 4 shots at an enemy plane moving away from it. The probability of hitting the plane at the first shot, 2nd, 3rd and 4th shots are 0.4, 0.3, 0.2 and 0.1 respectively. What is the probability that the gun hits the plane?
|
IIT 1981 |
02:45 min
|
|
29 |
The value of the expression 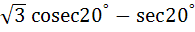 is equal to is equal to a) 2 b) 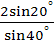 c) 4 d) 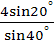
The value of the expression 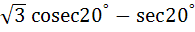 is equal to is equal to a) 2 b) 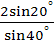 c) 4 d) 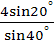
|
IIT 1988 |
02:02 min
|
|
30 |
Let f(x) = 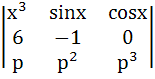 where p is a constant where p is a constant Then 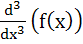 at x = 0 is at x = 0 is a) p b) 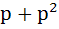 c) 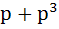 d) Independent of p
Let f(x) = 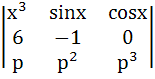 where p is a constant where p is a constant Then 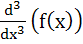 at x = 0 is at x = 0 is a) p b) 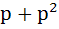 c) 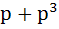 d) Independent of p
|
IIT 1997 |
04:22 min
|
|
31 |
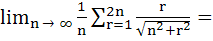
a) 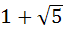 b) 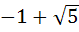 c) 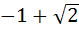 d) 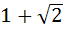
|
IIT 1997 |
02:03 min
|
|
32 |
A and B are independent events. The probability that both A and B occur is  and probability that neither of them occur is and probability that neither of them occur is  . Find the probability of the occurrence of A. . Find the probability of the occurrence of A.
A and B are independent events. The probability that both A and B occur is  and probability that neither of them occur is and probability that neither of them occur is  . Find the probability of the occurrence of A. . Find the probability of the occurrence of A.
|
IIT 1984 |
04:43 min
|
|
33 |
Let 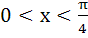 then then 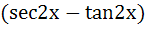 equals equals a) tan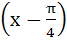 b) tan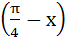 c) tan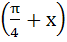 d) tan2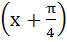
Let 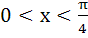 then then 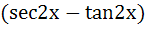 equals equals a) tan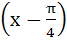 b) tan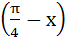 c) tan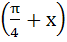 d) tan2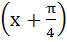
|
IIT 1994 |
02:33 min
|
|
34 |
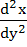 equals equals
a) 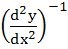 b) 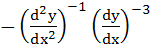 c) 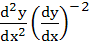 d) 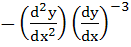
|
IIT 2007 |
01:21 min
|
|
35 |
If f(x) = x – [x] for every real number x, where [x] is the integral part of x, then 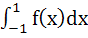 is is a) 1 b) 2 c) 0 d) 
If f(x) = x – [x] for every real number x, where [x] is the integral part of x, then 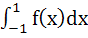 is is a) 1 b) 2 c) 0 d) 
|
IIT 1998 |
02:21 min
|
|
36 |
If a and b are two unit vectors such that 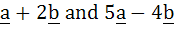 are perpendicular to each other then the angle between a and b is are perpendicular to each other then the angle between a and b is a) 45° b) 60° c) 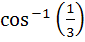 d) 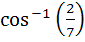
If a and b are two unit vectors such that 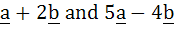 are perpendicular to each other then the angle between a and b is are perpendicular to each other then the angle between a and b is a) 45° b) 60° c) 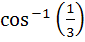 d) 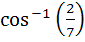
|
IIT 2003 |
01:56 min
|
|
37 |
A man takes a step forward with probability 0.4 and backward with probability 0.6. Find the probability that at the end of eleven steps he is one step away from the starting point.
A man takes a step forward with probability 0.4 and backward with probability 0.6. Find the probability that at the end of eleven steps he is one step away from the starting point.
|
IIT 1987 |
04:29 min
|
|
38 |
The length of longest interval in which the function 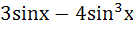 is increasing is is increasing is a)  b)  c) 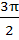 d) 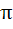
The length of longest interval in which the function 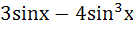 is increasing is is increasing is a)  b)  c) 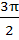 d) 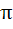
|
IIT 2002 |
01:29 min
|
|
39 |
Let p, q be the roots of the equation 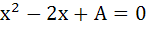 , and r and s are roots of the equation , and r and s are roots of the equation 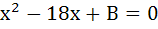 . If . If 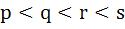 are in arithmetic progression then A = . . . . . , B = . . . . . are in arithmetic progression then A = . . . . . , B = . . . . .
|
IIT 1997 |
03:26 min
|
|
40 |
Let y = 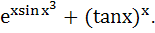 Find Find 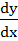 a) 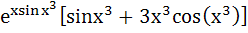 b) 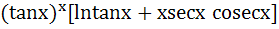 c) 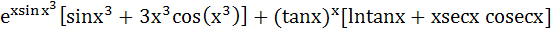 d) 0
Let y = 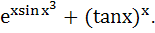 Find Find 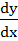 a) 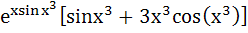 b) 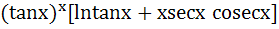 c) 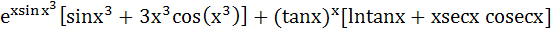 d) 0
|
IIT 1984 |
02:52 min
|
|
41 |
If 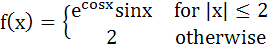 Then 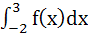 = = a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
If 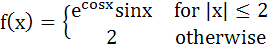 Then 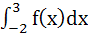 = = a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
|
IIT 2000 |
02:01 min
|
|
42 |
If 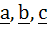 are non-coplanar vectors and are non-coplanar vectors and
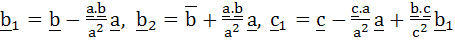 then a.b1 and a. then a.b1 and a.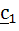 are orthogonal. are orthogonal.
|
IIT 2005 |
02:29 min
|
|
43 |
Let A be a set containing n elements. A subset P of A is constructed at random. The set A is reconstructed by replacing the elements of P. A subset of Q of A is again chosen at random. Find the probability that P and Q have no elements in common.
Let A be a set containing n elements. A subset P of A is constructed at random. The set A is reconstructed by replacing the elements of P. A subset of Q of A is again chosen at random. Find the probability that P and Q have no elements in common.
|
IIT 1990 |
04:10 min
|
|
44 |
The derivative of an even function is always an odd function. a) False b) True
The derivative of an even function is always an odd function. a) False b) True
|
IIT 1983 |
01:33 min
|
|
45 |
If 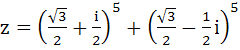 then then a) Re(z) = 0 b) Im(z) = 0 c) Re(z) = 0, Im(z) > 0 d) Re(z) > 0, Im(z) < 0
If 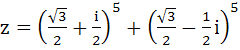 then then a) Re(z) = 0 b) Im(z) = 0 c) Re(z) = 0, Im(z) > 0 d) Re(z) > 0, Im(z) < 0
|
IIT 1982 |
02:07 min
|
|
46 |
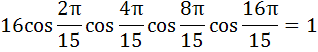
a) True b) False
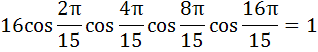
a) True b) False
|
IIT 1983 |
03:16 min
|
|
47 |
The derivative of 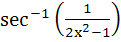 with respect to with respect to 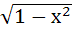 at x = at x =  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
The derivative of 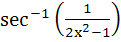 with respect to with respect to 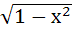 at x = at x =  is is a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4
|
IIT 1986 |
04:19 min
|
|
48 |
If f (x) is differentiable and 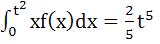 , then , then 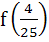 equals equals a)  b) 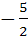 c) 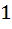 d) 
If f (x) is differentiable and 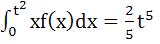 , then , then 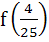 equals equals a)  b) 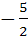 c) 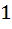 d) 
|
IIT 2004 |
01:33 min
|
|
49 |
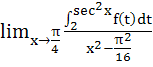 equals equals
a) 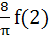 b) 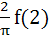 c) 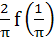 d) 4 f (2)
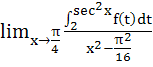 equals equals
a) 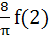 b) 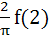 c) 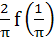 d) 4 f (2)
|
IIT 2007 |
03:41 min
|
|
50 |
Let z and ω be two non zero complex numbers such that |z| = |ω| and Arg(z) + Arg(ω) = π then z equals a) ω b) 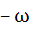 c) 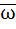 d) 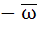
Let z and ω be two non zero complex numbers such that |z| = |ω| and Arg(z) + Arg(ω) = π then z equals a) ω b) 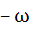 c) 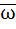 d) 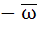
|
IIT 1995 |
02:03 min
|